
Stratified Squamous epithelium is found in
(a) Pharynx
(b) Trachea
(c) Ileum
(d) Bowman’s capsule
Answer
577.5k+ views
Hint: This is part of the digestive system and also of the conducting zone of the respiratory system which is lined by nonkeratinized squamous stratified epithelium. This tube in most people is about 4 inches long and less than an inch in diameter. It can be found just under the larynx (voice box) and runs down behind the breastbone (sternum).
Complete answer:
A cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all air-breathing animals with lungs is called the trachea or the windpipe which extends from the larynx and branches into the two primary bronchi. Structurally, a stratified squamous epithelium consists of squamous (flattened) epithelial cells arranged in layers upon a basal membrane where only one layer is in contact with the basement membrane; and the other layers adhere to one another to maintain structural integrity. They are of two types: Non-keratinized and keratinized. The surfaces of non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium must be kept moist by bodily secretions to prevent them from drying out. They include some parts of the oral cavity, esophagus, external female genitalia, and vagina. And the other one is keratinized stratified squamous epithelium which is protected from abrasion by keratin and kept hydrated and protected from dehydration by glycolipids produced in the stratum granulosum. This includes the epidermis of the palm and sole and the masticatory mucosa.
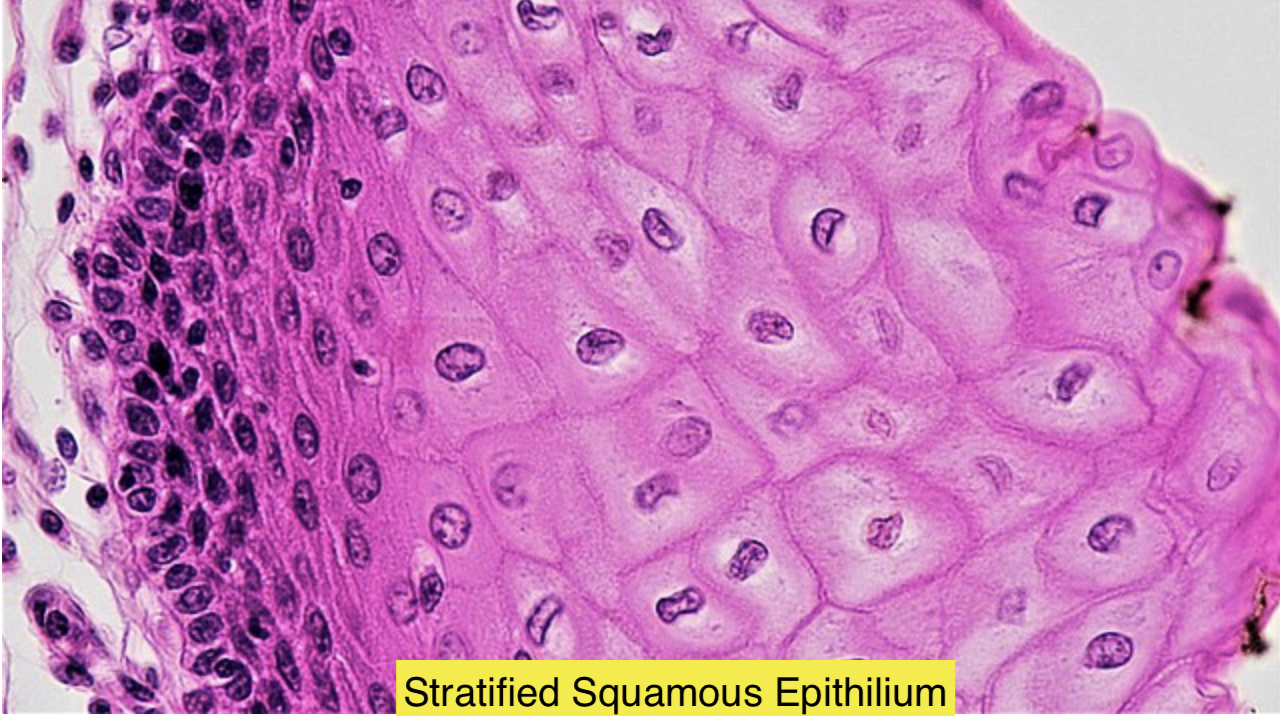
So, the correct answer is, ‘Trachea.’
Additional information:
1) Depending on the age of the epithelium and the damage it has experienced, non-keratinized surfaces consist of keratinocytes and have a minor superficial keratinized layer of varying thickness.
2) Stratified squamous epithelium is well suited to areas in the body subject to constant abrasion, as before the basement membrane is exposed the thickest layers can be sequentially sloughed off and replaced.
3) The prevalence and location of the epithelium reflect its principal functions which include: coverage, protection, absorption, secretion, sensation.
4) The movement of any substances can be either facilitated or inhibited by the epithelium making it a selective barrier for entering or leaving any tissue or organ must pass through the epithelium.
Note: These types of epithelial cells are found in nearly every organ system where the body comes into close contact with the outside environment starting from the skin to the respiratory, digestive, excretory, and reproductive systems and also it protects the body from desiccation and water loss.
Complete answer:
A cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all air-breathing animals with lungs is called the trachea or the windpipe which extends from the larynx and branches into the two primary bronchi. Structurally, a stratified squamous epithelium consists of squamous (flattened) epithelial cells arranged in layers upon a basal membrane where only one layer is in contact with the basement membrane; and the other layers adhere to one another to maintain structural integrity. They are of two types: Non-keratinized and keratinized. The surfaces of non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium must be kept moist by bodily secretions to prevent them from drying out. They include some parts of the oral cavity, esophagus, external female genitalia, and vagina. And the other one is keratinized stratified squamous epithelium which is protected from abrasion by keratin and kept hydrated and protected from dehydration by glycolipids produced in the stratum granulosum. This includes the epidermis of the palm and sole and the masticatory mucosa.

So, the correct answer is, ‘Trachea.’
Additional information:
1) Depending on the age of the epithelium and the damage it has experienced, non-keratinized surfaces consist of keratinocytes and have a minor superficial keratinized layer of varying thickness.
2) Stratified squamous epithelium is well suited to areas in the body subject to constant abrasion, as before the basement membrane is exposed the thickest layers can be sequentially sloughed off and replaced.
3) The prevalence and location of the epithelium reflect its principal functions which include: coverage, protection, absorption, secretion, sensation.
4) The movement of any substances can be either facilitated or inhibited by the epithelium making it a selective barrier for entering or leaving any tissue or organ must pass through the epithelium.
Note: These types of epithelial cells are found in nearly every organ system where the body comes into close contact with the outside environment starting from the skin to the respiratory, digestive, excretory, and reproductive systems and also it protects the body from desiccation and water loss.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




