
What is the structure and function of the Golgi Body?
Answer
503.7k+ views
Hint: Eukaryotic cells may contain a variety of organelles in addition to the nucleus, such as mitochondria, chloroplasts, the endoplasmic reticulum, the Golgi apparatus, and lysosomes. Each of these organelles serves a distinct purpose in the cell's survival.
Complete answer:
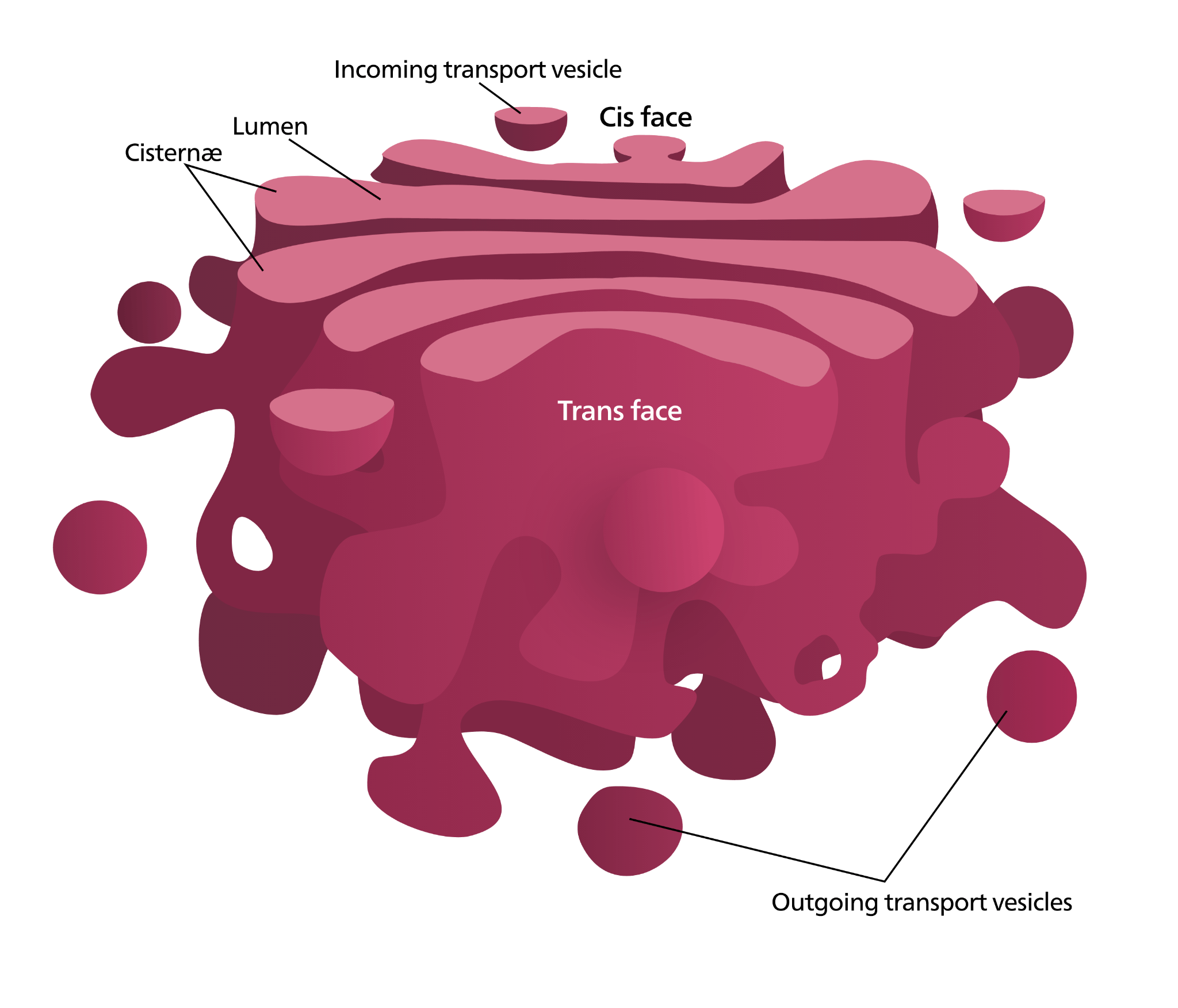
The Golgi Complex is also known as the Golgi Apparatus. It is a membrane-bound organelle made up primarily of cisternae, which are flattened, stacked pouches. This cell organelle is in charge of transporting, modifying, and packaging proteins and lipids to specific locations. The Golgi Apparatus is found within a cell's cytoplasm and is found in both plant and animal cells.
The Golgi body is made up of 5 to 8 cisternae, or cup-shaped compartments. The Golgi apparatus is made up of flattened, disk-shaped, stacked pouches called Cisternae. A Golgi stack usually has four to eight cisternae. Some protists, however, have up to 60 cisternae. There are 40 to 100 stacks of cisternae in a mammalian cell. Animal cells typically have 10 to 20 Golgi stacks per cell.
The functions of the Golgi Body is as follows:
The Golgi apparatus is responsible for protein packaging and secretion.
Endoplasmic Reticulum provides it with proteins.
It encapsulates it in membrane-bound vesicles that are then transported to various locations, including lysosomes, the plasma membrane, and secretion.
They also play a role in lipid transport and the formation of lysosomes.
Phosphorylation, glycosylation, and other post-translational modifications and enzymatic processing occur near the membrane surface in Golgi bodies.
The Golgi apparatus is where various glycolipids, sphingomyelin, and other proteins are synthesized.
In-plant cells, the Golgi apparatus synthesizes complex polysaccharides that make up the cell wall.
Note:
The Golgi apparatus differs structurally and organizationally between eukaryotes. Golgi stacking is not seen in all yeasts. Saccharomyces cerevisiae does not have stacked Golgi, whereas Pichia pastoris does. Individual stacks of the Golgi apparatus appear to operate independently in plants.
Complete answer:
The Golgi Complex is also known as the Golgi Apparatus. It is a membrane-bound organelle made up primarily of cisternae, which are flattened, stacked pouches. This cell organelle is in charge of transporting, modifying, and packaging proteins and lipids to specific locations. The Golgi Apparatus is found within a cell's cytoplasm and is found in both plant and animal cells.
The Golgi body is made up of 5 to 8 cisternae, or cup-shaped compartments. The Golgi apparatus is made up of flattened, disk-shaped, stacked pouches called Cisternae. A Golgi stack usually has four to eight cisternae. Some protists, however, have up to 60 cisternae. There are 40 to 100 stacks of cisternae in a mammalian cell. Animal cells typically have 10 to 20 Golgi stacks per cell.
The functions of the Golgi Body is as follows:
The Golgi apparatus is responsible for protein packaging and secretion.
Endoplasmic Reticulum provides it with proteins.
It encapsulates it in membrane-bound vesicles that are then transported to various locations, including lysosomes, the plasma membrane, and secretion.
They also play a role in lipid transport and the formation of lysosomes.
Phosphorylation, glycosylation, and other post-translational modifications and enzymatic processing occur near the membrane surface in Golgi bodies.
The Golgi apparatus is where various glycolipids, sphingomyelin, and other proteins are synthesized.
In-plant cells, the Golgi apparatus synthesizes complex polysaccharides that make up the cell wall.

Note:
The Golgi apparatus differs structurally and organizationally between eukaryotes. Golgi stacking is not seen in all yeasts. Saccharomyces cerevisiae does not have stacked Golgi, whereas Pichia pastoris does. Individual stacks of the Golgi apparatus appear to operate independently in plants.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




