
What is the structure of secondary butyl chloride?
Answer
490.2k+ views
Hint: The group of chemical compounds derived from alkanes which contain one or more halogens are known as alkyl halides. They are used as flame retardants, fire extinguishants, refrigerants, solvents and pharmaceuticals.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Halogens combine with functional groups, the chemical compounds formed are known as alkyl halides. The member of Halogens are fluorine $ \left( F \right) $ , chlorine $ \left( {Cl} \right) $ , bromine $ \left( {Br} \right) $ and iodine $ \left( I \right) $ . Halogens are placed in the $ 17 $ group in the periodic table. On moving down the group $ 17 $ , from $ F $ to $ I $ ; the size of the halogen increases and electronegativity decreases.
Like alkanes, alkyl halides are colourless, hydrophobic and odourless. As compared to alkanes, the melting and boiling points of alkyl halides are higher. As alkyl halide contains less $ C - H $ bonds than alkanes thus they are less flammable than alkanes.
The naming of alkyl halide should follow IUPAC nomenclature, in which we put halogen as a prefix to the alkane, like methane with chlorine forming chloromethane, propane with bromine forming bromopropane.
The IUPAC name of secondary butyl chloride is $ 2 - chloro{\text{butane}} $ and the structure of this compound is:
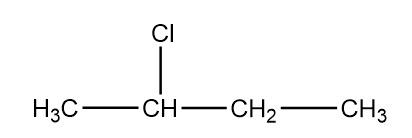
Additional information:
The structure of $ 2 - chloro{\text{butane}} $ has the stereochemistry configuration which are (R) and (S) enantiomers. This can be determined by assigning the priority to the groups present at the chiral carbon. First priority is given to chlorine as it has the highest mass, after that to ethyl group then to methyl group and at last to hydrogen atom. The structure of (R) enantiomer is the mirror image of (S) enantiomer. The structure of (R) enantiomer and (S) enantiomer are as follows:
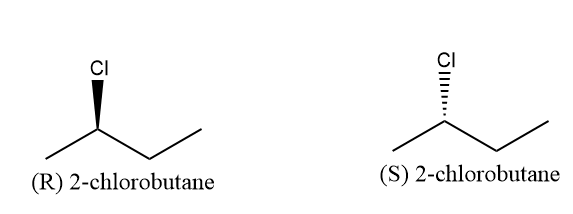
Note:
2-chlorobutane is used as a solvent and intermediate in organic synthesis. Moreover, 2-chlorobutane is associated with the production of active pharmaceutical ingredients, plasticizer, rubber, resin and surfactants.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Halogens combine with functional groups, the chemical compounds formed are known as alkyl halides. The member of Halogens are fluorine $ \left( F \right) $ , chlorine $ \left( {Cl} \right) $ , bromine $ \left( {Br} \right) $ and iodine $ \left( I \right) $ . Halogens are placed in the $ 17 $ group in the periodic table. On moving down the group $ 17 $ , from $ F $ to $ I $ ; the size of the halogen increases and electronegativity decreases.
Like alkanes, alkyl halides are colourless, hydrophobic and odourless. As compared to alkanes, the melting and boiling points of alkyl halides are higher. As alkyl halide contains less $ C - H $ bonds than alkanes thus they are less flammable than alkanes.
The naming of alkyl halide should follow IUPAC nomenclature, in which we put halogen as a prefix to the alkane, like methane with chlorine forming chloromethane, propane with bromine forming bromopropane.
The IUPAC name of secondary butyl chloride is $ 2 - chloro{\text{butane}} $ and the structure of this compound is:

Additional information:
The structure of $ 2 - chloro{\text{butane}} $ has the stereochemistry configuration which are (R) and (S) enantiomers. This can be determined by assigning the priority to the groups present at the chiral carbon. First priority is given to chlorine as it has the highest mass, after that to ethyl group then to methyl group and at last to hydrogen atom. The structure of (R) enantiomer is the mirror image of (S) enantiomer. The structure of (R) enantiomer and (S) enantiomer are as follows:
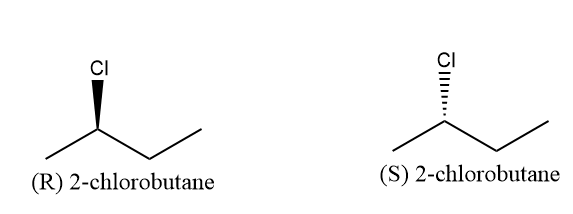
Note:
2-chlorobutane is used as a solvent and intermediate in organic synthesis. Moreover, 2-chlorobutane is associated with the production of active pharmaceutical ingredients, plasticizer, rubber, resin and surfactants.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




