
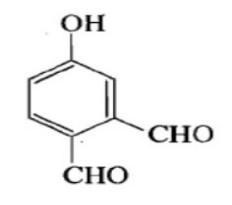
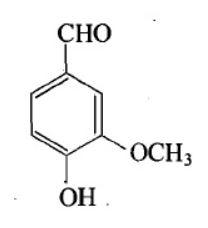
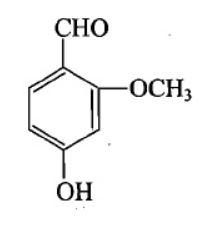
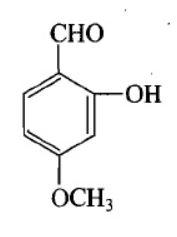
Structure of vanillin should be:
A.
B.
C.
D.




Answer
546.3k+ views
Hint: Vanillin is an organic compound having the molecular formula $ {C_8}{H_8}{O_3} $ . It is a phenolic aldehyde. It contains different functional groups including aldehyde, hydroxyl and ether. In the extraction of vanilla bean vanillin is obtained as the primary component.
Complete step by step solution:
The IUPAC name of vanillin is 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzaldehyde. This small aromatic compound contains three oxygen atoms in different functional groups: alcohol, aldehyde and ether. Vanillin is a white crystalline solid with a melting point of $ 81 - 83^\circ C $ . Vanillin is a member of the class benzaldehyde carrying methoxy and hydroxy substituents at 3 and 4 positions respectively. It acts as a plant metabolite, a flavouring agent, an antioxidant, and as an anticonvulsant. It is a member of both monomethoxy benzene and benzaldehydes.
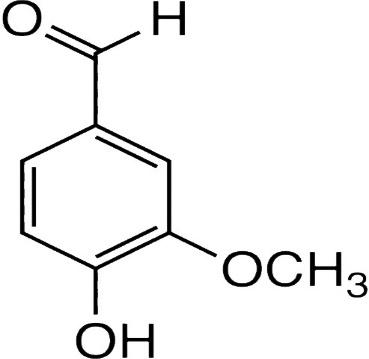
$ \therefore $ Option B is the answer.
Additional information:
As the name suggests vanillin is the major flavouring component of vanilla. In addition to vanillin natural vanilla is a mixture of seven hundred different components. Since vanillin is an expensive ingredient the industry always looks for a cheaper way to make the product. One of those ways is to make use of molecules that are highly available in nature and convert them into vanillin. Eugenol is one such a thing. The conversion of eugenol is done in two steps of chemical process. First step is the isomerisation of eugenol and the next step is the oxidation of isoeugenol. But at present the most significant method followed is by reacting glyoxylic acid by electrophilic aromatic substitution where the resulting vanillylmandelic acid is converted into vanillin by 4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl glyoxylic acid by oxidative decarboxylation.
Note:
Vanillin and ethyl vanillin are commonly used in the food industry where ethyl vanillin is expensive but has a stronger note. The difference between vanillin form ethyl vanillin is that instead of a methoxy group ( $ - O - C{H_3} $ ) they have an ethoxy group ( $ - O - C{H_2}C{H_3} $ ).
Complete step by step solution:
The IUPAC name of vanillin is 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzaldehyde. This small aromatic compound contains three oxygen atoms in different functional groups: alcohol, aldehyde and ether. Vanillin is a white crystalline solid with a melting point of $ 81 - 83^\circ C $ . Vanillin is a member of the class benzaldehyde carrying methoxy and hydroxy substituents at 3 and 4 positions respectively. It acts as a plant metabolite, a flavouring agent, an antioxidant, and as an anticonvulsant. It is a member of both monomethoxy benzene and benzaldehydes.

$ \therefore $ Option B is the answer.
Additional information:
As the name suggests vanillin is the major flavouring component of vanilla. In addition to vanillin natural vanilla is a mixture of seven hundred different components. Since vanillin is an expensive ingredient the industry always looks for a cheaper way to make the product. One of those ways is to make use of molecules that are highly available in nature and convert them into vanillin. Eugenol is one such a thing. The conversion of eugenol is done in two steps of chemical process. First step is the isomerisation of eugenol and the next step is the oxidation of isoeugenol. But at present the most significant method followed is by reacting glyoxylic acid by electrophilic aromatic substitution where the resulting vanillylmandelic acid is converted into vanillin by 4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl glyoxylic acid by oxidative decarboxylation.
Note:
Vanillin and ethyl vanillin are commonly used in the food industry where ethyl vanillin is expensive but has a stronger note. The difference between vanillin form ethyl vanillin is that instead of a methoxy group ( $ - O - C{H_3} $ ) they have an ethoxy group ( $ - O - C{H_2}C{H_3} $ ).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




