
Sunlight of intensity \[1.3\,{\text{kW}}{{\text{m}}^{{\text{ - 2}}}}\] is incident normally on a thin convex lens of focal length \[20\,{\text{cm}}\]. Ignore the energy loss of light due to the lens and assume that the lens aperture size is much smaller than its focal length. The average intensity of light, in \[{\text{kW}}{{\text{m}}^{{\text{ - 2}}}}\], at a distance \[22\,{\text{cm}}\] from the lens on the other side is _________.
Answer
558.3k+ views
Hint: This is a question of ray optics, so first draw a ray diagram with the given information and check where the rays after emerging from the lens would meet. In this question we will also have to use the properties of similar triangles and use the formula for intensity to find the required answer.
Complete step by step solution:
Given, intensity of sunlight, \[I = 1.3\,{\text{kW}}{{\text{m}}^{{\text{ - 2}}}}\]
Focal length of convex lens, \[f = 20\,{\text{cm}}\]
Distance at which the average intensity has to be found from the other side of the lens, \[d = 22\,{\text{cm}}\]
We draw the ray diagram with the given conditions,
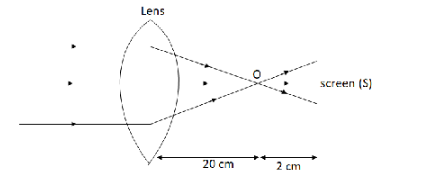
We know, rays from infinite distance or parallel to the optical axis fall on a converging lens, the emerging rays intersect at the focal point on the other side of the lens.
Here, the focal point on the other side is \[{\text{O}}\].
The distance of the screen from the other side is \[d = 22\,{\text{cm}}\] so distance of the screen from the focal point \[{\text{O}}\] will be \[d' = 2\,{\text{cm}}\].
Let \[R\] be the radius of the lens and \[r\] be the radius of the spot formed on the screen.
Now, let us redraw the figure
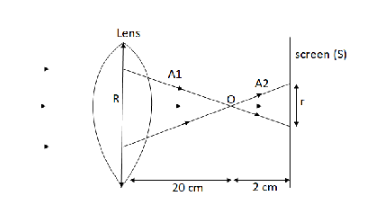
\[{\text{A1}}\] is the triangle formed on the left side of the focal point and \[{\text{A2}}\] is the triangle formed on the right side of focal length.
We can observe that the triangles \[{\text{A1}}\] and \[{\text{A2}}\] are similar triangles as, all their corresponding angles are congruent. We have one more property of similar triangle which says, their corresponding sides are proportional that is we can write for triangles \[{\text{A1}}\] and
\[{\text{A2}}\] ,
\[\dfrac{R}{r} = \dfrac{d}{{d'}}\]
Putting the values of \[d\] and \[d'\], we get
\[\dfrac{R}{r} = \dfrac{{20}}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{R}{r} = 10\] (i)
Intensity can be defined as energy per unit area, that is
\[I = \dfrac{{Energy}}{{area}}\]
When the rays on sunlight incident on the lens, its intensity will be
\[I = \dfrac{E}{A}\]
where \[E\] is the energy of sunlight and \[A\] is area of triangle \[{\text{A1}}\], which is \[A = \pi
{R^2}\].
Putting this value in above equation we get,
\[I = \dfrac{E}{{\pi {R^2}}}\] (ii)
The intensity on the screen will be (using the fact that there is no loss in energy so energy will be the same)
\[I' = \dfrac{E}{{A'}}\]
where \[A'\] is the area of triangle \[{\text{A2}}\], which is \[A' = \pi {r^2}\]. Putting this value in above equation we get,
\[I' = \dfrac{E}{{\pi {r^2}}}\] (iii)
Dividing equation (iii) by (ii), we get
\[\dfrac{{I'}}{I} = \dfrac{E}{{\pi {r^2}}} \times \dfrac{{\pi {R^2}}}{E}\]
\[ \Rightarrow I' = I\dfrac{{{R^2}}}{{{r^2}}} = I{\left( {\dfrac{R}{r}} \right)^2}\]
Putting the values of \[I\] and \[\dfrac{R}{r}\], we get
\[I' = 1.3{\left( {10} \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow I' = 130\,{\text{kW}}{{\text{m}}^{{\text{ - 2}}}}\]
Therefore, the average intensity of light at a distance of \[22\,{\text{cm}}\] from the lens on the other side is \[130\,{\text{kW}}{{\text{m}}^{{\text{ - 2}}}}\].
Note: Whenever you have a question of ray optics, always draw a ray diagram with the information given in the question. And with the help of the diagram find the required quantity. Also remember rays from infinite distance are considered as parallel rays, this is because as the distance between the source and the lens or mirror increases, the angle between rays from a distance source approaches zero.
Complete step by step solution:
Given, intensity of sunlight, \[I = 1.3\,{\text{kW}}{{\text{m}}^{{\text{ - 2}}}}\]
Focal length of convex lens, \[f = 20\,{\text{cm}}\]
Distance at which the average intensity has to be found from the other side of the lens, \[d = 22\,{\text{cm}}\]
We draw the ray diagram with the given conditions,

We know, rays from infinite distance or parallel to the optical axis fall on a converging lens, the emerging rays intersect at the focal point on the other side of the lens.
Here, the focal point on the other side is \[{\text{O}}\].
The distance of the screen from the other side is \[d = 22\,{\text{cm}}\] so distance of the screen from the focal point \[{\text{O}}\] will be \[d' = 2\,{\text{cm}}\].
Let \[R\] be the radius of the lens and \[r\] be the radius of the spot formed on the screen.
Now, let us redraw the figure

\[{\text{A1}}\] is the triangle formed on the left side of the focal point and \[{\text{A2}}\] is the triangle formed on the right side of focal length.
We can observe that the triangles \[{\text{A1}}\] and \[{\text{A2}}\] are similar triangles as, all their corresponding angles are congruent. We have one more property of similar triangle which says, their corresponding sides are proportional that is we can write for triangles \[{\text{A1}}\] and
\[{\text{A2}}\] ,
\[\dfrac{R}{r} = \dfrac{d}{{d'}}\]
Putting the values of \[d\] and \[d'\], we get
\[\dfrac{R}{r} = \dfrac{{20}}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{R}{r} = 10\] (i)
Intensity can be defined as energy per unit area, that is
\[I = \dfrac{{Energy}}{{area}}\]
When the rays on sunlight incident on the lens, its intensity will be
\[I = \dfrac{E}{A}\]
where \[E\] is the energy of sunlight and \[A\] is area of triangle \[{\text{A1}}\], which is \[A = \pi
{R^2}\].
Putting this value in above equation we get,
\[I = \dfrac{E}{{\pi {R^2}}}\] (ii)
The intensity on the screen will be (using the fact that there is no loss in energy so energy will be the same)
\[I' = \dfrac{E}{{A'}}\]
where \[A'\] is the area of triangle \[{\text{A2}}\], which is \[A' = \pi {r^2}\]. Putting this value in above equation we get,
\[I' = \dfrac{E}{{\pi {r^2}}}\] (iii)
Dividing equation (iii) by (ii), we get
\[\dfrac{{I'}}{I} = \dfrac{E}{{\pi {r^2}}} \times \dfrac{{\pi {R^2}}}{E}\]
\[ \Rightarrow I' = I\dfrac{{{R^2}}}{{{r^2}}} = I{\left( {\dfrac{R}{r}} \right)^2}\]
Putting the values of \[I\] and \[\dfrac{R}{r}\], we get
\[I' = 1.3{\left( {10} \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow I' = 130\,{\text{kW}}{{\text{m}}^{{\text{ - 2}}}}\]
Therefore, the average intensity of light at a distance of \[22\,{\text{cm}}\] from the lens on the other side is \[130\,{\text{kW}}{{\text{m}}^{{\text{ - 2}}}}\].
Note: Whenever you have a question of ray optics, always draw a ray diagram with the information given in the question. And with the help of the diagram find the required quantity. Also remember rays from infinite distance are considered as parallel rays, this is because as the distance between the source and the lens or mirror increases, the angle between rays from a distance source approaches zero.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




