
What is the symbol for a potentiometer?
Answer
474.9k+ views
Hint: When the potentiometer is understood, the working of the potentiometer may be explained. It's a three-terminal resistor with either sliding or rotating contacts that acts as a voltage divider that can be adjusted. The potentiometer should only have two terminals, one end, and the wiper if it is to be used as a rheostat or variable resistor.
Complete step by step answer:
A potentiometer is a three-terminal resistor with sliding or rotating contacts that act as a voltage divider that may be adjusted.
The potentiometer's symbol is seen in the image below:
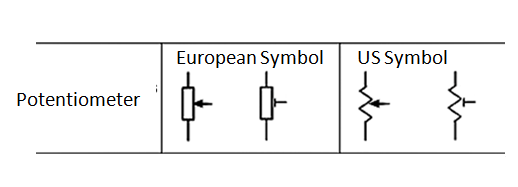
Additional information:
Construction of Potentiometer:
Three terminals, a resistor, a wiper, a shaft, and several wires are all included in a standard potentiometer. The body of the potentiometer is made of resistive materials. Cermet is made up of carbon particles found in graphite, plastic, resistive wires, and other materials made up of ceramics and metals.
Each potentiometer is divided into two sections: sliding and non-sliding. The wiper is the potentiometer's sliding contact that moves with the wire. Wipers can move in either a rotating or a translational manner, or even both of these directions.
Two of the potentiometers' terminals are linked to both ends of your resistive element (also known as the track), while the third is attached to the sliding contact (the wiper or sliding wiper). The variable resistor is controlled by this terminal. To alter the potential of the third terminal, change the applying potential at the resistor's end. It doesn't matter if the resistive element is inclined or flat. The wiper should travel rotational with the angled design and linearly with the flat design.
Note:
Potentiometers are used in a variety of applications. They are,
Audio control- Both linear and rotary potentiometers are used to change the volume and other audio signals in audio equipment.
Television- They are used to modify the brightness, color responsiveness, and contrast of television images.
Motion control- Potentiometers are utilized as position feedback devices known as servomechanisms in order to establish a closed-loop control.
Transducers- These are used in the design of displacement transducers since they produce huge output signals.
Complete step by step answer:
A potentiometer is a three-terminal resistor with sliding or rotating contacts that act as a voltage divider that may be adjusted.
The potentiometer's symbol is seen in the image below:

Additional information:
Construction of Potentiometer:
Three terminals, a resistor, a wiper, a shaft, and several wires are all included in a standard potentiometer. The body of the potentiometer is made of resistive materials. Cermet is made up of carbon particles found in graphite, plastic, resistive wires, and other materials made up of ceramics and metals.
Each potentiometer is divided into two sections: sliding and non-sliding. The wiper is the potentiometer's sliding contact that moves with the wire. Wipers can move in either a rotating or a translational manner, or even both of these directions.
Two of the potentiometers' terminals are linked to both ends of your resistive element (also known as the track), while the third is attached to the sliding contact (the wiper or sliding wiper). The variable resistor is controlled by this terminal. To alter the potential of the third terminal, change the applying potential at the resistor's end. It doesn't matter if the resistive element is inclined or flat. The wiper should travel rotational with the angled design and linearly with the flat design.
Note:
Potentiometers are used in a variety of applications. They are,
Audio control- Both linear and rotary potentiometers are used to change the volume and other audio signals in audio equipment.
Television- They are used to modify the brightness, color responsiveness, and contrast of television images.
Motion control- Potentiometers are utilized as position feedback devices known as servomechanisms in order to establish a closed-loop control.
Transducers- These are used in the design of displacement transducers since they produce huge output signals.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




