
Synapsis occurs during which phase?
(a)Anaphase I
(b)Telophase I
(c)Prophase I
(d)Cytokinesis
Answer
591.3k+ views
Hint: This is the most longest and complex phase in meiosis I under karyokinesis. This phase is the longest phase which includes five sub-phase: leptotene, zygotene, pachytene, diplotene, and diakinesis.
Complete answer:
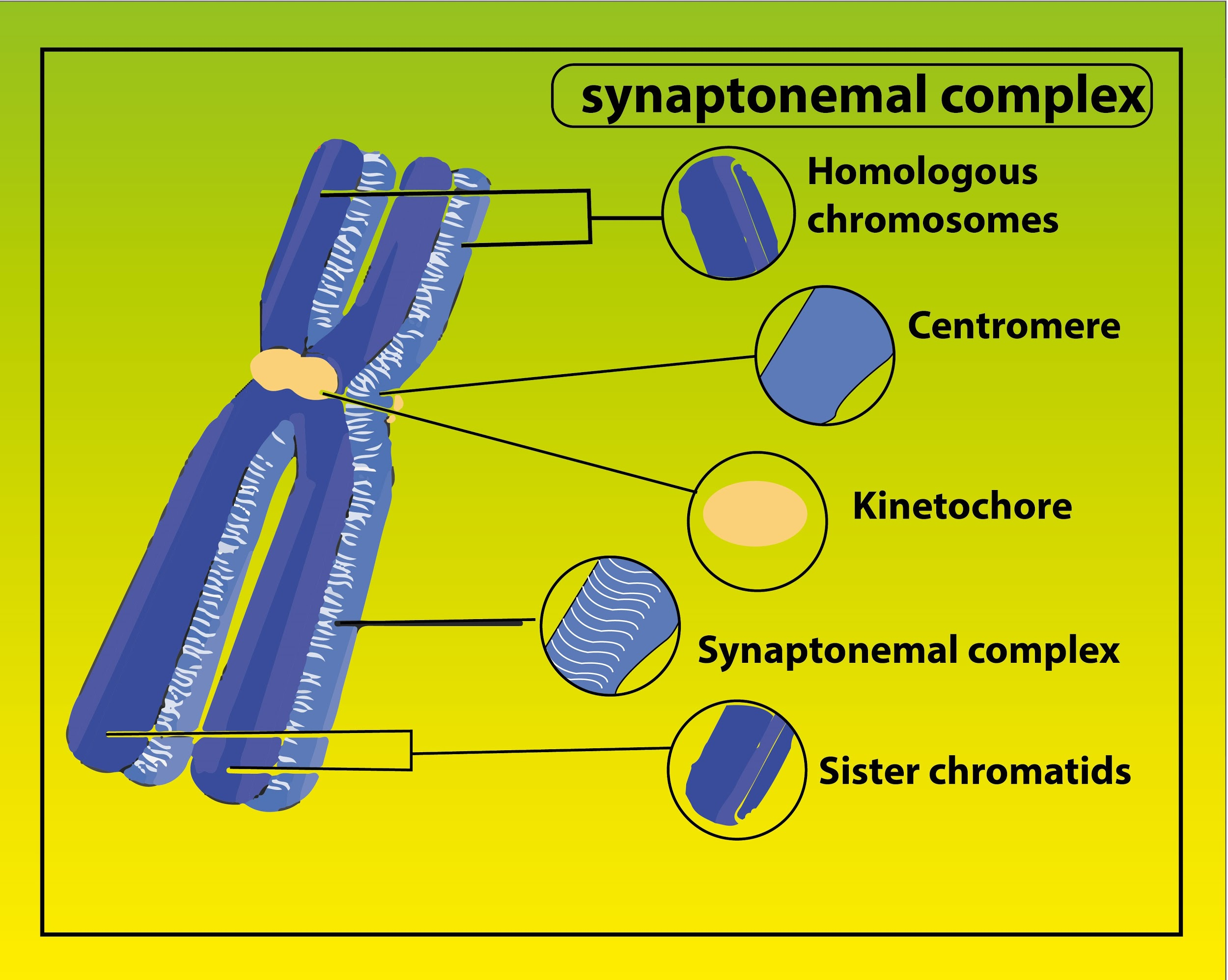
Zygotene is the second stage of prophase-I in which the process of pairing between homologous chromosomes at end to end takes place, which is known as synapsis. The synaptonemal complex is formed during these zygotene stages which results in the pairing of homologous. The formation of bivalents occurs in this phase.
Additional Information:
Prophase I is the longest in duration when compared with the prophase in mitosis, which takes about 85-95 %of the total time for meiosis. The first of prophase-I is leptotene where the chromosome begins to condense. The second stage is zygotene also known as zygonema marked by the beginning of pairing between homologous chromosomes and ends with complete pairing. The third stage is pachytene in which synapsis takes place. The fourth stage is diplotene or diplonema in which DNA recombination is completed. The last stage of prophase-I is diakinesis where the chromosome becomes shorter and thicker because of condensation and marked by the disappearance of the nucleolus and nuclear envelope at the end of prophase I.
So, the correct answer is, ‘prophase I.’
Note: -The term ‘meiosis’ was coined by J.B. Farmer and J.E.S. Moore in 1905.
-Meiosis is a special method of division that occurs in the maturation of the sex cells, which results in each daughter's nucleus receives half the number of chromosomes characteristic of the somatic cell of the species.
-Meiosis is divided into two events: meiosis I or reductional division and meiosis II or mitotic division.
-The difference between mitosis and meiosis is that sister chromatids remain joined after metaphase in meiosis I but in mitosis, they separate.
Complete answer:
Zygotene is the second stage of prophase-I in which the process of pairing between homologous chromosomes at end to end takes place, which is known as synapsis. The synaptonemal complex is formed during these zygotene stages which results in the pairing of homologous. The formation of bivalents occurs in this phase.

Additional Information:
Prophase I is the longest in duration when compared with the prophase in mitosis, which takes about 85-95 %of the total time for meiosis. The first of prophase-I is leptotene where the chromosome begins to condense. The second stage is zygotene also known as zygonema marked by the beginning of pairing between homologous chromosomes and ends with complete pairing. The third stage is pachytene in which synapsis takes place. The fourth stage is diplotene or diplonema in which DNA recombination is completed. The last stage of prophase-I is diakinesis where the chromosome becomes shorter and thicker because of condensation and marked by the disappearance of the nucleolus and nuclear envelope at the end of prophase I.
So, the correct answer is, ‘prophase I.’
Note: -The term ‘meiosis’ was coined by J.B. Farmer and J.E.S. Moore in 1905.
-Meiosis is a special method of division that occurs in the maturation of the sex cells, which results in each daughter's nucleus receives half the number of chromosomes characteristic of the somatic cell of the species.
-Meiosis is divided into two events: meiosis I or reductional division and meiosis II or mitotic division.
-The difference between mitosis and meiosis is that sister chromatids remain joined after metaphase in meiosis I but in mitosis, they separate.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




