
Where should we take the valency of iron 2 and where should 3?
Answer
492k+ views
Hint: The valency of an element is defined as the no. of electrons gained or lost from the outermost orbital which is also known as the valence orbital, in a chemical reaction. The valency of the electron is similar to the Oxidation state of the element, which also indicates the no. of electrons lost or gained.
Complete answer:
The atomic number of Iron is 26 and the electronic configuration of Iron is given as: $ Fe(26):1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6}3{s^2}3{p^6}4{s^2}3{d^6} $
Iron belongs to the d-block of the periodic table. Which are also known as the transition metal elements. The outermost valence orbital is the 4s and 3d orbital. When an electron is removed from the atom, it is first lost from the 4s orbital as the energy of 4s is slightly greater than the 3d orbital. The outer valence shell electronic configuration can be given as:
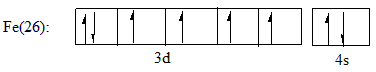
For $ F{e^{ + 2}} $ two electrons are lost from the 4s orbital making the configuration $ F{e^{ + 2}}:1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6}3{s^2}3{p^6}3{d^6} $
When iron loses two electrons from the 4s orbital, it has 24 electrons left, the valency of Iron would be considered as +2. $ F{e^{ + 2}} $ is known as Ferrous ion.
For $ F{e^{ + 3}} $ three electrons are lost, two from 4s and 1 from the paired electrons in 3d. When one electron from 3d is lost, the electronic configuration becomes $ 3{d^5} $ making the d orbital very stable (half-filled orbital stability) . $ F{e^{ + 3}} $ is known as Ferric ion. The electronic configuration becomes:
$ F{e^{ + 3}}:1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6}3{s^2}3{p^6}3{d^5} $
Hence when iron loses three electrons to form $ F{e^{ + 3}} $ the valency of Iron is considered as +3.
Note:
There are three electronic configurations that are considered highly stable. First is the zero filled orbital, which means the orbital with no electrons is stable. Second is the fully filled orbital, when the orbital is fully filled means p orbital has 6 electrons or d orbital has 10 electrons it attains stability. Third is the half-filled orbital, when the orbital is half filled i.e., p orbital with 3 electrons or d with 5 electrons is highly stable.
Complete answer:
The atomic number of Iron is 26 and the electronic configuration of Iron is given as: $ Fe(26):1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6}3{s^2}3{p^6}4{s^2}3{d^6} $
Iron belongs to the d-block of the periodic table. Which are also known as the transition metal elements. The outermost valence orbital is the 4s and 3d orbital. When an electron is removed from the atom, it is first lost from the 4s orbital as the energy of 4s is slightly greater than the 3d orbital. The outer valence shell electronic configuration can be given as:

For $ F{e^{ + 2}} $ two electrons are lost from the 4s orbital making the configuration $ F{e^{ + 2}}:1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6}3{s^2}3{p^6}3{d^6} $
When iron loses two electrons from the 4s orbital, it has 24 electrons left, the valency of Iron would be considered as +2. $ F{e^{ + 2}} $ is known as Ferrous ion.
For $ F{e^{ + 3}} $ three electrons are lost, two from 4s and 1 from the paired electrons in 3d. When one electron from 3d is lost, the electronic configuration becomes $ 3{d^5} $ making the d orbital very stable (half-filled orbital stability) . $ F{e^{ + 3}} $ is known as Ferric ion. The electronic configuration becomes:
$ F{e^{ + 3}}:1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6}3{s^2}3{p^6}3{d^5} $
Hence when iron loses three electrons to form $ F{e^{ + 3}} $ the valency of Iron is considered as +3.
Note:
There are three electronic configurations that are considered highly stable. First is the zero filled orbital, which means the orbital with no electrons is stable. Second is the fully filled orbital, when the orbital is fully filled means p orbital has 6 electrons or d orbital has 10 electrons it attains stability. Third is the half-filled orbital, when the orbital is half filled i.e., p orbital with 3 electrons or d with 5 electrons is highly stable.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




