
How can you tell the difference between an ester, ketone, carboxylic acid, aldehyde, amines, amides and phenol?
Answer
550.8k+ views
Hint: Let that be ester, ketone, carboxylic acid, aldehyde, amines, amides or phenol; each one of them is just the additional part to a molecule hampering its general physical and chemical properties. But each one of them added to the molecule defines new properties different from each other.
Complete answer:
Let us see all of them one by one;
Ester-
A chemical compound in which at least one hydroxyl group is replaced by an alkoxy group.
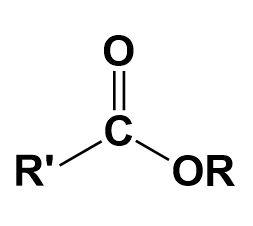
Ketone-
It is a functional group attached to a molecular chain. It contains a carbonyl group.
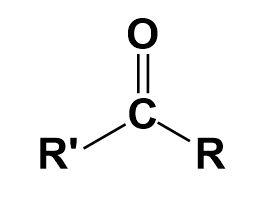
Carboxylic acid-
It is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group. They occur widely and the most common ones are amino acids and fatty acids.
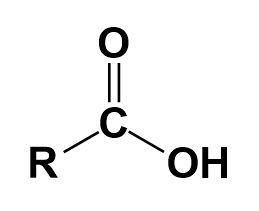
Aldehyde-
It is a functional group with the structure -CHO, consisting of carbonyl in the centre.
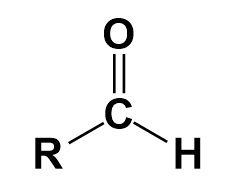
Amines-
These are the organic compounds that contain nitrogen atoms with a lone pair of electrons.
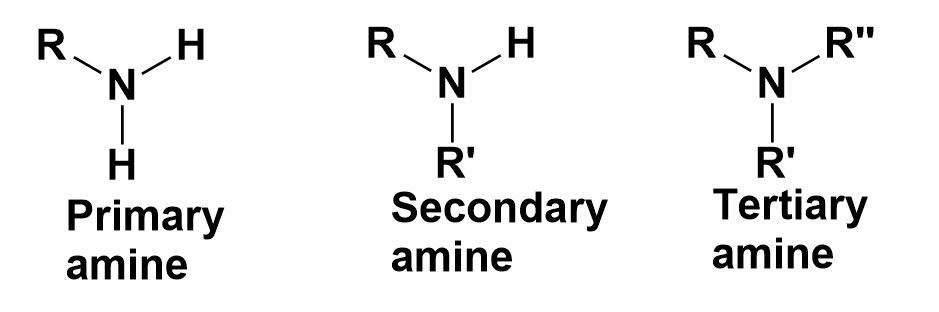
Amides-
They are the organic compounds that contain a functional group consisting of an acyl group linked to a nitrogen atom.
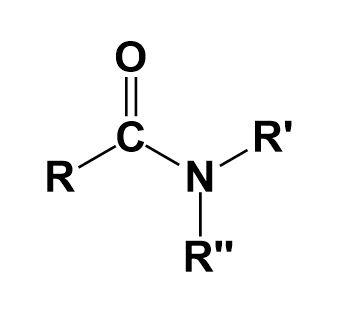
Phenol-
It is an aromatic organic compound, basically we can consider it as an alcohol. It consists of a phenyl group bonded to the hydroxyl group.

Now, by looking at the above diagrams we can find the differences easily.
Note:
During old times, scientists used to use Infra-red spectroscopy to determine the differences between the above given compounds. Modern methods include X-ray crystallography and NMR spectroscopy.
Complete answer:
Let us see all of them one by one;
Ester-
A chemical compound in which at least one hydroxyl group is replaced by an alkoxy group.

Ketone-
It is a functional group attached to a molecular chain. It contains a carbonyl group.

Carboxylic acid-
It is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group. They occur widely and the most common ones are amino acids and fatty acids.

Aldehyde-
It is a functional group with the structure -CHO, consisting of carbonyl in the centre.

Amines-
These are the organic compounds that contain nitrogen atoms with a lone pair of electrons.

Amides-
They are the organic compounds that contain a functional group consisting of an acyl group linked to a nitrogen atom.

Phenol-
It is an aromatic organic compound, basically we can consider it as an alcohol. It consists of a phenyl group bonded to the hydroxyl group.

Now, by looking at the above diagrams we can find the differences easily.
Note:
During old times, scientists used to use Infra-red spectroscopy to determine the differences between the above given compounds. Modern methods include X-ray crystallography and NMR spectroscopy.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




