
What is tetrahedral? Give an example
Answer
504.3k+ views
Hint: Tetrahedral is a kind of geometry exhibited by those molecules in which the central atom is bonded to four other atoms. \[s{{p}^{3}}\] hybridized orbitals lead to tetrahedral geometry. In this case, the central atom doesn’t have a lone pair of electrons.
Complete answer:
Tetrahedral is a kind of geometry exhibited by those molecules in which the central atom is bonded to four other atoms and doesn’t contain any lone pair of electrons. Methane \[\left( CH_4 \right)\] is the simplest hydrocarbon which exhibits tetrahedral geometry. The tetrahedral geometry of methane is illustrated in the following diagram:
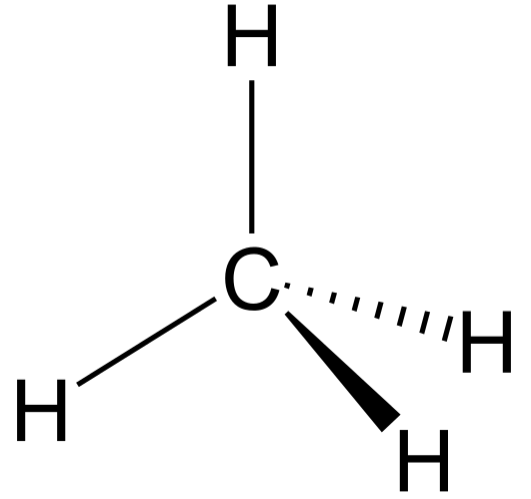
In the above diagram, four hydrogen atoms are present at the four vertices of the tetrahedron. The HCH bond angle is \[{{109}^{\circ }}28'\]. Two simple lines between carbon and hydrogen represent those bonds which lie in the plane of paper. While dashed and bold lines represent those bonds which lie below and above the plane of paper, respectively.
Therefore, the central atom is surrounded by four atoms and doesn’t contain any lone pair of electrons exhibiting tetrahedral molecular geometry. Methane \[\left( CH_4 \right)\], carbon tetrachloride \[\left( CCl_4 \right)\]are some examples which have tetrahedral geometry.
Additional information:
In valence bond theory, hybridization concept is used in which intermixing between atomic orbitals of comparable size takes place and obtains new hybrid orbitals. In \[s{{p}^{3}}\] hybridization, one s and three p orbitals undergo intermixing to obtain four \[s{{p}^{3}}\]orbitals.
Note:
It is important to note that those molecules in which the central atom is bonded to four other atoms and doesn’t contain a lone pair of electrons have tetrahedral geometry. In this geometry, the central atom of a molecule undergoes \[s{{p}^{3}}\] hybridization. Methane \[\left( CH_4 \right)\] is the simplest hydrocarbon which exhibits tetrahedral geometry.
Complete answer:
Tetrahedral is a kind of geometry exhibited by those molecules in which the central atom is bonded to four other atoms and doesn’t contain any lone pair of electrons. Methane \[\left( CH_4 \right)\] is the simplest hydrocarbon which exhibits tetrahedral geometry. The tetrahedral geometry of methane is illustrated in the following diagram:

In the above diagram, four hydrogen atoms are present at the four vertices of the tetrahedron. The HCH bond angle is \[{{109}^{\circ }}28'\]. Two simple lines between carbon and hydrogen represent those bonds which lie in the plane of paper. While dashed and bold lines represent those bonds which lie below and above the plane of paper, respectively.
Therefore, the central atom is surrounded by four atoms and doesn’t contain any lone pair of electrons exhibiting tetrahedral molecular geometry. Methane \[\left( CH_4 \right)\], carbon tetrachloride \[\left( CCl_4 \right)\]are some examples which have tetrahedral geometry.
Additional information:
In valence bond theory, hybridization concept is used in which intermixing between atomic orbitals of comparable size takes place and obtains new hybrid orbitals. In \[s{{p}^{3}}\] hybridization, one s and three p orbitals undergo intermixing to obtain four \[s{{p}^{3}}\]orbitals.
Note:
It is important to note that those molecules in which the central atom is bonded to four other atoms and doesn’t contain a lone pair of electrons have tetrahedral geometry. In this geometry, the central atom of a molecule undergoes \[s{{p}^{3}}\] hybridization. Methane \[\left( CH_4 \right)\] is the simplest hydrocarbon which exhibits tetrahedral geometry.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




