
The 2 images of 1,2-dichloromethane are given. Can we call them isomers?
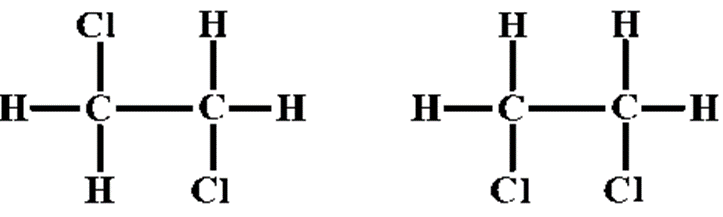
(A) Yes
(B) No
(C) May be
(D) Can’t says
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The C-C bonds undergo rotation about a single bond. In this question we need to see if there is any change in the structure of the molecule. If there is no change in the structure then they will be identical molecules. The C-C single bond has an ability to rotate itself and hence has a structure in which the arrangement in the space is such that it gives the most stable structure.
Step by step explanation:
We have 2 structures of 1,2-dichloromethane in which there is a C-C single bond. This single bond is able to rotate about itself. Thus, on rotation they will be converted to the same structure. Thus, they are homomers.
The isomers when not specified are to be considered as structural isomers and not configurational isomers. Structurally these structures are identical to each other.
Hence option B is the correct answer.
Additional information:
Isomers are compounds in which the molecular formula is the same but the structure is different.
They are mainly of 2 type structural and stereoisomers. In the case of stereoisomers the orientation in the space is different.
Structural isomer is of different types:
Chain isomerism: when 2 or more compounds have the same molecular formula but different carbon skeletons. Example: pentane, isopentane and neopentane.
Positional isomerism:
When 2 or more compounds differ in the position of the functional group. Example: butan-1-ol and Butan-2-ol
Functional group:
2 or more compounds have the same molecular formula but different functional groups. Example: acetaldehyde and acetone.
Metamerism:
It arises due to different alkyl groups on either side of the functional group. It is mostly seen in cases of ether. Ex: methoxypropane and ethoxypropane.
Stereoisomerism:
The compounds that have the same constituent and same sequence on the double bond but differ in relative position of the bond.
Note: We may have a thought that the structures are isomer as the arrangement of the molecules in the space are different. Some can even come to the conclusion that as both the chlorine are on the same side in case of one structure and they are on different sides but the C-C single bond will rotate along itself and hence the structure are same
Step by step explanation:
We have 2 structures of 1,2-dichloromethane in which there is a C-C single bond. This single bond is able to rotate about itself. Thus, on rotation they will be converted to the same structure. Thus, they are homomers.
The isomers when not specified are to be considered as structural isomers and not configurational isomers. Structurally these structures are identical to each other.
Hence option B is the correct answer.
Additional information:
Isomers are compounds in which the molecular formula is the same but the structure is different.
They are mainly of 2 type structural and stereoisomers. In the case of stereoisomers the orientation in the space is different.
Structural isomer is of different types:
Chain isomerism: when 2 or more compounds have the same molecular formula but different carbon skeletons. Example: pentane, isopentane and neopentane.
Positional isomerism:
When 2 or more compounds differ in the position of the functional group. Example: butan-1-ol and Butan-2-ol
Functional group:
2 or more compounds have the same molecular formula but different functional groups. Example: acetaldehyde and acetone.
Metamerism:
It arises due to different alkyl groups on either side of the functional group. It is mostly seen in cases of ether. Ex: methoxypropane and ethoxypropane.
Stereoisomerism:
The compounds that have the same constituent and same sequence on the double bond but differ in relative position of the bond.
Note: We may have a thought that the structures are isomer as the arrangement of the molecules in the space are different. Some can even come to the conclusion that as both the chlorine are on the same side in case of one structure and they are on different sides but the C-C single bond will rotate along itself and hence the structure are same
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

In Carius method of estimation of halogens 015g of class 11 chemistry JEE_Main

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry in Hindi Chapter 1 Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry in Hindi Chapter 8 Redox Reactions (2025-26)

An ideal gas is at pressure P and temperature T in class 11 chemistry JEE_Main

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses




