
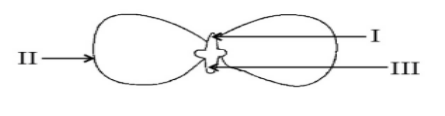
The above diagram shows the structure of the embryo of a dicot seed. Name the parts marked i, ii and iii sequentially.
A. Plumule, cotyledon, radicle
B. Plumule, radicle, cotyledon
C. Cotyledon, plumule, radicle
D. Radicle, plumule, cotyledon

Answer
471.6k+ views
Hint: The process of germination occurs when a micropyle in one section of the hilum absorbs water. which it uses up for the seedlings to develop into tiny, immature embryonic plants from the seed coverings under favorable conditions such as sufficient light, temperature, air, and so on.
The following steps are involved in germination:
1. Seeds swell, plumules sprout, and shoots emerge.
2. The roots emerge from the radicle of the seeds.
3. Cotyledon formation is the formation of cotyledons (one in monocots and two in dicots).
Complete answer:
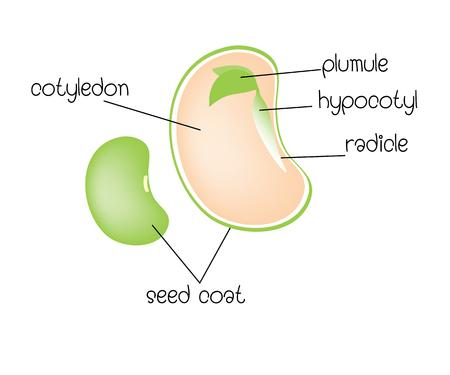
1. The seed, along with the ovule, is covered by a seed coat made up of the ovule sac's integuments. The seed coat of dicots is further separated into an exterior coat called the Testa and an interior coat called the tegmen. The plumule, radicle, and hypocotyl are the three elements of the embryonic axis. The embryonic axis ends in a radicle, which is where the root will grow.
2. Seeds with two embryonic leaves, or cotyledons, are known as dicot seeds. Dicot seeds comprise a single embryo surrounded by two cotyledons and an embryo axis. Dicot seed pods often contain more seeds than monocot seed pods. The seeds of most dicots are symmetrical and can be separated into two parts.
Hence option A is the correct answer.
Note:
The following steps are involved in germination:
1. Seeds swell, plumules sprout, and shoots emerge.
2. The roots emerge from the radicle of the seeds.
3. Cotyledon formation is the formation of cotyledons (one in monocots and two in dicots).
Complete answer:
1. The seed, along with the ovule, is covered by a seed coat made up of the ovule sac's integuments. The seed coat of dicots is further separated into an exterior coat called the Testa and an interior coat called the tegmen. The plumule, radicle, and hypocotyl are the three elements of the embryonic axis. The embryonic axis ends in a radicle, which is where the root will grow.
2. Seeds with two embryonic leaves, or cotyledons, are known as dicot seeds. Dicot seeds comprise a single embryo surrounded by two cotyledons and an embryo axis. Dicot seed pods often contain more seeds than monocot seed pods. The seeds of most dicots are symmetrical and can be separated into two parts.
Hence option A is the correct answer.

Note:
| MONOCOTS | DICOTS |
| Embryo with single cotyledon | Embryo with two cotyledons |
| Pollen with single furrow or pore | Pollen with three furrows or pores |
| Flower parts in multiples of three | Flower parts in multiples of four or five |
| Major leaf veins parallel | Major leaf veins reticulated |
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




