
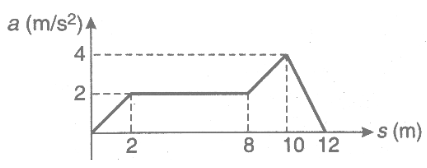
The acceleration-displacement graph of a particle moving in a straight line is as shown in the figure, initial velocity of particle is zero. Find the velocity of the particle when displacement of the particle is $s = 12\,m$.
A. \[3\sqrt 2\,m/s\]
B. \[2\sqrt 5 \,m/s\]
C. \[4\sqrt 3 \,m/s\]
D. \[4\,m/s\]

Answer
518.4k+ views
Hint: The rate of change of an object's velocity with respect to time is called acceleration in mechanics. Accelerations are quantities that are measured in vectors (in that they have magnitude and direction). The orientation of the net force acting on an object determines the orientation of its acceleration.
Complete step by step answer:
A displacement vector is a line drawn from an object's original location to its final position.Acceleration is a vector that depicts the degree and direction of velocity changes. Meters per second per second, or metres per second squared, are the normal units.
The initial velocity multiplied by time plus one-half the acceleration multiplied by the square of time equals displacement. Displacement can be measured by subtracting the original distance from the final distance away from a point. When it comes to deciding velocity, displacement is crucial (which is also a vector). We know that
\[a = v\dfrac{{dv}}{{dx}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow adx = vdv\]
Upon integrating
\[\int_0^v v dv = \int_0^{12} a ds\]
Here, area under the curve \[ = \dfrac{{{V^2}}}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{V^2}}}{2} = 24\]
\[ \therefore V = 4\sqrt 3 \]
Hence option (C) is correct.
Note: The metre is the SI unit for displacement (m). The vector variation between an object's finishing and beginning points is known as displacement. The rate at which displacement varies over time is referred to as velocity. The derivative of position with respect to time is instantaneous velocity. Acceleration is a vector that depicts the degree and direction of velocity changes.
Complete step by step answer:
A displacement vector is a line drawn from an object's original location to its final position.Acceleration is a vector that depicts the degree and direction of velocity changes. Meters per second per second, or metres per second squared, are the normal units.
The initial velocity multiplied by time plus one-half the acceleration multiplied by the square of time equals displacement. Displacement can be measured by subtracting the original distance from the final distance away from a point. When it comes to deciding velocity, displacement is crucial (which is also a vector). We know that
\[a = v\dfrac{{dv}}{{dx}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow adx = vdv\]
Upon integrating
\[\int_0^v v dv = \int_0^{12} a ds\]
Here, area under the curve \[ = \dfrac{{{V^2}}}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{V^2}}}{2} = 24\]
\[ \therefore V = 4\sqrt 3 \]
Hence option (C) is correct.
Note: The metre is the SI unit for displacement (m). The vector variation between an object's finishing and beginning points is known as displacement. The rate at which displacement varies over time is referred to as velocity. The derivative of position with respect to time is instantaneous velocity. Acceleration is a vector that depicts the degree and direction of velocity changes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




