
The alkylation of benzene with n-propyl chloride in the presence of anhydrous $AlC{{l}_{3}}$ produces:
(A) n-propyl benzene
(B) isopropyl benzene
(C) o-dipropyl benzene
(D) a mixture of all of these
Answer
531.9k+ views
Hint: In this question, we can see that the alkylation of an aromatic ring, benzene is done with an alkyl halide, n-propyl chloride, in the presence of a strong Lewis acid, anhydrous $AlC{{l}_{3}}$. Hence the given reaction is an example of Friedel-Crafts alkylation.
Complete answer:
The Friedel-Crafts reactions are reactions that can be used to add substituents to an aromatic ring. They were developed by chemists James Crafts and Charles Friedel in 1877.
They are mainly of two types, Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction, and Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction.
Both the alkylation and acylation reactions follow the electrophilic aromatic substitution mechanism.
In the given question, Friedel-Crafts alkylation takes place.
When n-propyl chloride is taken in the presence of aluminum chloride, it forms an electrophilic propyl carbocation.
\[C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}Cl+AlC{{l}_{3}}\to C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}CH_{2}^{+}+AlCl_{4}^{-}\]
Since primary carbocations are unstable, a more stable secondary isopropyl carbocation is formed by hydride shift.
\[C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}CH_{2}^{+}\to C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}^{+}}C{{H}_{3}}\]
When this carbocation attacks the benzene ring, an isopropyl cyclohexane carbocation intermediate is formed. This results in the loss of its aromaticity since carbon-carbon double bond C=C is broken.
When this intermediate is deprotonated, the carbon-carbon double bond C=C is reformed and the compound restores aromaticity to form isopropyl benzene. The protons and chlorine ion from $AlCl_{4}^{-}$ form hydrochloric acid and hence aluminum chloride $AlC{{l}_{3}}$ is restored.
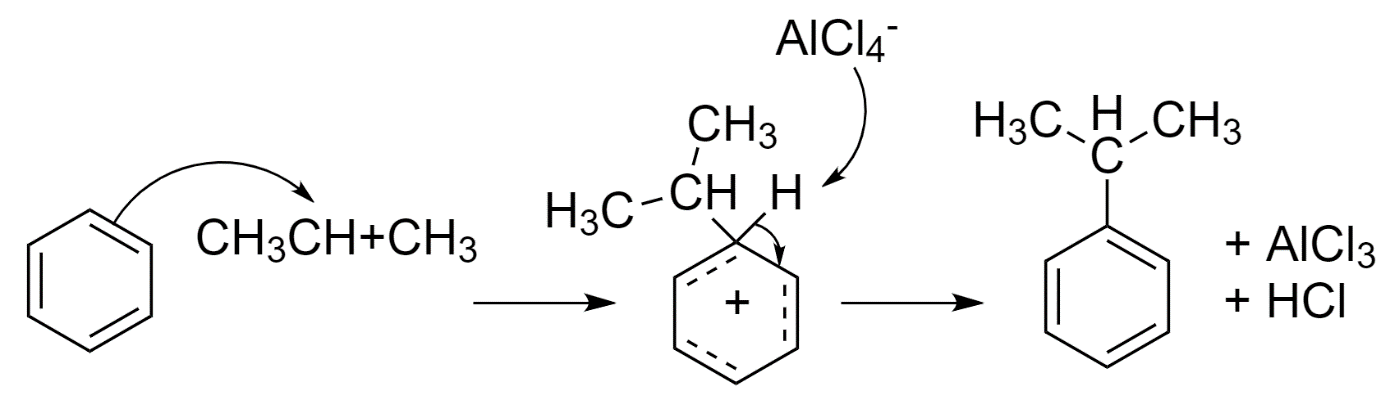
So, option (B) isopropyl benzene is formed when n-propyl chloride is reacted with benzene in presence of anhydrous $AlC{{l}_{3}}$.
Note:
This question can be tricky and confusing as one can forget to factor in the stability of the carbocation formed. When the stability of a carbocation intermediate is increased, the activation energy of the reaction is lowered, and hence the speed of the reaction increases.
The common name of isopropyl benzene is cumene.
Complete answer:
The Friedel-Crafts reactions are reactions that can be used to add substituents to an aromatic ring. They were developed by chemists James Crafts and Charles Friedel in 1877.
They are mainly of two types, Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction, and Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction.
Both the alkylation and acylation reactions follow the electrophilic aromatic substitution mechanism.
In the given question, Friedel-Crafts alkylation takes place.
When n-propyl chloride is taken in the presence of aluminum chloride, it forms an electrophilic propyl carbocation.
\[C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}Cl+AlC{{l}_{3}}\to C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}CH_{2}^{+}+AlCl_{4}^{-}\]
Since primary carbocations are unstable, a more stable secondary isopropyl carbocation is formed by hydride shift.
\[C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}CH_{2}^{+}\to C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}^{+}}C{{H}_{3}}\]
When this carbocation attacks the benzene ring, an isopropyl cyclohexane carbocation intermediate is formed. This results in the loss of its aromaticity since carbon-carbon double bond C=C is broken.
When this intermediate is deprotonated, the carbon-carbon double bond C=C is reformed and the compound restores aromaticity to form isopropyl benzene. The protons and chlorine ion from $AlCl_{4}^{-}$ form hydrochloric acid and hence aluminum chloride $AlC{{l}_{3}}$ is restored.

So, option (B) isopropyl benzene is formed when n-propyl chloride is reacted with benzene in presence of anhydrous $AlC{{l}_{3}}$.
Note:
This question can be tricky and confusing as one can forget to factor in the stability of the carbocation formed. When the stability of a carbocation intermediate is increased, the activation energy of the reaction is lowered, and hence the speed of the reaction increases.
The common name of isopropyl benzene is cumene.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




