
The amplitude of a simple pendulum is $10\;cm$. When the pendulum is at a displacement of $4\;cm$ from the mean position, the ratio of kinetic and potential energies at that point is:
\[\begin{align}
& \text{A}\text{.5}\text{.25} \\
& \text{B}\text{.2}\text{.5} \\
& \text{C}\text{.4}\text{.5} \\
& \text{D}\text{.7}\text{.5} \\
\end{align}\]
Answer
528.9k+ views
Hint: We know that the total energy due to the to and fro motion of the pendulum is given by the kinetic energy and the potential energy of the pendulum. Here, we need to calculate the ratio between them from the given data.
Formula used:
$K.E=\dfrac{1}{2}m\omega^{2}(A^2-y^2)$ and
$P.E=\dfrac{1}{2} m\omega^2 y^2$
Complete step-by-step solution:
Consider the energy diagram of the pendulum, as shown below:
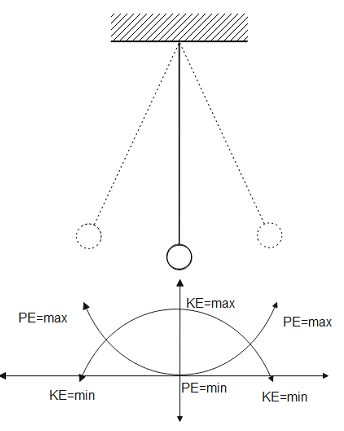
Here, given that amplitude is $a=10\;cm$ and the displacement of $y=4\;cm$ from the mean position. We know that the kinetic energy and the potential energy is given as follows: $K.E=\dfrac{1}{2}m\omega^{2}(A^2-y^2)$ and $P.E=\dfrac{1}{2} m\omega^2 y^2$
Then ratio of the kinetic and potential energies at the midpoint is given as
$\dfrac{K.E}{P.E}=\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2}m\omega^{2}(A^2-y^2)}{\dfrac{1}{2} m\omega^2 y^2}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{K.E}{P.E}=\dfrac{A^2-y^2}{y^2}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{K.E}{P.E}=\dfrac{100-16}{16}=\dfrac{84}{16}$
$\therefore \dfrac{K.E}{P.E}=5.25$
Thus the correct answer is option $A.\;5.25$
Additional Information:
A pendulum is a small bob, which is suspended on an inelastic, weightless thread. When the bob is disturbed, it undergoes SHM motion. When no external force acts on the bob, i.e. assuming there is no resistive force acting on it. Then we can say that the total energy due to the bob, is the sum of its potential and kinetic energies. The total energy of the system is minimum at the mean position and maximum at the end points.
The time period of the oscillation depends on the length of the bob and the acceleration due to gravity acting on it.
Note: The total energy of the pendulum is always a constant. The individual terms, i.e. the kinetic energy and the potential energy each varies, but the sum of the two always remains a constant. Also, at the mean position, the total energy is equal to the kinetic energy and at the end positions; the total energy is equal to the potential energy.
Formula used:
$K.E=\dfrac{1}{2}m\omega^{2}(A^2-y^2)$ and
$P.E=\dfrac{1}{2} m\omega^2 y^2$
Complete step-by-step solution:
Consider the energy diagram of the pendulum, as shown below:

Here, given that amplitude is $a=10\;cm$ and the displacement of $y=4\;cm$ from the mean position. We know that the kinetic energy and the potential energy is given as follows: $K.E=\dfrac{1}{2}m\omega^{2}(A^2-y^2)$ and $P.E=\dfrac{1}{2} m\omega^2 y^2$
Then ratio of the kinetic and potential energies at the midpoint is given as
$\dfrac{K.E}{P.E}=\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2}m\omega^{2}(A^2-y^2)}{\dfrac{1}{2} m\omega^2 y^2}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{K.E}{P.E}=\dfrac{A^2-y^2}{y^2}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{K.E}{P.E}=\dfrac{100-16}{16}=\dfrac{84}{16}$
$\therefore \dfrac{K.E}{P.E}=5.25$
Thus the correct answer is option $A.\;5.25$
Additional Information:
A pendulum is a small bob, which is suspended on an inelastic, weightless thread. When the bob is disturbed, it undergoes SHM motion. When no external force acts on the bob, i.e. assuming there is no resistive force acting on it. Then we can say that the total energy due to the bob, is the sum of its potential and kinetic energies. The total energy of the system is minimum at the mean position and maximum at the end points.
The time period of the oscillation depends on the length of the bob and the acceleration due to gravity acting on it.
Note: The total energy of the pendulum is always a constant. The individual terms, i.e. the kinetic energy and the potential energy each varies, but the sum of the two always remains a constant. Also, at the mean position, the total energy is equal to the kinetic energy and at the end positions; the total energy is equal to the potential energy.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




