
The angular shape of ozone molecule \[{O_3}\] consists of:
A. 1 sigma and 1 pi bonds
B. 2 sigma and 1 pi bonds
C. 1 sigma and 2 pi bonds
D. 2 sigma and 2 pi bonds
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Oxygen molecule has valency of -2. That is why it can form two sigma bonds with the other atoms. It has three lone pairs to form pi bonds with other atoms. Ozone has all three oxygen atoms and it’s a dihedral molecule with \[s{p^2}\] hybridisation.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The Lewis structure for ozone \[{O_3}\] consists of a central oxygen atom that has a double bond to one of the outer oxygen atoms and a single bond to the other oxygen atom. Lewis structure is based on the octet rule which states that there should be eight electrons in the outermost shell or orbit of an atom for the molecule to be stable.
Here, the lone pair on the central atom repels the electrons in the two side bonds present, forcing the atom to adopt a bent molecular geometry. Expected geometry is the trigonal planar, where O-O-O bond angle to be \[{120^o}\]. However, as per the context of the VSEPR model, lone pairs of electrons are considered slightly more repulsive than bonding pairs of electrons due to their closer proximity to the central atom. Therefore, the O-O-O angle is slightly less than \[{120^o}\] i.e. \[{116.8^o}\].
There are six valence electrons for each molecule of Oxygen in ozone and thus the total number of valence electrons is \[6 \times 3 = 18\]. As the octet rule applies, the central atom should have eight electrons in its outer shell. So, one molecule of the Oxygen is in the centre with the other two on the opposite sides of it.
The central atom has only one lone pair of electrons which is making it stable due to the eight electrons in its outermost orbit. To satisfy the octet rule, central atom requires to form a double bond on either of its sides with an Oxygen molecule. As both the atoms of Oxygen on sides have the same electronegativity and structure, the double bond keeps on shifting from both and results in resonance.
Therefore, the structure of Ozone is unique because the central atom has one double bond and one single bond with its neighbouring oxygen molecules which keeps interchanging their positions, and hence the angular shape of the ozone molecule has 2 sigma bonds and one pi bond.
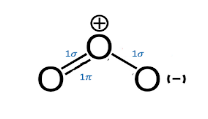
Hence, the correct option is (B).
Note: Ozone molecule is polar because the distribution of electrons across the molecule is uneven. This leads to less electron density on the central atom. The negative half charge on the two side oxygen atoms and +1 formal charge on the central atom makes it polar.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The Lewis structure for ozone \[{O_3}\] consists of a central oxygen atom that has a double bond to one of the outer oxygen atoms and a single bond to the other oxygen atom. Lewis structure is based on the octet rule which states that there should be eight electrons in the outermost shell or orbit of an atom for the molecule to be stable.
Here, the lone pair on the central atom repels the electrons in the two side bonds present, forcing the atom to adopt a bent molecular geometry. Expected geometry is the trigonal planar, where O-O-O bond angle to be \[{120^o}\]. However, as per the context of the VSEPR model, lone pairs of electrons are considered slightly more repulsive than bonding pairs of electrons due to their closer proximity to the central atom. Therefore, the O-O-O angle is slightly less than \[{120^o}\] i.e. \[{116.8^o}\].
There are six valence electrons for each molecule of Oxygen in ozone and thus the total number of valence electrons is \[6 \times 3 = 18\]. As the octet rule applies, the central atom should have eight electrons in its outer shell. So, one molecule of the Oxygen is in the centre with the other two on the opposite sides of it.
The central atom has only one lone pair of electrons which is making it stable due to the eight electrons in its outermost orbit. To satisfy the octet rule, central atom requires to form a double bond on either of its sides with an Oxygen molecule. As both the atoms of Oxygen on sides have the same electronegativity and structure, the double bond keeps on shifting from both and results in resonance.
Therefore, the structure of Ozone is unique because the central atom has one double bond and one single bond with its neighbouring oxygen molecules which keeps interchanging their positions, and hence the angular shape of the ozone molecule has 2 sigma bonds and one pi bond.

Hence, the correct option is (B).
Note: Ozone molecule is polar because the distribution of electrons across the molecule is uneven. This leads to less electron density on the central atom. The negative half charge on the two side oxygen atoms and +1 formal charge on the central atom makes it polar.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




