
The \[As{F_5}\] molecule is trigonal bipyramidal. The hybrid orbitals used by the atoms for bonding are:
(A) \[{d_{{x^2} - {y^2}}},{d_{{z^2}}},{p_x},{p_y}\]
(B) \[{d_{xy}},s,{p_x},{p_y},{p_z}\]
(C) \[{d_{{x^2} - {y^2}}},\]s,\[{p_x},{p_y}\]
(D) \[s,{p_x},{p_y},{p_z}\],\[{d_{{z^2}}}\]
Answer
594.3k+ views
Hint: Ground state electronic configuration of Arsenic atom is \[[Ar]3{d^{10}}4{s^2}4{p^3}\]. \[{d_{{x^2} - {y^2}}}\] orbital is situated in the xy plane and \[{d_{{z^2}}}\] is situated at the z-axis and perpendicular to xy plane.
Complete answer:
We know that Arsenic is the element of the Nitrogen group. So, its ground state electronic configuration is \[[Ar]3{d^{10}}4{s^2}4{p^3}\] and excited state configuration will be \[[Ar]3{d^{10}}4{s^1}4{p^3}4{d^1}\].
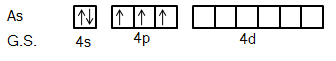
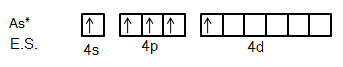
So, we can say from this excited state of Arsenic atom that it can bind with five Fluorine atoms with five different orbitals.
It is clear from the figure that five fluorine atoms will give one electron each to five half-filled orbitals of Arsenic atoms. So, hybridization in this compound will be \[s{p^3}d\].
So, it is evident that \[s,{p_x},{p_y},{p_z}\] orbitals will take part because they are only available orbitals.
Now, if \[s{p^3}d\] hybridized compounds have trigonal bipyramidal geometry, then it has to form bonds in a plane and two more bonds perpendicular to the plane. If we take the plane in xy direction, then only one orbital is there which can form bonds perpendicular to it and it is \[{d_{{z^2}}}\] as it is along the z-axis.
So, orbitals involved are \[s,{p_x},{p_y},{p_z}\],\[{d_{{z^2}}}\]
So, the correct answer is (D) \[s,{p_x},{p_y},{p_z}\],\[{d_{{z^2}}}\].
Additional Information:
- In \[s{p^3}d\] hybridization, compound can have either trigonal bipyramidal or square pyramidal geometry.
- If a compound is having trigonal bipyramidal geometry, then it uses \[{d_{{z^2}}}\] orbital as one of the d-orbitals to form bonds. If a compound has square pyramidal geometry, then \[{d_{{x^2} - {y^2}}}\] is used as one of the d-orbitals to make bonds.
Note: Do not consider that more than one d-orbitals take part in the hybridization as one s-orbital and 3 p-orbitals are already taking part in the hybridization. Make sure that you decide hybridization from the excited state of the atom and not the ground state.
Complete answer:
We know that Arsenic is the element of the Nitrogen group. So, its ground state electronic configuration is \[[Ar]3{d^{10}}4{s^2}4{p^3}\] and excited state configuration will be \[[Ar]3{d^{10}}4{s^1}4{p^3}4{d^1}\].


So, we can say from this excited state of Arsenic atom that it can bind with five Fluorine atoms with five different orbitals.
It is clear from the figure that five fluorine atoms will give one electron each to five half-filled orbitals of Arsenic atoms. So, hybridization in this compound will be \[s{p^3}d\].
So, it is evident that \[s,{p_x},{p_y},{p_z}\] orbitals will take part because they are only available orbitals.
Now, if \[s{p^3}d\] hybridized compounds have trigonal bipyramidal geometry, then it has to form bonds in a plane and two more bonds perpendicular to the plane. If we take the plane in xy direction, then only one orbital is there which can form bonds perpendicular to it and it is \[{d_{{z^2}}}\] as it is along the z-axis.
So, orbitals involved are \[s,{p_x},{p_y},{p_z}\],\[{d_{{z^2}}}\]
So, the correct answer is (D) \[s,{p_x},{p_y},{p_z}\],\[{d_{{z^2}}}\].
Additional Information:
- In \[s{p^3}d\] hybridization, compound can have either trigonal bipyramidal or square pyramidal geometry.
- If a compound is having trigonal bipyramidal geometry, then it uses \[{d_{{z^2}}}\] orbital as one of the d-orbitals to form bonds. If a compound has square pyramidal geometry, then \[{d_{{x^2} - {y^2}}}\] is used as one of the d-orbitals to make bonds.
Note: Do not consider that more than one d-orbitals take part in the hybridization as one s-orbital and 3 p-orbitals are already taking part in the hybridization. Make sure that you decide hybridization from the excited state of the atom and not the ground state.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




