
The axonal membrane is ___ to negatively charged proteins present in the axoplasm:-
A. Selectively permeable
B. Permeable
C. Semipermeable
D. Impermeable
Answer
593.1k+ views
Hint: Neurons are excitable cells because their membranes are in a polarized state. Different types of ion channels are present on the nerve membrane.
These ion channels are selectively permeable to different ions.
When a neuron is not conducting any impulse, i.e., resting, the axonal membrane is comparatively more permeable to potassium ions ($K^+$) and nearly impermeable to sodium ions ($Na^+$).
Similarly, the membrane is impermeable to negatively charged proteins present in the axoplasm.
Consequently, the axoplasm inside the axon contains a high concentration of K+ and negatively charged proteins and a low concentration of $Na^+$.
Complete answer: The fluid outside the axon contains a low concentration of $K^+$, a high concentration of $Na^+$, and thus forms a concentration gradient.
These Neurons are excitable cells because their membranes are in a polarized state.
Different types of ion channels are present on the nerve membrane.
These ion channels are selectively permeable to different ions.
Additional information: When a neuron is not conducting any impulse, i.e., resting, the axonal membrane is comparatively more permeable to potassium ions (K+) and nearly impermeable to sodium ions (Na+).
1. Similarly, the membrane is impermeable to negatively charged proteins present in the axoplasm.
2. Consequently, the axoplasm inside the axon contains a high concentration of K+ and negatively charged proteins and a low concentration of $Na^+$.
3. These ionic gradients across the resting membrane are maintained by the active transport of ions by the sodium-potassium pump which transports 3 Na+ outwards for 2 K+ into the cell.
4. As a result, the outer surface of the axonal membrane possesses a positive charge while its inner surface becomes negatively charged and therefore is polarised.
So the correct answer is D. Impermeable
Note: The electrical potential difference across the resting plasma membrane is called the resting potential.
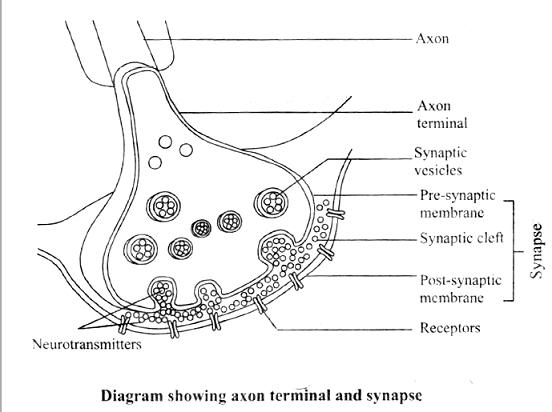
At a chemical synapse, the membranes of the pre- and postsynaptic neurons are separated by a fluid-filled space called the synaptic cleft.
The rise in the stimulus-induced permeability to Na+ is extremely short lived.
It is quickly followed by a rise in permeability to K+.
Within a fraction of a second, K+ diffuses outside the membrane and restores the resting potential of the membrane at the site of excitation and the fiber becomes once more responsive to further stimulation.
These ion channels are selectively permeable to different ions.
When a neuron is not conducting any impulse, i.e., resting, the axonal membrane is comparatively more permeable to potassium ions ($K^+$) and nearly impermeable to sodium ions ($Na^+$).
Similarly, the membrane is impermeable to negatively charged proteins present in the axoplasm.
Consequently, the axoplasm inside the axon contains a high concentration of K+ and negatively charged proteins and a low concentration of $Na^+$.
Complete answer: The fluid outside the axon contains a low concentration of $K^+$, a high concentration of $Na^+$, and thus forms a concentration gradient.
These Neurons are excitable cells because their membranes are in a polarized state.
Different types of ion channels are present on the nerve membrane.
These ion channels are selectively permeable to different ions.

Additional information: When a neuron is not conducting any impulse, i.e., resting, the axonal membrane is comparatively more permeable to potassium ions (K+) and nearly impermeable to sodium ions (Na+).
1. Similarly, the membrane is impermeable to negatively charged proteins present in the axoplasm.
2. Consequently, the axoplasm inside the axon contains a high concentration of K+ and negatively charged proteins and a low concentration of $Na^+$.
3. These ionic gradients across the resting membrane are maintained by the active transport of ions by the sodium-potassium pump which transports 3 Na+ outwards for 2 K+ into the cell.
4. As a result, the outer surface of the axonal membrane possesses a positive charge while its inner surface becomes negatively charged and therefore is polarised.
So the correct answer is D. Impermeable
Note: The electrical potential difference across the resting plasma membrane is called the resting potential.
At a chemical synapse, the membranes of the pre- and postsynaptic neurons are separated by a fluid-filled space called the synaptic cleft.
The rise in the stimulus-induced permeability to Na+ is extremely short lived.
It is quickly followed by a rise in permeability to K+.
Within a fraction of a second, K+ diffuses outside the membrane and restores the resting potential of the membrane at the site of excitation and the fiber becomes once more responsive to further stimulation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




