
The beta pleated sheet structure of protein is due to
(a)Formation of peptide bonds
(b)Linking together of two or more polypeptide chains
(c)Folding of the coiled polypeptide chains
(d)None of the above
Answer
583.5k+ views
Hint: Beta sheet is a local 3D conformations of amino acids that are in close proximity with each other in their linear sequences. Beta sheet and alpha structure is a type of secondary structure of protein.
Complete answer:
Beta sheet consists of two or more beta strands, which are polypeptide chains that hydrogen bond to each other. Beta strands as zigzag lines that run in parallel to each other whereas the side chains of the constituent amino acid residues give each beta strand their zigzag shape, and multiple strands linked together give the beta sheet as a pleated shape. Beta sheets is the second secondary structure proposed, thus their name: "beta" sheets.
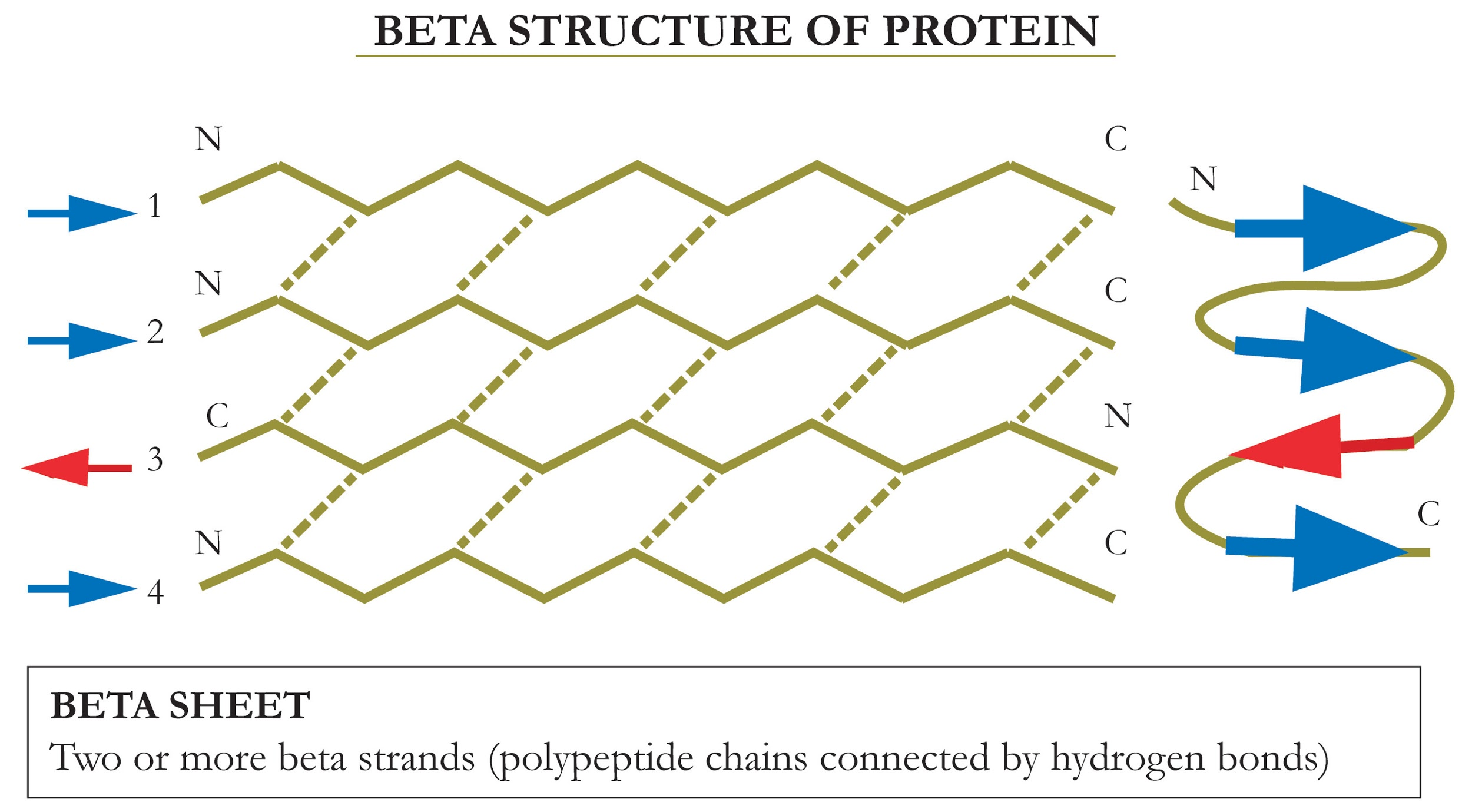
Additional Information:
Antiparallel Strands
-The amino and carboxy amino groups for each amino acid group on opposite sides to show that the strands run in the opposite direction.
-In this orientation amino groups on one beta strand aligned with the carbonyl group on the other strand.
-Each amino and carboxyl group are linked with hydrogen bonds between them.
Parallel Strands
-The carboxyl and amino groups for each amino acid residue both going N terminus to C terminus to show they run in parallel.
-Although they run in parallel, the carboxy and amino groups on the two strands yet they aren't perfectly aligned.
-From N to C terminal, dashes to connect the amino groups with their closest free carboxyl residue.
-The lines representing hydrogen bonds create V shapes, unlike in the antiparallel strand where the hydrogen bonds were straight lines that connected to two strands.
-The distance between individual amino acids along a beta strand is about 3.5 angstroms. The distance between amino acids in an alpha helix is only 1.5 angstroms. Thus, the amino acid residues in a beta sheet are much more extended, whereas the alpha helix are rigid.
Favorable amino acid
-Two sub-groups of amino acids are preferentially found as internal amino acid residues: amino acids with beta branched side chains and those with aromatic side chains.
-Amino acids with beta branching include Threonine, Valine and Isoleucine.
-Aromatic amino acids include Tyrosine, Tryptophan and Phenylalanine.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Linking together two or more polypeptide chains.’
Note: -Proline and Glycine residues are often found in beta-turns or loops that connect beta sheet or alpha helical segments in a protein's secondary structure.
-Proline's imino ring structure prevents it from acting as a hydrogen bond acceptor, making it unfavorable within the beta strand, but a good choice for turns.
-Glycine, which lacks an R-group, is small in size and flexible and also facilitates turns.
Complete answer:
Beta sheet consists of two or more beta strands, which are polypeptide chains that hydrogen bond to each other. Beta strands as zigzag lines that run in parallel to each other whereas the side chains of the constituent amino acid residues give each beta strand their zigzag shape, and multiple strands linked together give the beta sheet as a pleated shape. Beta sheets is the second secondary structure proposed, thus their name: "beta" sheets.

Additional Information:
Antiparallel Strands
-The amino and carboxy amino groups for each amino acid group on opposite sides to show that the strands run in the opposite direction.
-In this orientation amino groups on one beta strand aligned with the carbonyl group on the other strand.
-Each amino and carboxyl group are linked with hydrogen bonds between them.
Parallel Strands
-The carboxyl and amino groups for each amino acid residue both going N terminus to C terminus to show they run in parallel.
-Although they run in parallel, the carboxy and amino groups on the two strands yet they aren't perfectly aligned.
-From N to C terminal, dashes to connect the amino groups with their closest free carboxyl residue.
-The lines representing hydrogen bonds create V shapes, unlike in the antiparallel strand where the hydrogen bonds were straight lines that connected to two strands.
-The distance between individual amino acids along a beta strand is about 3.5 angstroms. The distance between amino acids in an alpha helix is only 1.5 angstroms. Thus, the amino acid residues in a beta sheet are much more extended, whereas the alpha helix are rigid.
Favorable amino acid
-Two sub-groups of amino acids are preferentially found as internal amino acid residues: amino acids with beta branched side chains and those with aromatic side chains.
-Amino acids with beta branching include Threonine, Valine and Isoleucine.
-Aromatic amino acids include Tyrosine, Tryptophan and Phenylalanine.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Linking together two or more polypeptide chains.’
Note: -Proline and Glycine residues are often found in beta-turns or loops that connect beta sheet or alpha helical segments in a protein's secondary structure.
-Proline's imino ring structure prevents it from acting as a hydrogen bond acceptor, making it unfavorable within the beta strand, but a good choice for turns.
-Glycine, which lacks an R-group, is small in size and flexible and also facilitates turns.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




