
The bond orders in the pairs of bonded oxygen atoms in ozone molecules are:
(A)- (1, 2)
(B)- (\[\dfrac{1}{2},1\dfrac{1}{2}\])
(C)- ($1\dfrac{1}{2},1\dfrac{1}{2}$)
(D)- ($\dfrac{1}{2},2\dfrac{1}{2}$)
Answer
591k+ views
Hint: Ozone (${{O}_{3}}$) molecule shows resonance as one Lewis structure cannot explain all of its properties. Due to resonance, the bond orders in ${{O}_{3}}$ are taken as the average of the bond orders in the bonded oxygen atoms in any of one of the contributing structures.
Complete answer:
Let us try to draw the structure of an ozone molecule.
Each oxygen has six valence electrons and in order to draw the Lewis structure every oxygen atom should have its octet complete.
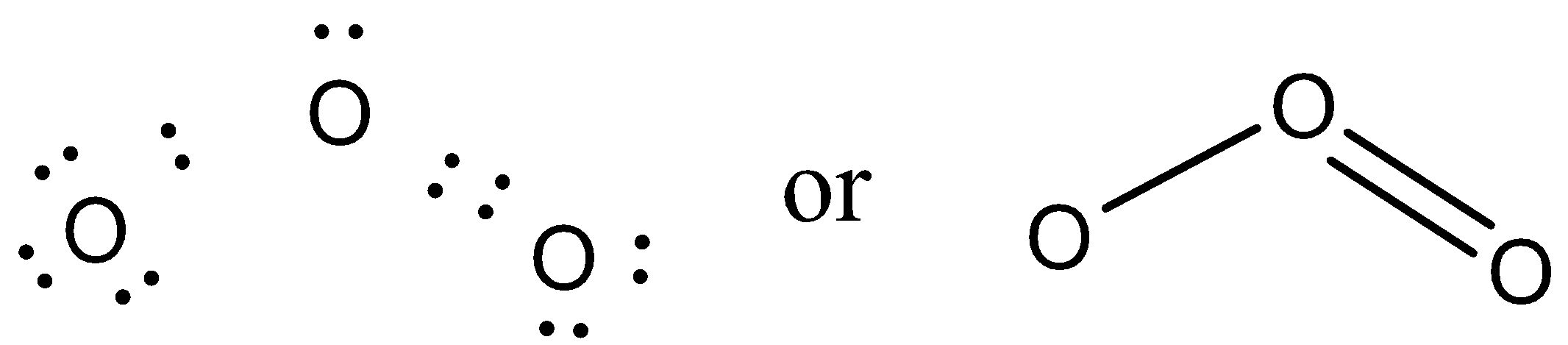
We can see that the central oxygen has one single bond and one double, it has been found experimentally that the both the bond lengths in ${{O}_{3}}$ are equal, which is unlikely as a single bond is generally longer than a double bond.
This can be explained by the concept of resonance. The central oxygen can give its pair of electrons to either of the two oxygen atoms to form a single bond. Therefore, two resonating structures are possible for ${{O}_{3}}$. These structures are called contributing structures. The actual structure of ${{O}_{3}}$ is the resonance hybrid of these two contributing structures and has electronic arranging intermediate between them.
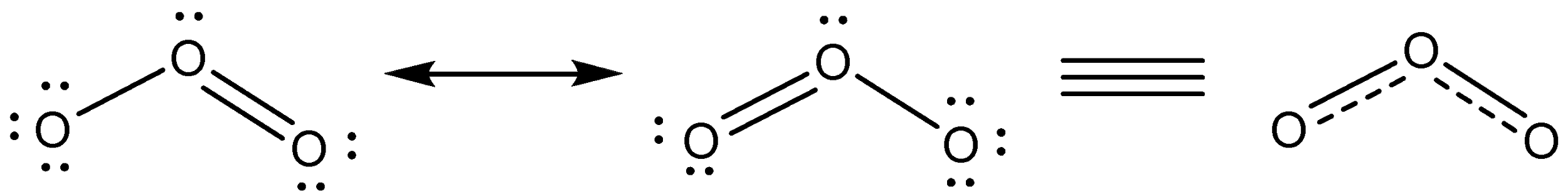
Bond order tells us the number of bonds present in a molecule. Since the actual structure of ${{O}_{3}}$ is the result of the two structures, the bond order in the pairs of bonded oxygen atoms will be the same and equal to the average of the single bond and the double bond.
Bond order = $\dfrac{1+2}{2}=1.5$ or $1\dfrac{1}{2}$
Since the bond order in the two pairs of the bonded oxygen atoms is the same, i.e.$1\dfrac{1}{2}$
Therefore, the correct option is (C).
Note:
Some students may simply see one single and double bond in the structure of the ozone molecule to have the total bond order 3. Do not make the mistake of marking the first option. Note that the single and double are not stationary but are exchanging constantly.
Complete answer:
Let us try to draw the structure of an ozone molecule.
Each oxygen has six valence electrons and in order to draw the Lewis structure every oxygen atom should have its octet complete.
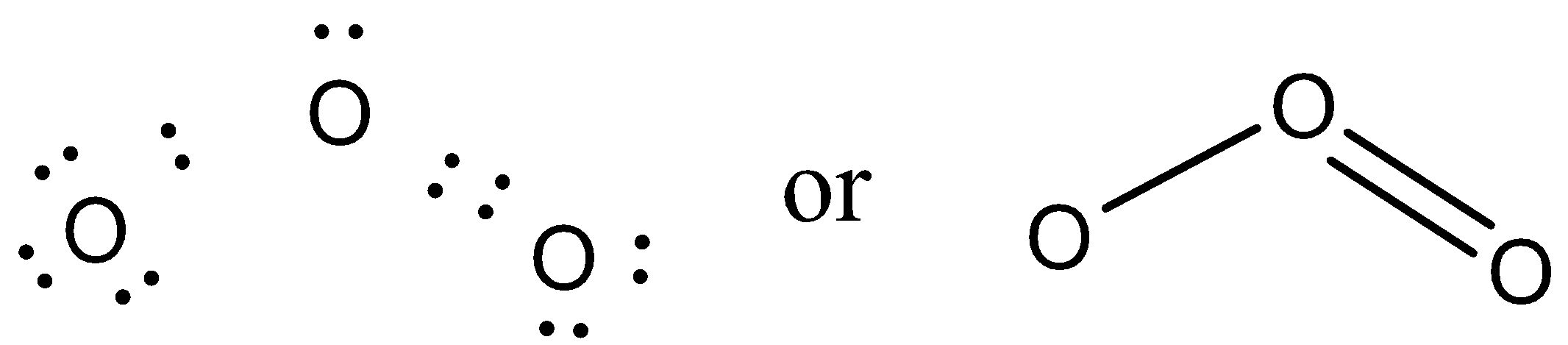
We can see that the central oxygen has one single bond and one double, it has been found experimentally that the both the bond lengths in ${{O}_{3}}$ are equal, which is unlikely as a single bond is generally longer than a double bond.
This can be explained by the concept of resonance. The central oxygen can give its pair of electrons to either of the two oxygen atoms to form a single bond. Therefore, two resonating structures are possible for ${{O}_{3}}$. These structures are called contributing structures. The actual structure of ${{O}_{3}}$ is the resonance hybrid of these two contributing structures and has electronic arranging intermediate between them.

Bond order tells us the number of bonds present in a molecule. Since the actual structure of ${{O}_{3}}$ is the result of the two structures, the bond order in the pairs of bonded oxygen atoms will be the same and equal to the average of the single bond and the double bond.
Bond order = $\dfrac{1+2}{2}=1.5$ or $1\dfrac{1}{2}$
Since the bond order in the two pairs of the bonded oxygen atoms is the same, i.e.$1\dfrac{1}{2}$
Therefore, the correct option is (C).
Note:
Some students may simply see one single and double bond in the structure of the ozone molecule to have the total bond order 3. Do not make the mistake of marking the first option. Note that the single and double are not stationary but are exchanging constantly.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




