
The breaking stress of a wire depends upon
A. The length of the wire
B. The radius of the wire
C. The material of the wire
D. The shape of the cross-section
Answer
583.2k+ views
Hint: We know that the equation for the relation of stress and strain is $\dfrac{{Stress}}{{Strain}} = \gamma $ . This means that the stress on an object depends on $\gamma $ . Now $\gamma $ as we already know depends upon the material that makes up the wire.
Complete answer:
Before starting the actual solution, it would be good to discuss stress, stress, and their relationship.
Stress – Stress is the force applied per unit area on a material.
Strain – Strain is the change in the dimensions of material when it is under stress.
The relation of stress-strain is given below
$\dfrac{{Stress}}{{Strain}} = \gamma $
Here, $\gamma = $ The proportionality of linear expansion
The stress-strain graph is shown below
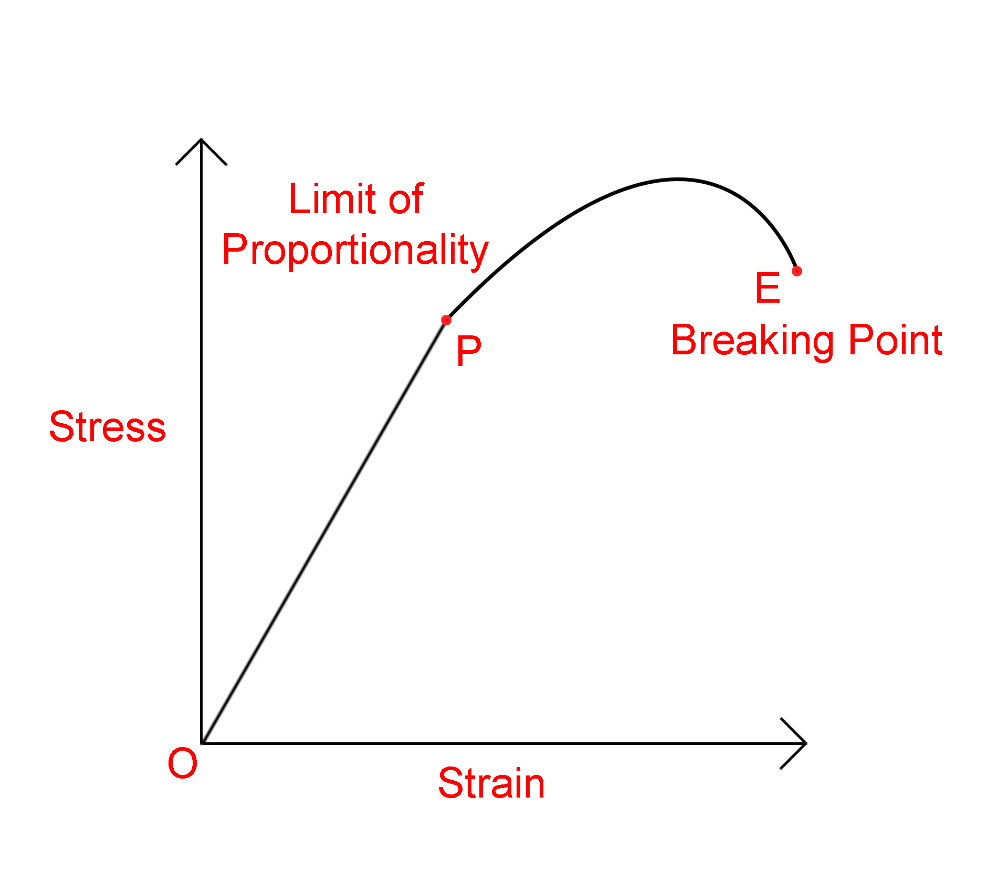
In this graph, you can see the point E which is called the breaking point where the object can longer bear the stress and just breaks into two. At this point even if we reduce the stress the strain still increases.
By the stress-strain equation, i.e. $\dfrac{{Stress}}{{Strain}} = \gamma $ , we can see that the strain of a body does not depend on the length of the wire, the shape of the cross-section of the wire, and the radius of the wire.
But stress does depend on $\gamma $ . Now $\gamma $ depends on the material of the wire, so the breaking stress also depends on the material of the wire.
In simple words, it means that two objects made of different material will have different breaking stress (the limit of strain the body can bear)
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
The concept of breaking stress that we discussed in the solution above is of great importance to us. Every object that we use whether it be lifts, bridges, mobiles phones, etc. are designed in such a manner that the stress on the object does not exceed the safe limit in normal day to day usage.
Complete answer:
Before starting the actual solution, it would be good to discuss stress, stress, and their relationship.
Stress – Stress is the force applied per unit area on a material.
Strain – Strain is the change in the dimensions of material when it is under stress.
The relation of stress-strain is given below
$\dfrac{{Stress}}{{Strain}} = \gamma $
Here, $\gamma = $ The proportionality of linear expansion
The stress-strain graph is shown below

In this graph, you can see the point E which is called the breaking point where the object can longer bear the stress and just breaks into two. At this point even if we reduce the stress the strain still increases.
By the stress-strain equation, i.e. $\dfrac{{Stress}}{{Strain}} = \gamma $ , we can see that the strain of a body does not depend on the length of the wire, the shape of the cross-section of the wire, and the radius of the wire.
But stress does depend on $\gamma $ . Now $\gamma $ depends on the material of the wire, so the breaking stress also depends on the material of the wire.
In simple words, it means that two objects made of different material will have different breaking stress (the limit of strain the body can bear)
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
The concept of breaking stress that we discussed in the solution above is of great importance to us. Every object that we use whether it be lifts, bridges, mobiles phones, etc. are designed in such a manner that the stress on the object does not exceed the safe limit in normal day to day usage.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




