
The bundle of axons in the central nervous system is known as
(a) Nerve
(b) Ganglion
(c) Tract
(d) Neuron
Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint: The central nervous system is made up of two major components, which are the brain and spinal cord, in which the brain controls almost all body functions and reflexes are controlled by the spinal cord without the involvement of the brain. The cerebral cortex of the brain and spinal cord are connected by these bundles of axons.
Complete answer:
Nerve fibres in the central nervous system are organized in bundles which are called the tracts. There are two types of tracts movement, which are ascending tracts and descending tracts in which ascending tracts take impulses along the spinal cord to the brain, and the descending tracts take them from the brain or higher areas in the spinal cord to the bottom areas.
Additional information:
- Associate tracts are the tracts that join cortical areas to its adjective hemisphere, and associate tracts are connected to the brain’s memory centres.
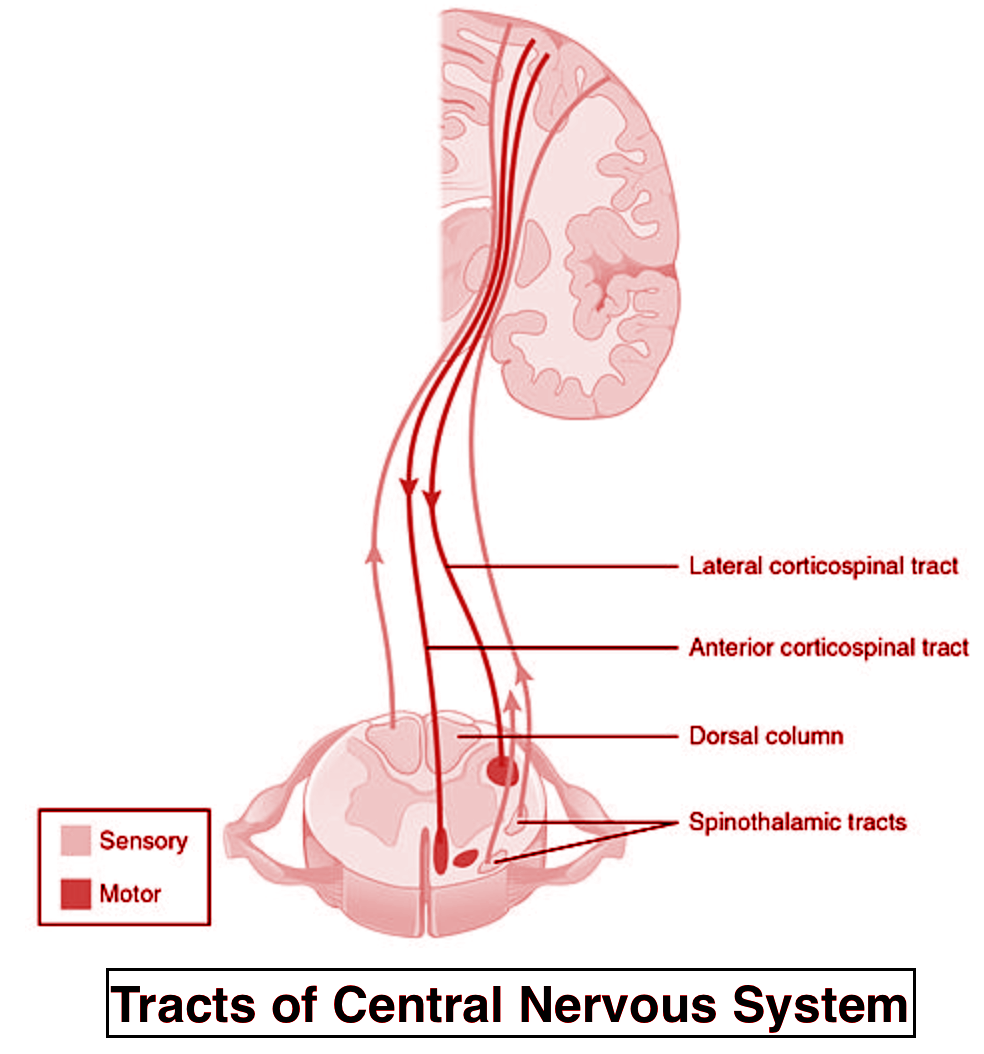
- If the tracts connect the cortical region to two hemispheres, they are called commissural tracts. The left and right sides of the cerebrum are linked by commissural tracts and it also aids in the communication of both sides.
- The cerebral cortex and spinal cord are linked by projection tracts. It also connects the corpus striatum and brainstem to the cerebral cortex.
So, the correct answer is ‘(c) Tract’.
Note:
- The spinal cord takes signals to and fro from the brain and peripheral nerves, the spinal cord is connected to the brainstorm and it goes through the spinal canal.
- Cerebrospinal fluid which provides immunogenic and mechanical protection to the brain also covers the spinal cord and ventricles of the central nervous system.
- Neurons are the basic unit of the nervous system and unlike the other cells, neurons don't replicate often.
Complete answer:
Nerve fibres in the central nervous system are organized in bundles which are called the tracts. There are two types of tracts movement, which are ascending tracts and descending tracts in which ascending tracts take impulses along the spinal cord to the brain, and the descending tracts take them from the brain or higher areas in the spinal cord to the bottom areas.
Additional information:
- Associate tracts are the tracts that join cortical areas to its adjective hemisphere, and associate tracts are connected to the brain’s memory centres.

- If the tracts connect the cortical region to two hemispheres, they are called commissural tracts. The left and right sides of the cerebrum are linked by commissural tracts and it also aids in the communication of both sides.
- The cerebral cortex and spinal cord are linked by projection tracts. It also connects the corpus striatum and brainstem to the cerebral cortex.
So, the correct answer is ‘(c) Tract’.
Note:
- The spinal cord takes signals to and fro from the brain and peripheral nerves, the spinal cord is connected to the brainstorm and it goes through the spinal canal.
- Cerebrospinal fluid which provides immunogenic and mechanical protection to the brain also covers the spinal cord and ventricles of the central nervous system.
- Neurons are the basic unit of the nervous system and unlike the other cells, neurons don't replicate often.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




