
The cambium located in between xylem and phloem in the dicot stem is
A. Interfascicular
B. Intrafascicular
C. Both A and B
D. None of the above
Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint: Plants can be classified as non-flowering and flowering plants which are further divided into two categories that include monocotyledons and dicotyledons. Cotyledons are present in seed-bearing plants and are called the embryonic leaf.
Complete answer: The dicot stem is a part of the dicotyledons. Dicotyledons are flowering plants that consist of two embryonic leaves also known as cotyledons as mentioned earlier. Dicot stems consist of an epidermis which comprises cuticle and multicellular stem hair. A dicot stems internal structure consists of epidermis, cortex endodermis (Collenchyma, parenchyma, and endodermis), pericycle (sclerenchyma), vascular bundles (xylem, phloem, cambium, and wood parenchyma), and a pith. Examples of flowering plants that have a dicot stem include Cucurbita and sunflower.
The cambium is a layer of cells that divides phloem and xylem tissues. The cambium cells are responsible for the stem girth expansion, the secondary growth of roots, and the stem. The cambium which is located within the vascular bundles, that is between the primary phloem and primary xylem is called the intrafascicular cambium. Whereas, during the occurrence of secondary growth, interfascicular cambium is formed due to the medullary ray cells becoming meristematic in nature. Both the intrafascicular cambium and interfascicular cambia join to form a cambium ring that separates the primary xylem and phloem.
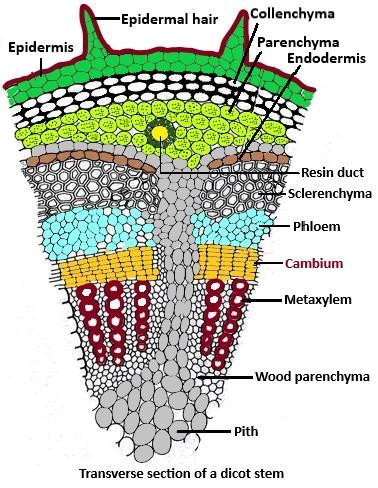
Therefore, the correct answer is option B, i.e., Intrafascicular.
Note: The shoot system, simply known as the stem provides structural support and carries out functions such as producing new living tissues, transporting nutrients and water from the roots to different parts of the plant such as leaves, flowers, and fruits via xylem and phloem. The Kingdom Plantae consists of about 320,000 different species of plants out of these approximately 100,000 to 150,000 are dicot plant species.
Complete answer: The dicot stem is a part of the dicotyledons. Dicotyledons are flowering plants that consist of two embryonic leaves also known as cotyledons as mentioned earlier. Dicot stems consist of an epidermis which comprises cuticle and multicellular stem hair. A dicot stems internal structure consists of epidermis, cortex endodermis (Collenchyma, parenchyma, and endodermis), pericycle (sclerenchyma), vascular bundles (xylem, phloem, cambium, and wood parenchyma), and a pith. Examples of flowering plants that have a dicot stem include Cucurbita and sunflower.
The cambium is a layer of cells that divides phloem and xylem tissues. The cambium cells are responsible for the stem girth expansion, the secondary growth of roots, and the stem. The cambium which is located within the vascular bundles, that is between the primary phloem and primary xylem is called the intrafascicular cambium. Whereas, during the occurrence of secondary growth, interfascicular cambium is formed due to the medullary ray cells becoming meristematic in nature. Both the intrafascicular cambium and interfascicular cambia join to form a cambium ring that separates the primary xylem and phloem.

Therefore, the correct answer is option B, i.e., Intrafascicular.
Note: The shoot system, simply known as the stem provides structural support and carries out functions such as producing new living tissues, transporting nutrients and water from the roots to different parts of the plant such as leaves, flowers, and fruits via xylem and phloem. The Kingdom Plantae consists of about 320,000 different species of plants out of these approximately 100,000 to 150,000 are dicot plant species.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




