
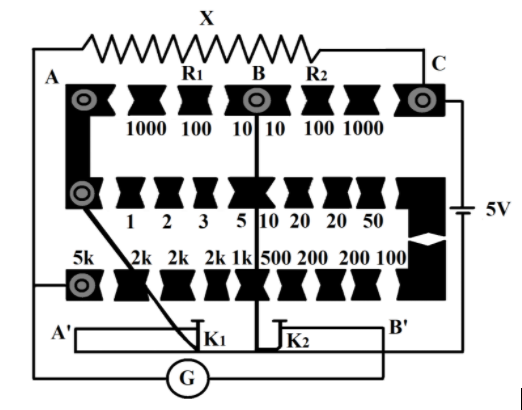
The circuit shown is of a post office box while using it for measuring the unknown resistance. All the keys except the two 100 ohms in the first row and both 2 ohms along with the 5 ohms are not used while measuring the resistance of the unknown wire. Find the resistance of an unknown wire in ohm.

Answer
587.4k+ views
Hint: A post office box is a Wheatstone bridge composed of three known arms’ resistances and one unknown resistance, whose value we calculate using the working principle and expression for a post office box.
Complete step-by-step solution:
A Post Office Box is used to measure an unknown resistance. It is basically a Wheatstone bridge with three arms known as P, Q, and R; while the fourth arm is the unknown resistance, denoted by S. P and Q are called the ratio arms while R is called the rheostat arm.
Simple circuit connection of a post office box:
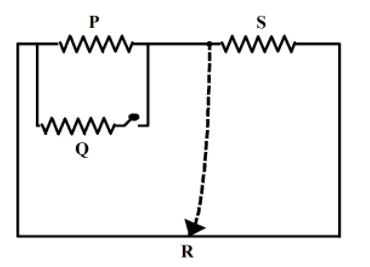
At balance or null point, the unknown resistance $S$ is given as,
$S=\left( \dfrac{P}{Q} \right)R$
The ratio arms, P and Q, are first adjusted so that they carry $100\Omega $ resistance each. The resistance in the rheostat arm is adjusted in a way such that the deflection in the galvanometer is in one direction.
If $R={{R}_{o}}\Omega $ and $R=\left( {{R}_{o}}+1 \right)\Omega $ are the resistance in rheostat arm, for which the galvanometer deflection is in opposite direction, then it implies that the unknown resistance $S$ lies between ${{R}_{o}}$ and $\left( {{R}_{o}}+1 \right)\Omega $.
We are given a post office circuit in which all the keys except the two 100 ohms in the first row and both 2 ohms along with the 5 ohms are not used, and we have to calculate the value of unknown resistance in the given situation.
In order to get the null point,
$\dfrac{{{R}_{1}}}{{{R}_{2}}}=\dfrac{X}{S}$
Here, we have,
${{R}_{1}}={{R}_{2}}=100\Omega $
And,
$S=\left( 2+2+5 \right)\Omega $
Therefore,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{100}{100}=\dfrac{X}{2+2+5}=\dfrac{X}{9} \\
& X=9\Omega \\
\end{align}$
Note: The major sources of error which can occur while calculating the value of unknown resistance are the connecting wires, unclear resistance plugs, change in resistance due to Joule heating, and the insensitivity of the Wheatstone bridge. These errors can be removed by using thick connecting wires in the circuit, using clean plugs, keeping the circuit on for very short periods of time to avoid the Joule heating, and carefully calculating the sensitivity of the Wheatstone bridge.
Complete step-by-step solution:
A Post Office Box is used to measure an unknown resistance. It is basically a Wheatstone bridge with three arms known as P, Q, and R; while the fourth arm is the unknown resistance, denoted by S. P and Q are called the ratio arms while R is called the rheostat arm.
Simple circuit connection of a post office box:

At balance or null point, the unknown resistance $S$ is given as,
$S=\left( \dfrac{P}{Q} \right)R$
The ratio arms, P and Q, are first adjusted so that they carry $100\Omega $ resistance each. The resistance in the rheostat arm is adjusted in a way such that the deflection in the galvanometer is in one direction.
If $R={{R}_{o}}\Omega $ and $R=\left( {{R}_{o}}+1 \right)\Omega $ are the resistance in rheostat arm, for which the galvanometer deflection is in opposite direction, then it implies that the unknown resistance $S$ lies between ${{R}_{o}}$ and $\left( {{R}_{o}}+1 \right)\Omega $.
We are given a post office circuit in which all the keys except the two 100 ohms in the first row and both 2 ohms along with the 5 ohms are not used, and we have to calculate the value of unknown resistance in the given situation.
In order to get the null point,
$\dfrac{{{R}_{1}}}{{{R}_{2}}}=\dfrac{X}{S}$
Here, we have,
${{R}_{1}}={{R}_{2}}=100\Omega $
And,
$S=\left( 2+2+5 \right)\Omega $
Therefore,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{100}{100}=\dfrac{X}{2+2+5}=\dfrac{X}{9} \\
& X=9\Omega \\
\end{align}$
Note: The major sources of error which can occur while calculating the value of unknown resistance are the connecting wires, unclear resistance plugs, change in resistance due to Joule heating, and the insensitivity of the Wheatstone bridge. These errors can be removed by using thick connecting wires in the circuit, using clean plugs, keeping the circuit on for very short periods of time to avoid the Joule heating, and carefully calculating the sensitivity of the Wheatstone bridge.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




