
The colour code of carbon resistor is brown is, Brown, Black and Red. The value of the resistor is?
A) \[10\Omega \pm 5\% \]
B) \[1k\Omega \pm 2\% \]
C) \[100\Omega \pm 2\% \]
D) \[10\Omega \pm 2\% \]
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Carbon resistor is one of the most common compact-sized types of electronic passive device. Carbon resistances are made from solid cylindrical resistive elements with embedded wire leads or metal end caps. Due to the compact size of carbon resistors color coding helps to quickly identify its resistive value and the percentage of tolerance of the carbon resistors.
Complete answer:
Carbon resistors are commercially used passive devices because they offer a very high resistance with a very compact size. The colors are used for the coding of carbon resistors mainly because in the small electronic circuit it is very difficult to calibrate the resistance of the tiny bunch of carbon resistors so for our sake of simplicity we are using colors in the coding purpose.
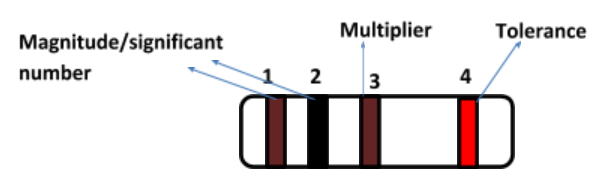 Coding of colors
Coding of colors
1. Brown = 1(Magnitude/Significant Number)
2. Black = 0(Magnitude/Significant Number)
3. Brown = 10(Multiplier)
4. Red = ±2%(Tolerance)
So we get the required value for resistance as:
\[R = (10 \times 10)\Omega \pm 2\% \]
\[ \Rightarrow R = 100\Omega \pm 2\% \]
Hence, option (C) is the correct answer.
Note: In order to tackle these kinds of questions from the topic of color-coded carbon resistors we have to remember the different values for the codes for different bands on the carbon resistor. For the sake of simplicity, one should learn the mnemonics for coding as – B B R O Y of Great Britain has a Very Good Wife.
Tolerance in the carbon coded resistor indicates up to how much percentage the original value of resistance will differ. We can also call it a percentage error in the resistance. One should also note that the value of tolerance percentage in the carbon resistor also varies with colors that are other than Gold, Silver, and No color. For example, for red, the tolerance percentage will be ± 2%.
Complete answer:
Carbon resistors are commercially used passive devices because they offer a very high resistance with a very compact size. The colors are used for the coding of carbon resistors mainly because in the small electronic circuit it is very difficult to calibrate the resistance of the tiny bunch of carbon resistors so for our sake of simplicity we are using colors in the coding purpose.
 Coding of colors
Coding of colors1. Brown = 1(Magnitude/Significant Number)
2. Black = 0(Magnitude/Significant Number)
3. Brown = 10(Multiplier)
4. Red = ±2%(Tolerance)
So we get the required value for resistance as:
\[R = (10 \times 10)\Omega \pm 2\% \]
\[ \Rightarrow R = 100\Omega \pm 2\% \]
Hence, option (C) is the correct answer.
Note: In order to tackle these kinds of questions from the topic of color-coded carbon resistors we have to remember the different values for the codes for different bands on the carbon resistor. For the sake of simplicity, one should learn the mnemonics for coding as – B B R O Y of Great Britain has a Very Good Wife.
| Colors | Magnitude | Multiplier | Tolerance(%) |
| Black | 0 | \[{10^0}\] | Gold - \[ \pm 5\] |
| Brown | 1 | \[{10^1}\] | Silver- \[ \pm 10\] |
| Red | 2 | \[{10^2}\] | No color- \[ \pm 20\] |
| Orange | 3 | \[{10^3}\] | |
| Yellow | 4 | \[{10^4}\] | |
| Green | 5 | \[{10^5}\] | |
| Blue | 6 | \[{10^6}\] | |
| Violet | 7 | \[{10^7}\] | |
| Grey | 8 | \[{10^8}\] | |
| White | 9 | \[{10^9}\] |
Tolerance in the carbon coded resistor indicates up to how much percentage the original value of resistance will differ. We can also call it a percentage error in the resistance. One should also note that the value of tolerance percentage in the carbon resistor also varies with colors that are other than Gold, Silver, and No color. For example, for red, the tolerance percentage will be ± 2%.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students




