
The colour of caustic soda turns pink when phenolphthalein is added.
A. True
B. False
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Phenolphthalein is generally used as an indicator in acid–base titrations. It turns colourless when added to an acid and pink when added to basic solutions. Caustic soda is a strong base and will ionise more when phenolphthalein is added into it.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Caustic soda is a chemical compound named sodium hydroxide, NaOH. It is a strong alkali used in many things such as water treatment, metal processing, food, etc. It is also called Lye. It is corrosive in nature and has a wide range of applications. It is also used as a cleansing agent, in the production of washing soda. It can be prepared by many methods. One such method is the Castner-Kellner method. In this method, electrolysis of brine solution (aqueous NaCl) is performed in order to get sodium hydroxide.
Phenolphthalein is another chemical compound organically synthesised as \[{C_{20}}{H_{14}}{O_4}\]. It is used in laboratories as an acid-base indicator in various titrations performed. It is colourless below pH 8.5 i.e. in acidic solutions and attains a pink to deep red hue above pH 9.0 i.e. in basic solutions.
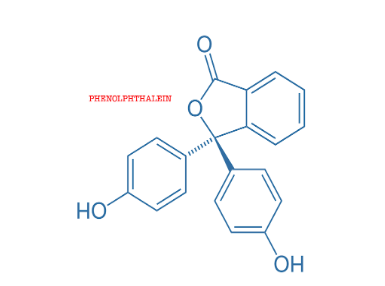
Therefore, when phenolphthalein is added to caustic soda which is a strong base, it turns pink in colour. This is because the compound in aqueous form has anions present in it. It is itself a weak acid and does not react with acid and thus remains colourless. But being a weak acid, it reacts with a strong base, resulting in partial dissociation of the base.

This is a true statement. Hence, the correct option is (A).
Note: Since it is a weak acid, it loses protons in solution form. It is less soluble in water and usually dissolved in alcohols when used in laboratories. In titration, it acts as an indicator that tells us the end point, a point where the reaction completes.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Caustic soda is a chemical compound named sodium hydroxide, NaOH. It is a strong alkali used in many things such as water treatment, metal processing, food, etc. It is also called Lye. It is corrosive in nature and has a wide range of applications. It is also used as a cleansing agent, in the production of washing soda. It can be prepared by many methods. One such method is the Castner-Kellner method. In this method, electrolysis of brine solution (aqueous NaCl) is performed in order to get sodium hydroxide.
Phenolphthalein is another chemical compound organically synthesised as \[{C_{20}}{H_{14}}{O_4}\]. It is used in laboratories as an acid-base indicator in various titrations performed. It is colourless below pH 8.5 i.e. in acidic solutions and attains a pink to deep red hue above pH 9.0 i.e. in basic solutions.

Therefore, when phenolphthalein is added to caustic soda which is a strong base, it turns pink in colour. This is because the compound in aqueous form has anions present in it. It is itself a weak acid and does not react with acid and thus remains colourless. But being a weak acid, it reacts with a strong base, resulting in partial dissociation of the base.

This is a true statement. Hence, the correct option is (A).
Note: Since it is a weak acid, it loses protons in solution form. It is less soluble in water and usually dissolved in alcohols when used in laboratories. In titration, it acts as an indicator that tells us the end point, a point where the reaction completes.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




