
The compound with the highest boiling point is _______.
A.HCl
B.${\rm{HN}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{3}}}$
C.${{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{S}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{4}}}$
D.HF
Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint: We know that the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid becomes equal to the atmospheric pressure surrounding the liquid is termed as boiling point. At this temperature, the conversion of liquid to vapor takes place. $100^\circ {\rm{C}}$is the boiling point of water that means at hundred-degree water changes to vapor.
Complete step by step answer:
of the molecule, nature of bonding, etc. The presence of hydrogen bonding makes the molecule less volatile which results in the higher boiling point of the molecule.
Let’s understand the hydrogen bond in detail. The hydrogen bond is a chemical bond in which the formation of a covalent link of hydrogen atoms with other electronegative atoms, such as, fluorine, nitrogen, and oxygen atoms takes place in the same or another molecule.
Due to hydrogen bonding, a molecule cannot escape from the solution and becomes non-volatile.
Let’s identify the correct answer from the solution.
Option A is HCl. In hydrogen bonding, H forms bonds with smaller atoms such as fluorine, nitrogen, etc. But chlorine is a relatively larger atom that results in relatively low electron density. So, very weak hydrogen bonding is present in HCl. Therefore, HCl is volatile and has a very low boiling point.
Option B is HBr. Similarly, bromine is also a larger atom. So, it also forms weaker hydrogen bonds. So, it is also volatile. Thus, it also has a very low boiling point.
Option C is ${{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{S}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{4}}}$. Sulphuric acid is an asymmetrical molecule having a permanent dipole and the hydrogen atoms bonded to oxygen forms hydrogen bonding with other sulphuric acid molecules.
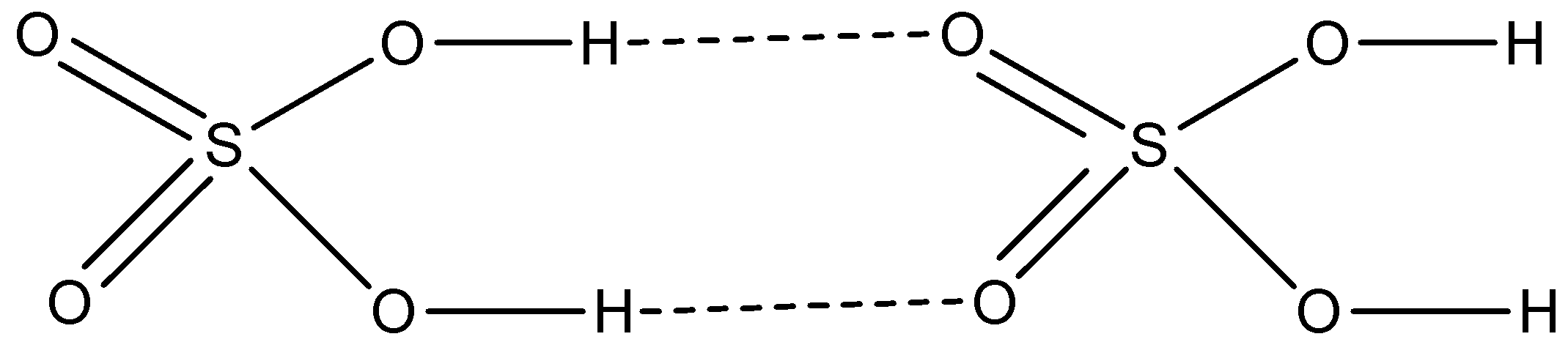
So, we get to know that in sulphuric acid intermolecular hydrogen bonding is present. That means it is non-volatile and thus has a very high boiling point.
Option D is HF. In HF also, strong hydrogen bonding is present but strength of hydrogen bonding is more in case of sulphuric acid. So, it has lower boiling point than ${{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{S}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{4}}}$
.
So, the correct answer is Option D.
Note: There are two types of hydrogen bonding namely, intermolecular hydrogen bonding and intramolecular hydrogen bonding. If H-bonding forms within the molecule, the bonding is termed intramolecular hydrogen bonding. And if the H-bonding forms with other molecules, then the bonding is termed as intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
Complete step by step answer:
of the molecule, nature of bonding, etc. The presence of hydrogen bonding makes the molecule less volatile which results in the higher boiling point of the molecule.
Let’s understand the hydrogen bond in detail. The hydrogen bond is a chemical bond in which the formation of a covalent link of hydrogen atoms with other electronegative atoms, such as, fluorine, nitrogen, and oxygen atoms takes place in the same or another molecule.
Due to hydrogen bonding, a molecule cannot escape from the solution and becomes non-volatile.
Let’s identify the correct answer from the solution.
Option A is HCl. In hydrogen bonding, H forms bonds with smaller atoms such as fluorine, nitrogen, etc. But chlorine is a relatively larger atom that results in relatively low electron density. So, very weak hydrogen bonding is present in HCl. Therefore, HCl is volatile and has a very low boiling point.
Option B is HBr. Similarly, bromine is also a larger atom. So, it also forms weaker hydrogen bonds. So, it is also volatile. Thus, it also has a very low boiling point.
Option C is ${{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{S}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{4}}}$. Sulphuric acid is an asymmetrical molecule having a permanent dipole and the hydrogen atoms bonded to oxygen forms hydrogen bonding with other sulphuric acid molecules.

So, we get to know that in sulphuric acid intermolecular hydrogen bonding is present. That means it is non-volatile and thus has a very high boiling point.
Option D is HF. In HF also, strong hydrogen bonding is present but strength of hydrogen bonding is more in case of sulphuric acid. So, it has lower boiling point than ${{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{S}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{4}}}$
.
So, the correct answer is Option D.
Note: There are two types of hydrogen bonding namely, intermolecular hydrogen bonding and intramolecular hydrogen bonding. If H-bonding forms within the molecule, the bonding is termed intramolecular hydrogen bonding. And if the H-bonding forms with other molecules, then the bonding is termed as intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




