
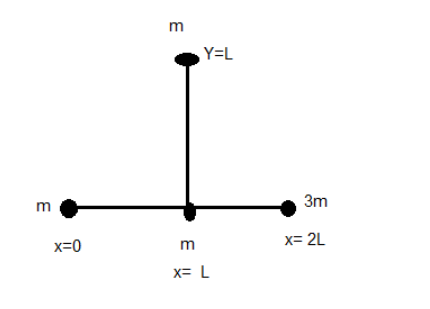
The coordinates of the centre of mass of the system as shown in the figure is?
a- (0,0)
b- (1.33L, 0.167L)
c- (L, L)
d- (0.33L, 1.67L)

Answer
570k+ views
Hint: The centre of mass is a point defined relative to an object or system of objects. It is the aggregate position of all the parts of the system, weighted according to their masses and at this point, it is assumed that the entire mass of the system is contained.
Complete Step by step answer:Assuming that all these are point masses, we can find out the coordinates of the centre of mass. We assume that the first mass is at the origin of the coordinate system. Thus, the masses which are at x=0, x=L and x=2L are situated on the x-axis and the mass at y=L is situated at the y-axis.
The (x, y) coordinates of the masses along with their masses can be written as m (0,0), m (L,0), 3m (2L,0) m (L, L). These are the coordinates that we usually write in geometry and mathematics. Here there is no z coordinate of the system. Now we calculate the x coordinate of the centre of mass and the y coordinate of the centre of mass separately and then write them together to find out the coordinates of the centre of mass of the system.
$ {{X}_{cm}}=\dfrac{{{M}_{1}}{{x}_{1}}+{{M}_{2}}{{x}_{2}}+{{M}_{3}}{{x}_{3}}+{{M}_{4}}{{x}_{4}}}{{{M}_{1}}+{{M}_{2}}+{{M}_{3}}+{{M}_{4}}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{(m\times 0)+(m\times L)+(3m\times 2L)+(m\times 0)}{m+m+3m+m} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{7mL}{6m} \\
\therefore \dfrac{7L}{6} \\
$
Now for the y coordinate,
$
{{Y}_{cm}}=\dfrac{{{M}_{1}}{{y}_{1}}+{{M}_{2}}{{y}_{2}}+{{M}_{3}}{{y}_{3}}+{{M}_{4}}{{y}_{4}}}{{{M}_{1}}+{{M}_{2}}+{{M}_{3}}+{{M}_{4}}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{0+0+0+mL}{m+m+3m+m} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{mL}{6m} \\
\therefore \dfrac{L}{6} \\
$
Thus, the coordinates of the centre of mass are \[(\dfrac{7L}{6},\dfrac{L}{6})\]. Converting them into decimals we get, \[(1.33L,0.167L)\]
So, the correct option is (b).
Note: For simple rigid objects with uniform density, the centre of mass is located at the geometrical centre, for example, the centre of mass of a ring for example is located at its centre. It is not necessary that the centre of mass will always lie inside the body. Also, the distribution of mass is one of the most deciding factors of the location of the centre of mass.
Complete Step by step answer:Assuming that all these are point masses, we can find out the coordinates of the centre of mass. We assume that the first mass is at the origin of the coordinate system. Thus, the masses which are at x=0, x=L and x=2L are situated on the x-axis and the mass at y=L is situated at the y-axis.
The (x, y) coordinates of the masses along with their masses can be written as m (0,0), m (L,0), 3m (2L,0) m (L, L). These are the coordinates that we usually write in geometry and mathematics. Here there is no z coordinate of the system. Now we calculate the x coordinate of the centre of mass and the y coordinate of the centre of mass separately and then write them together to find out the coordinates of the centre of mass of the system.
$ {{X}_{cm}}=\dfrac{{{M}_{1}}{{x}_{1}}+{{M}_{2}}{{x}_{2}}+{{M}_{3}}{{x}_{3}}+{{M}_{4}}{{x}_{4}}}{{{M}_{1}}+{{M}_{2}}+{{M}_{3}}+{{M}_{4}}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{(m\times 0)+(m\times L)+(3m\times 2L)+(m\times 0)}{m+m+3m+m} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{7mL}{6m} \\
\therefore \dfrac{7L}{6} \\
$
Now for the y coordinate,
$
{{Y}_{cm}}=\dfrac{{{M}_{1}}{{y}_{1}}+{{M}_{2}}{{y}_{2}}+{{M}_{3}}{{y}_{3}}+{{M}_{4}}{{y}_{4}}}{{{M}_{1}}+{{M}_{2}}+{{M}_{3}}+{{M}_{4}}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{0+0+0+mL}{m+m+3m+m} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{mL}{6m} \\
\therefore \dfrac{L}{6} \\
$
Thus, the coordinates of the centre of mass are \[(\dfrac{7L}{6},\dfrac{L}{6})\]. Converting them into decimals we get, \[(1.33L,0.167L)\]
So, the correct option is (b).
Note: For simple rigid objects with uniform density, the centre of mass is located at the geometrical centre, for example, the centre of mass of a ring for example is located at its centre. It is not necessary that the centre of mass will always lie inside the body. Also, the distribution of mass is one of the most deciding factors of the location of the centre of mass.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




