
The correct IUPAC name of the compound is:
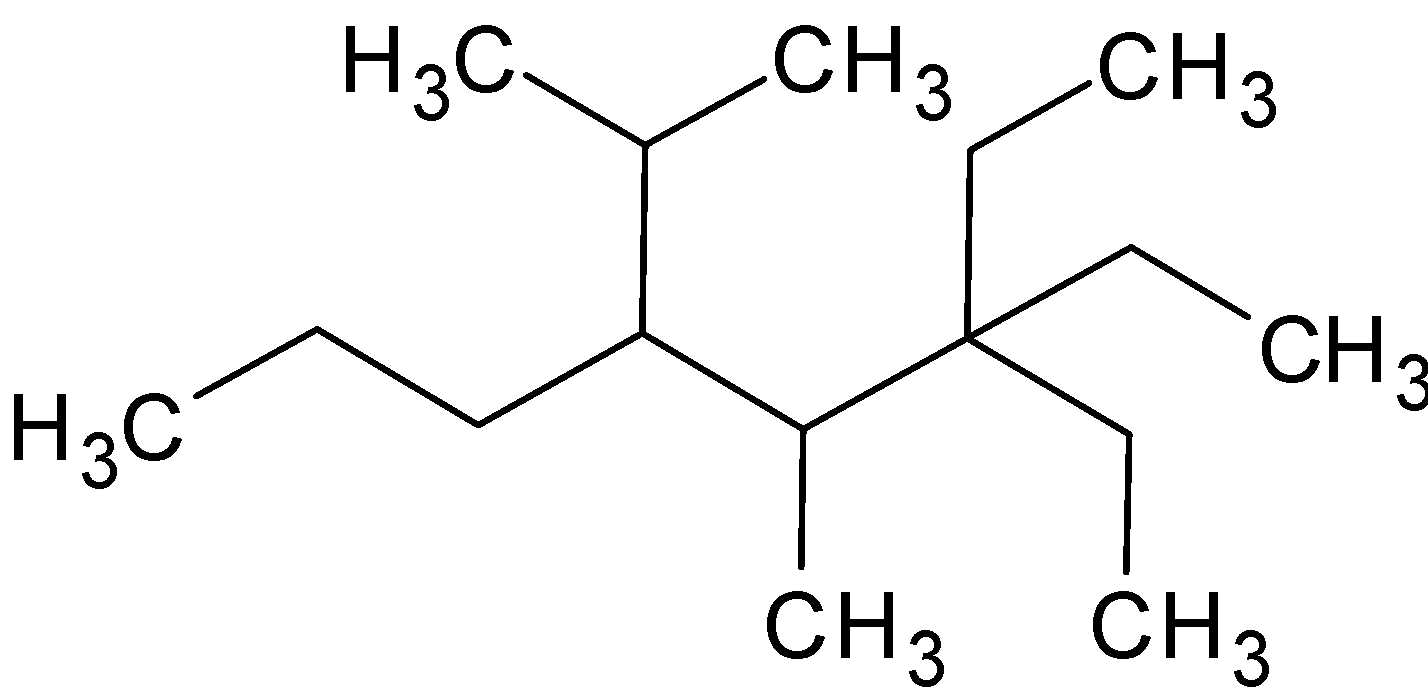
A. $3,3 - $ Diethyl $ - 4 - $ methyl $ - 5 - $ $\left( {1 - } \right.$ methylethyl) octane
B. $6,6 - $ Diethyl $ - 4 - $ methyl $ - 5 - $ isopropyloctane
C. $6,6 - $ Diethyl $ - 3 - $ methyl $ - 5 - $ $\left( {1 - } \right.$methylethyl) octane
D. $6,6 - $ Diethyl $ - 4 - $ isopropyl $ - 5 - $ methyloctane

Answer
577.5k+ views
Hint: IUPAC system of nomenclature is a system of naming compounds in chemistry. IUPAC stands for International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry. By using this IUPAC system one can name any complex organic compound easily.
Complete step by step solution:
The name assigned to an organic compound on the basis of latest IUPAC rules is known as systematic name. According to the IUPAC system, a given compound can be assigned only one name. This system is helpful in naming the complex organic compounds. It is also helpful in naming the multifunctional groups. This is a simple, systematic and scientific method for the nomenclature of organic compounds.
Arrangement of prefixes, root word and suffixes in IUPAC name is given below:
Prefix + root word + primary suffix + secondary suffix
In the given compound, there is no unsaturation. Thus it is an alkane. So it is ended with –ane. The parent chain will be the longest carbon chain.
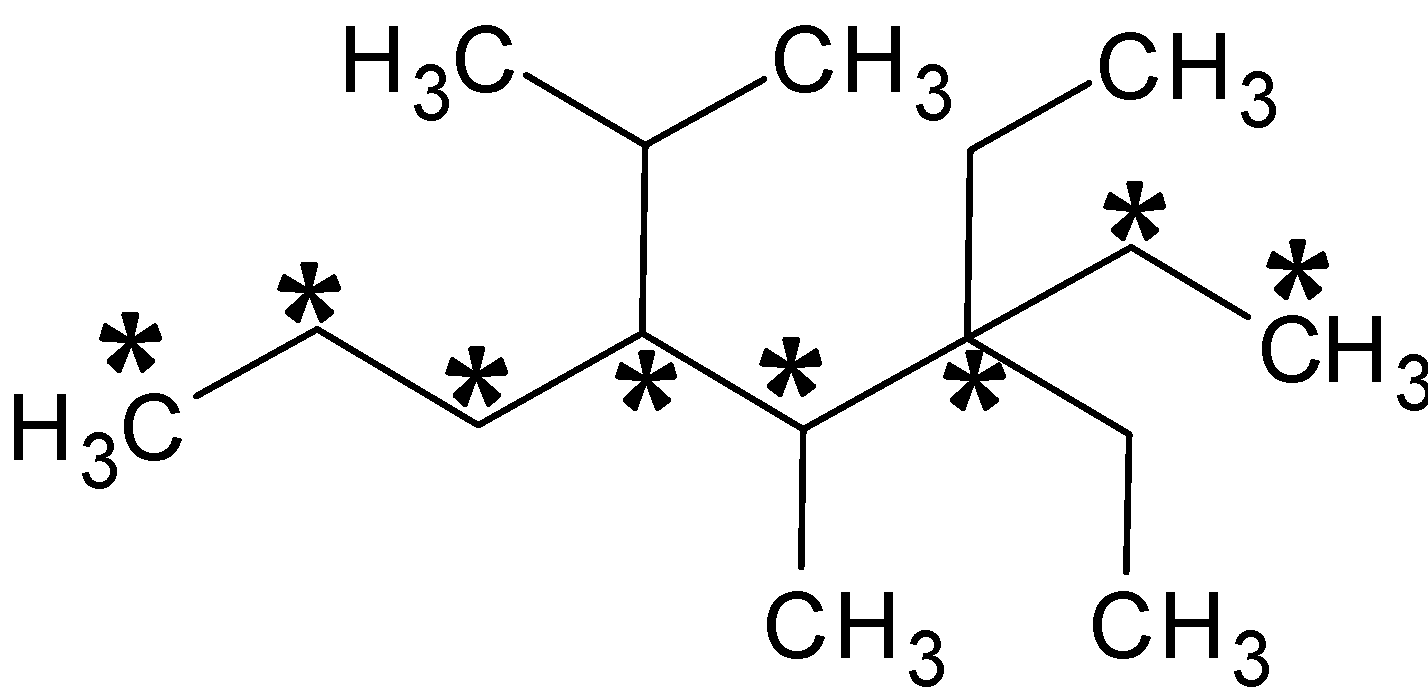
The carbon atoms in the parent chain are given an asterisk above. From the above structure, the number of carbon atoms is $8$. So octane will be the parent name. Moreover, the substituents should be attached to the minimum number of carbon atoms. So the numbering starts from back.
There are two substituents, ethyl groups, in third carbon. Thus naming $3,3 - $ Diethyl. And there is a methyl group in fourth carbon, $4 - $ methyl. In fifth carbon, there is further grouping of an ethyl and methyl group. Thus the name of the compound is $3,3 - $ Diethyl $ - 4 - $ methyl $ - 5 - $ $\left( {1 - } \right.$ methylethyl) octane.
Hence the correct option is A.
Note:
For naming the organic compounds systematically first we have to study about the following three features:
1.Root word: Root word is the basic unit in organic nomenclature. Its names depend upon the number of carbons.
2.Primary suffix: Primary suffixes are added to the root word to show saturation or unsaturation in a carbon chain.
3.Secondary suffix: They are added after the primary suffixes to indicate the presence of a particular functional group in the carbon chain.
Prefix
Complete step by step solution:
The name assigned to an organic compound on the basis of latest IUPAC rules is known as systematic name. According to the IUPAC system, a given compound can be assigned only one name. This system is helpful in naming the complex organic compounds. It is also helpful in naming the multifunctional groups. This is a simple, systematic and scientific method for the nomenclature of organic compounds.
Arrangement of prefixes, root word and suffixes in IUPAC name is given below:
Prefix + root word + primary suffix + secondary suffix
In the given compound, there is no unsaturation. Thus it is an alkane. So it is ended with –ane. The parent chain will be the longest carbon chain.

The carbon atoms in the parent chain are given an asterisk above. From the above structure, the number of carbon atoms is $8$. So octane will be the parent name. Moreover, the substituents should be attached to the minimum number of carbon atoms. So the numbering starts from back.
There are two substituents, ethyl groups, in third carbon. Thus naming $3,3 - $ Diethyl. And there is a methyl group in fourth carbon, $4 - $ methyl. In fifth carbon, there is further grouping of an ethyl and methyl group. Thus the name of the compound is $3,3 - $ Diethyl $ - 4 - $ methyl $ - 5 - $ $\left( {1 - } \right.$ methylethyl) octane.
Hence the correct option is A.
Note:
For naming the organic compounds systematically first we have to study about the following three features:
1.Root word: Root word is the basic unit in organic nomenclature. Its names depend upon the number of carbons.
2.Primary suffix: Primary suffixes are added to the root word to show saturation or unsaturation in a carbon chain.
3.Secondary suffix: They are added after the primary suffixes to indicate the presence of a particular functional group in the carbon chain.
Prefix
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




