
The critical velocity of a satellite is
A. The minimum velocity given to the satellite to escape from the gravitational pull
B. The constant horizontal velocity given to the satellite to keep it in a stable orbit.
C. The constant horizontal velocity given to the satellite to keep its acceleration equal to zero.
D. The constant horizontal velocity given to the satellite to keep its acceleration due to gravity.
Answer
606.6k+ views
Hint – Critical velocity of a satellite is the constant horizontal velocity given to the satellite to keep it in a stable circular orbit.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have to explain the critical velocity of a satellite.
So, the critical velocity is the constant horizontal velocity given to the satellite so as to put it into a stable circular orbit around the earth. It is denoted by \[{V_c}\] . It is also known as orbital speed or proper speed.
The critical velocity of a satellite is given by-
The expression for critical velocity can be obtained by:
Let us consider a satellite of mass m orbiting at height h from the surface of earth around the earth with critical velocity \[{V_c}\] .
Refer the figure shown below for better understanding-
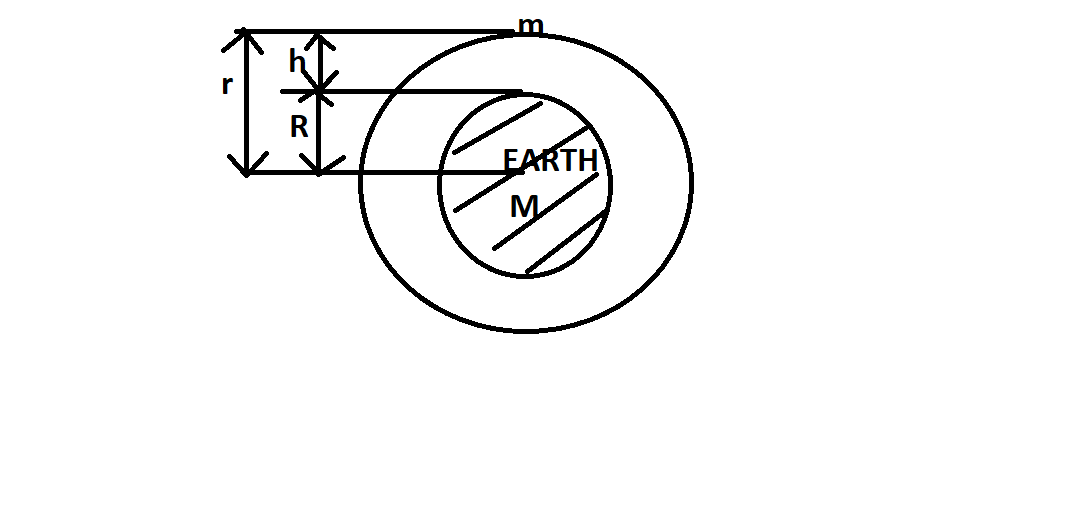
Now, M and R are the mass and radius of the earth respectively.
Now, from the above figure we can see that the radius ‘r’ of the orbit is $r = R + h$
Now, while revolving around the earth, the necessary centripetal force for the circular motion of the satellite is provided by the gravitational attraction between the satellite and the earth.
So, Centripetal force = Gravitational force
So, we can write-
$\dfrac{{m{V_c}^2}}{r} = G.\dfrac{{M.m}}{{{r^2}}}$
We can also write the above expression in terms of critical velocity as-
\[{V_c}^2 = \dfrac{{GM}}{r}\]
Now keeping the value of r as, $r = R + h$ , we get-
\[{V_c}^2 = \dfrac{{GM}}{{R + h}}\]
$ \Rightarrow {V_c} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{GM}}{{R + h}}} $
If the satellite is orbiting very close to the earth’s surface, i.e., $h \ll R$ then h may be neglected in comparison of R, so critical velocity is given by-
${V_c} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{GM}}{R}} $
The above expression is of critical velocity of a satellite moving in a circular orbit around the earth.
We can see that the critical velocity depends on the radius of the earth, mass of the earth and gravitational constant, so we can say that critical velocity is constant.
Therefore, the constant horizontal velocity given to the satellite to keep it in a stable orbit is known as critical velocity.
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note – Whenever such types of questions appear, then first try to explain about the critical velocity, obtain its expression. Draw the figure so that it will be easier to understand, as mentioned in the solution. Also, keep in mind that critical velocity is the minimum velocity required to put a satellite into an orbit.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have to explain the critical velocity of a satellite.
So, the critical velocity is the constant horizontal velocity given to the satellite so as to put it into a stable circular orbit around the earth. It is denoted by \[{V_c}\] . It is also known as orbital speed or proper speed.
The critical velocity of a satellite is given by-
The expression for critical velocity can be obtained by:
Let us consider a satellite of mass m orbiting at height h from the surface of earth around the earth with critical velocity \[{V_c}\] .
Refer the figure shown below for better understanding-

Now, M and R are the mass and radius of the earth respectively.
Now, from the above figure we can see that the radius ‘r’ of the orbit is $r = R + h$
Now, while revolving around the earth, the necessary centripetal force for the circular motion of the satellite is provided by the gravitational attraction between the satellite and the earth.
So, Centripetal force = Gravitational force
So, we can write-
$\dfrac{{m{V_c}^2}}{r} = G.\dfrac{{M.m}}{{{r^2}}}$
We can also write the above expression in terms of critical velocity as-
\[{V_c}^2 = \dfrac{{GM}}{r}\]
Now keeping the value of r as, $r = R + h$ , we get-
\[{V_c}^2 = \dfrac{{GM}}{{R + h}}\]
$ \Rightarrow {V_c} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{GM}}{{R + h}}} $
If the satellite is orbiting very close to the earth’s surface, i.e., $h \ll R$ then h may be neglected in comparison of R, so critical velocity is given by-
${V_c} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{GM}}{R}} $
The above expression is of critical velocity of a satellite moving in a circular orbit around the earth.
We can see that the critical velocity depends on the radius of the earth, mass of the earth and gravitational constant, so we can say that critical velocity is constant.
Therefore, the constant horizontal velocity given to the satellite to keep it in a stable orbit is known as critical velocity.
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note – Whenever such types of questions appear, then first try to explain about the critical velocity, obtain its expression. Draw the figure so that it will be easier to understand, as mentioned in the solution. Also, keep in mind that critical velocity is the minimum velocity required to put a satellite into an orbit.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




