
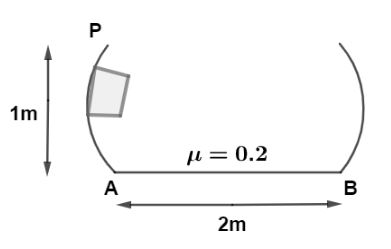
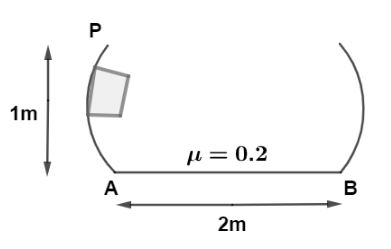
The curved portion is smooth and the horizontal portion is rough. The block is released from P. At what distance from A the block will stop. $(\mu = 0.2)?$

Answer
492.3k+ views
Hint: In order to solve this question, we will first calculate potential energy due to height and then will balance it by kinetic energy to find velocity at point A and later we will use equation of motion to find final distance it which object came at rest.
Complete step by step answer:
According to the question, we have given that
$h = 1m$ height between point P and A.
let ‘m’ be the mass of the block
$g = 9.8m{s^{ - 2}}$
then using law of conservation of energy, if ${v_A}$ be the velocity of block at point A then,
Potential energy due to height will be equal to kinetic energy at point A, so
$P.E = mgh$ and $K.E = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v_A}^2$ equating, both energies we get,
$mgh = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v_A}^2$
$\Rightarrow {v_A}^2 = 2 \times 9.8 \times 1$
$\Rightarrow {v_A}^2 = 19.6\,m{s^{ - 1}}$
Let, f be the friction force on horizontal surface and its balanced by accelerated force with acceleration a so, $f = ma$ and friction force is given by $f = \mu mg$ equating both forces we get,
$a = \mu g$
On putting the value of parameters we get,
$a = 0.2 \times 9.8$
$\Rightarrow a = 1.96\,m{s^{ - 2}}$
Now, we have initial velocity in horizontal surface of block as ${v_A}^2 = 19.6m{s^{ - 1}}$ and acceleration will be negative because block has to came at rest so, $a = - 1.96m{s^{ - 2}}$ let x be the distance it covered before coming at rest, so final velocity will be zero.
using equations of motion as
${v^2}_{final} - {v^2}_{initial} = 2aS$ on putting the values of parameters respectively we get,
$0 - 19.6 = - 2 \times 1.96 \times x$
$\Rightarrow x = 5\,m$
Since the horizontal distance is only of $2\,m$ as shown in diagram so, block must rises again in right sided curved part, let us find the velocity of block at point B as,
${v_B}^2 - {v_A}^2 = 2aS$
here $S = 2m$
$\Rightarrow {v_B}^2 - 19.6 = - 4 \times 1.96$
$\Rightarrow {v_B}^2 = 11.76\,m{s^{ - 2}}$
Now, with this same velocity block will pass when returning down from right sided curved part again we will check for its stopping case, as
${v^2}_{final} - {v^2}_B = 2ax$
here, x is measured from point B
$ - 11.76 = - 3.92x$
$\Rightarrow x = 3\,m$
So, block will again rises to left sided curved part now, let us find the velocity at point A again, as
${v_A}^2 - {v_B}^2 = 2aS$
here again $S = 2\,m$
${v_A}^2 - 11.76 = - 7.84$
$\Rightarrow {v_A}^2 = 3.92\,m{s^{ - 1}}$
Now, with this same velocity block will pass when returning down from left sided curved part again we will check for its stopping case, as
${v^2}_{final} - {v^2}_A = 2ax$
here, x is measured from point A
$ - 3.92 = - 3.92x$
$\therefore x = 1\,m$
So, this distance is less than total horizontal distance so the block will finally come to rest at this distance.
Hence, the distance from point A at which block came at rest is $x = 1\,m$.
Note:It should be remembered that, due to the friction force acting on the horizontal surface on the block the acceleration produced will be negative which is the main cause which brings the block at rest finally and always checks the signs of various parameters while solving such numerical equations.
Complete step by step answer:
According to the question, we have given that
$h = 1m$ height between point P and A.
let ‘m’ be the mass of the block
$g = 9.8m{s^{ - 2}}$
then using law of conservation of energy, if ${v_A}$ be the velocity of block at point A then,
Potential energy due to height will be equal to kinetic energy at point A, so

$P.E = mgh$ and $K.E = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v_A}^2$ equating, both energies we get,
$mgh = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v_A}^2$
$\Rightarrow {v_A}^2 = 2 \times 9.8 \times 1$
$\Rightarrow {v_A}^2 = 19.6\,m{s^{ - 1}}$
Let, f be the friction force on horizontal surface and its balanced by accelerated force with acceleration a so, $f = ma$ and friction force is given by $f = \mu mg$ equating both forces we get,
$a = \mu g$
On putting the value of parameters we get,
$a = 0.2 \times 9.8$
$\Rightarrow a = 1.96\,m{s^{ - 2}}$
Now, we have initial velocity in horizontal surface of block as ${v_A}^2 = 19.6m{s^{ - 1}}$ and acceleration will be negative because block has to came at rest so, $a = - 1.96m{s^{ - 2}}$ let x be the distance it covered before coming at rest, so final velocity will be zero.
using equations of motion as
${v^2}_{final} - {v^2}_{initial} = 2aS$ on putting the values of parameters respectively we get,
$0 - 19.6 = - 2 \times 1.96 \times x$
$\Rightarrow x = 5\,m$
Since the horizontal distance is only of $2\,m$ as shown in diagram so, block must rises again in right sided curved part, let us find the velocity of block at point B as,
${v_B}^2 - {v_A}^2 = 2aS$
here $S = 2m$
$\Rightarrow {v_B}^2 - 19.6 = - 4 \times 1.96$
$\Rightarrow {v_B}^2 = 11.76\,m{s^{ - 2}}$
Now, with this same velocity block will pass when returning down from right sided curved part again we will check for its stopping case, as
${v^2}_{final} - {v^2}_B = 2ax$
here, x is measured from point B
$ - 11.76 = - 3.92x$
$\Rightarrow x = 3\,m$
So, block will again rises to left sided curved part now, let us find the velocity at point A again, as
${v_A}^2 - {v_B}^2 = 2aS$
here again $S = 2\,m$
${v_A}^2 - 11.76 = - 7.84$
$\Rightarrow {v_A}^2 = 3.92\,m{s^{ - 1}}$
Now, with this same velocity block will pass when returning down from left sided curved part again we will check for its stopping case, as
${v^2}_{final} - {v^2}_A = 2ax$
here, x is measured from point A
$ - 3.92 = - 3.92x$
$\therefore x = 1\,m$
So, this distance is less than total horizontal distance so the block will finally come to rest at this distance.
Hence, the distance from point A at which block came at rest is $x = 1\,m$.
Note:It should be remembered that, due to the friction force acting on the horizontal surface on the block the acceleration produced will be negative which is the main cause which brings the block at rest finally and always checks the signs of various parameters while solving such numerical equations.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




