
The cycle in which pyruvic acid is broken down in the presence of oxygen is known as
(a) Glycolysis
(b) Kreb's cycle
(c) Anaerobic respiration
(d) None of the above
Answer
566.4k+ views
Hint: In plants, respiration involves the exchange of gases between cell and surrounding, the organic substances which are established in living cells to release energy are respiratory substances. Respiration is of two types aerobic and anaerobic, anaerobic respiration is common in all plants and animals but aerobic respiration takes place in aerobes only.
Complete answer:
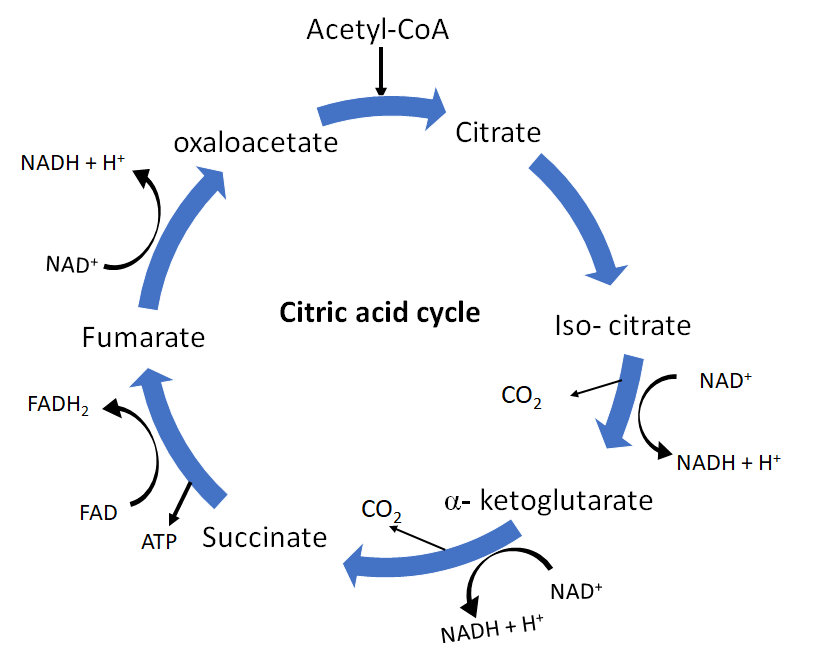
Glycolysis is the first stage of respiration in which the breakdown of glucose into pyruvic acid takes place. Pyruvic acid is generated in the cytosol and transported to mitochondria which initiate the second phase of respiration. Pyruvic acid first shows oxidative decarboxylation in which pyruvic acid oxidized to carbon dioxide by the formation of Acetyl CoA in presence of enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase. Kreb's cycle begins when acetyl CoA enters into the reaction to form citric acid. Kreb's cycle involves the following steps:
Condensation involves the combination of acetyl CoA with oxaloacetate to form citrate and CoA in presence of enzyme citrate synthase.
Citrate dehydrate to form cis-aconitate with the liberation of water in presence of enzyme aconitase.
Cis-aconitate rehydrate to form Isocitrate in presence of enzyme aconitase.
Isocitrate shows dehydrogenation in presence of enzyme isocitrate dehydrogenase to form oxalosuccinate with the liberation of NADH.
Oxalosuccinate decarboxylates to form alpha-ketoglutarate in presence of enzyme decarboxylase where the liberation of carbon dioxide takes place.
Alpha-ketoglutarate is dehydrogenated and decarboxylated to form succinyl CoA in presence of enzyme alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase.
Succinyl CoA splits into succinate and CoA in presence of the enzyme succinyl thiokinase. This reaction liberates ATP.
Succinate undergoes dehydrogenation in presence of enzyme succinate dehydrogenase to form fumarate with the liberation of FADH. Fumarate changed into malate with the presence of the enzyme fumarase with the absorption of water.
Malate dehydrogenases to produce oxaloacetate in presence of enzyme malate dehydrogenase.
Oxaloacetate further picks another molecule of activated acetate to repeat the cycle.
So, the correct answer is Kreb's cycle.
Note: In the citric acid, cycle decarboxylation takes place at two-step. Total 12 ATP molecules liberated from per molecule of pyruvic acid and from each molecule of glucose total of 24 molecules of ATP formed during a citric acid cycle.
Complete answer:
Glycolysis is the first stage of respiration in which the breakdown of glucose into pyruvic acid takes place. Pyruvic acid is generated in the cytosol and transported to mitochondria which initiate the second phase of respiration. Pyruvic acid first shows oxidative decarboxylation in which pyruvic acid oxidized to carbon dioxide by the formation of Acetyl CoA in presence of enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase. Kreb's cycle begins when acetyl CoA enters into the reaction to form citric acid. Kreb's cycle involves the following steps:
Condensation involves the combination of acetyl CoA with oxaloacetate to form citrate and CoA in presence of enzyme citrate synthase.
Citrate dehydrate to form cis-aconitate with the liberation of water in presence of enzyme aconitase.
Cis-aconitate rehydrate to form Isocitrate in presence of enzyme aconitase.
Isocitrate shows dehydrogenation in presence of enzyme isocitrate dehydrogenase to form oxalosuccinate with the liberation of NADH.
Oxalosuccinate decarboxylates to form alpha-ketoglutarate in presence of enzyme decarboxylase where the liberation of carbon dioxide takes place.
Alpha-ketoglutarate is dehydrogenated and decarboxylated to form succinyl CoA in presence of enzyme alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase.
Succinyl CoA splits into succinate and CoA in presence of the enzyme succinyl thiokinase. This reaction liberates ATP.
Succinate undergoes dehydrogenation in presence of enzyme succinate dehydrogenase to form fumarate with the liberation of FADH. Fumarate changed into malate with the presence of the enzyme fumarase with the absorption of water.
Malate dehydrogenases to produce oxaloacetate in presence of enzyme malate dehydrogenase.
Oxaloacetate further picks another molecule of activated acetate to repeat the cycle.
So, the correct answer is Kreb's cycle.
Note: In the citric acid, cycle decarboxylation takes place at two-step. Total 12 ATP molecules liberated from per molecule of pyruvic acid and from each molecule of glucose total of 24 molecules of ATP formed during a citric acid cycle.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




