
The dehydrohalogenation of neopentyl bromide with alcoholic KOH mainly gives
A) 2-methyl-1-butene
B) 2-methyl-2-butene
C) 2, 2-dimethyl-1-butene
D) 2-butene
Answer
362.7k+ views
Hint: The dehydrohalogenation reaction is a type of elimination reaction. In this reaction a carbocation is formed as an intermediate which further reacts to give an alkene.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
When an alkyl bromide is treated with an alcoholic base then an elimination reaction takes place.
In this reaction at first step the halogen atom that is bromine atom is removed from the alkyl halide that is neopentyl bromide to form a carbocation intermediate that is neopentyl carbocation in reaction with an alcoholic base that is potassium hydroxide.
In the next step one methyl group is shifted to the next carbon atom due to unavailability of beta hydrogen. Now the newly formed carbocation contains beta hydrogen and the beta hydrogen is easily removed and forms the desired product that is 2-methyl-2-butene. In this reaction hydrogen bromide is removed as a side product.
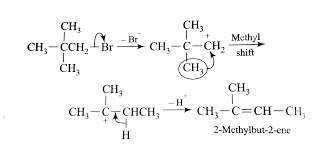
Thus the dehydrohalogenation of neopentyl bromide with alcoholic KOH mainly gives 2-methyl-2-butene as a major product.
Thus the correct option is B.
Note: In general E1 elimination reaction no shifting of any group takes place. If no beta hydrogen is present in the produced intermediate that is the carbocation then shifting of a group takes place to generate beta hydrogen which helps to produce the desired product.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
When an alkyl bromide is treated with an alcoholic base then an elimination reaction takes place.
In this reaction at first step the halogen atom that is bromine atom is removed from the alkyl halide that is neopentyl bromide to form a carbocation intermediate that is neopentyl carbocation in reaction with an alcoholic base that is potassium hydroxide.
In the next step one methyl group is shifted to the next carbon atom due to unavailability of beta hydrogen. Now the newly formed carbocation contains beta hydrogen and the beta hydrogen is easily removed and forms the desired product that is 2-methyl-2-butene. In this reaction hydrogen bromide is removed as a side product.

Thus the dehydrohalogenation of neopentyl bromide with alcoholic KOH mainly gives 2-methyl-2-butene as a major product.
Thus the correct option is B.
Note: In general E1 elimination reaction no shifting of any group takes place. If no beta hydrogen is present in the produced intermediate that is the carbocation then shifting of a group takes place to generate beta hydrogen which helps to produce the desired product.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

The value of 6 more than 7 is A 1 B 1 C 13 D 13 class 7 maths CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell




