
The diagonals of a rectangle \[ABCD\] intersect at \[O\]. If \[\angle BOC = 70^\circ \]. Find \[\angle ODA\]
Answer
558.9k+ views
Hint:
Here we will first use the vertically opposite angle property to find the opposite angle of the given angle. We will use the fact that the two diagonal rectangles are equal in length to find the angle of the triangle. We will then use the angle sum property of the triangle and solve it further to get the required measure of angle.
Complete step by step solution:
Here we need to find the value of the given angle of rectangle i.e. we need to find the value of \[\angle ODA\].
We will first draw the rectangle using the given information.
It is given that \[ABCD\] is a rectangle and the diagonals of the rectangle intersect at the point \[O\] and \[\angle BOC = 70^\circ \].
Let \[\angle ODA = X\] and \[\angle OAD = Y\]
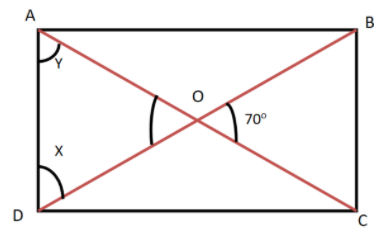
We know that the two diagonals of a rectangle are equal in length and also they bisect each other.
So we can say that \[OD = OA\].
It is given that \[\angle BOC = 70^\circ \] and \[\angle AOD\] is the vertical opposite angle of the rectangle, so these must be equal.
Therefore, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \angle AOD = 70^\circ \]
In $\vartriangle AOD$,
As \[OD = OA\] so \[\angle OAD = \angle ODA = X\]
This is because we know that the angles opposite to the equal sides are always equal.
As we know that the sum of the angles of the triangle is equal to \[180^\circ \]. We will apply the same property of triangles in $\vartriangle AOD$. Therefore, we get
\[\angle OAD + \angle ODA + \angle AOD = 180^\circ \]
Now, we will substitute the value of all the angles of the triangles.
\[ \Rightarrow X + Y + 70^\circ = 180^\circ \]
We know that \[\angle OAD = \angle ODA\]. So we can write \[\angle OAD = \angle ODA = X = Y\].
\[ \Rightarrow X + X + 70^\circ = 180^\circ \]
On adding the like terms, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 2X + 70^\circ = 180^\circ \]
Now, subtracting \[70^\circ \] from the sides, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 2X + 70^\circ - 70^\circ = 180^\circ - 70^\circ \]
\[ \Rightarrow 2X = 110^\circ \]
Now, we will divide both sides by 2. Therefore, we get
\[\begin{array}{l} \Rightarrow \dfrac{{2X}}{2} = \dfrac{{110^\circ }}{2}\\ \Rightarrow X = 55^\circ \end{array}\]
Therefore, \[\angle ODA = X = 55^\circ \]. This is the required value of this angle.
Note:
Here we need to remember the important properties of the rectangle as well as the triangle to solve the problem. A rectangle is a two dimensional geometrical figure having four sides and the angle between the adjacent sides is \[90^\circ \]. The opposite sides of a rectangle are equal in length and the sum of all the interior angles of a rectangle is equal to \[360^\circ \].
Here we will first use the vertically opposite angle property to find the opposite angle of the given angle. We will use the fact that the two diagonal rectangles are equal in length to find the angle of the triangle. We will then use the angle sum property of the triangle and solve it further to get the required measure of angle.
Complete step by step solution:
Here we need to find the value of the given angle of rectangle i.e. we need to find the value of \[\angle ODA\].
We will first draw the rectangle using the given information.
It is given that \[ABCD\] is a rectangle and the diagonals of the rectangle intersect at the point \[O\] and \[\angle BOC = 70^\circ \].
Let \[\angle ODA = X\] and \[\angle OAD = Y\]

We know that the two diagonals of a rectangle are equal in length and also they bisect each other.
So we can say that \[OD = OA\].
It is given that \[\angle BOC = 70^\circ \] and \[\angle AOD\] is the vertical opposite angle of the rectangle, so these must be equal.
Therefore, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \angle AOD = 70^\circ \]
In $\vartriangle AOD$,
As \[OD = OA\] so \[\angle OAD = \angle ODA = X\]
This is because we know that the angles opposite to the equal sides are always equal.
As we know that the sum of the angles of the triangle is equal to \[180^\circ \]. We will apply the same property of triangles in $\vartriangle AOD$. Therefore, we get
\[\angle OAD + \angle ODA + \angle AOD = 180^\circ \]
Now, we will substitute the value of all the angles of the triangles.
\[ \Rightarrow X + Y + 70^\circ = 180^\circ \]
We know that \[\angle OAD = \angle ODA\]. So we can write \[\angle OAD = \angle ODA = X = Y\].
\[ \Rightarrow X + X + 70^\circ = 180^\circ \]
On adding the like terms, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 2X + 70^\circ = 180^\circ \]
Now, subtracting \[70^\circ \] from the sides, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 2X + 70^\circ - 70^\circ = 180^\circ - 70^\circ \]
\[ \Rightarrow 2X = 110^\circ \]
Now, we will divide both sides by 2. Therefore, we get
\[\begin{array}{l} \Rightarrow \dfrac{{2X}}{2} = \dfrac{{110^\circ }}{2}\\ \Rightarrow X = 55^\circ \end{array}\]
Therefore, \[\angle ODA = X = 55^\circ \]. This is the required value of this angle.
Note:
Here we need to remember the important properties of the rectangle as well as the triangle to solve the problem. A rectangle is a two dimensional geometrical figure having four sides and the angle between the adjacent sides is \[90^\circ \]. The opposite sides of a rectangle are equal in length and the sum of all the interior angles of a rectangle is equal to \[360^\circ \].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




