
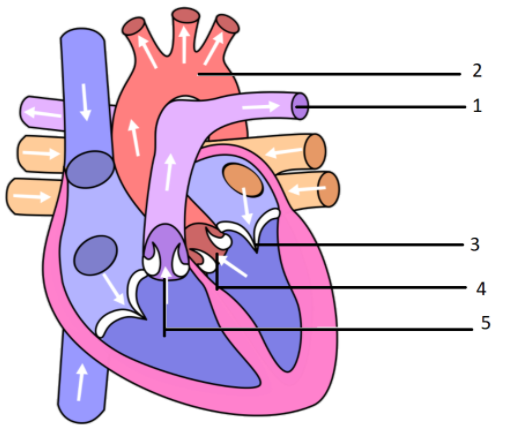
The diagram given alongside represents the human heart in one phase of its activity. Study the same and then answer the questions that follow:
(a) Name the phase.
(b) Which part of the heart is contracting in this phase? Give a reason to support your answer.
(c) Name the parts numbered 1 to 6.
(d) What type of blood flows through the parts marked 1 and 2 respectively?
(e) How many valves are closed in this phase?

Answer
541.5k+ views
Hint: The heart is a fist-sized muscular organ positioned just above and just left of the breastbone. In the network of arteries and nerves, called the cardiovascular system, the heart pumps blood.
Complete answer:
a) The diagram presented reflects the ventricular systole phase.
b) Since the semilunar valves are open, both heart ventricles contract in this process.
c) 1 - A pulmonary artery- It supplies deoxygenated blood from heart to lungs.
2 - The aorta -It is the largest artery.
3 - Mitral valve
4 - Left Auricle/atrium
5 - Semilunar valves – It is located between the pulmonary artery and right atrium.
d) Deoxygenated and oxygenated blood passes into the corresponding pulmonary arteries and pulmonary veins.
e) In this process, the Bicuspid and Tricuspid valves are closed to avoid blood flow into the atria. The bicuspid valve contains two cusps whereas the tricuspid valve contains 2 cusps.
Additional information:The coronary arteries run along the heart's surface and provide the heart muscle with oxygen-rich blood. A nerve tissue network also passes through the heart, carrying out the complicated signals that control contraction and relaxation. A sac called the pericardium covers the nucleus.
Note: The cardiac cycle is the human heart's performance from the end of one heartbeat to the start of the next. It consists of two periods: one during which, after a duration of robust contraction called systole and pumping of blood, the heart muscle relaxes and refills with blood called diastole.
Complete answer:
a) The diagram presented reflects the ventricular systole phase.
b) Since the semilunar valves are open, both heart ventricles contract in this process.
c) 1 - A pulmonary artery- It supplies deoxygenated blood from heart to lungs.
2 - The aorta -It is the largest artery.
3 - Mitral valve
4 - Left Auricle/atrium
5 - Semilunar valves – It is located between the pulmonary artery and right atrium.
d) Deoxygenated and oxygenated blood passes into the corresponding pulmonary arteries and pulmonary veins.
e) In this process, the Bicuspid and Tricuspid valves are closed to avoid blood flow into the atria. The bicuspid valve contains two cusps whereas the tricuspid valve contains 2 cusps.
Additional information:The coronary arteries run along the heart's surface and provide the heart muscle with oxygen-rich blood. A nerve tissue network also passes through the heart, carrying out the complicated signals that control contraction and relaxation. A sac called the pericardium covers the nucleus.
Note: The cardiac cycle is the human heart's performance from the end of one heartbeat to the start of the next. It consists of two periods: one during which, after a duration of robust contraction called systole and pumping of blood, the heart muscle relaxes and refills with blood called diastole.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




