
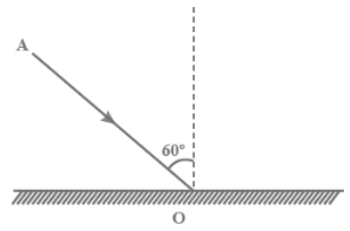
The diagram in fig. shows an incident ray AO and the normal ON on a plane mirror.Draw the reflected ray. State the law you use to draw the direction of the reflected ray.

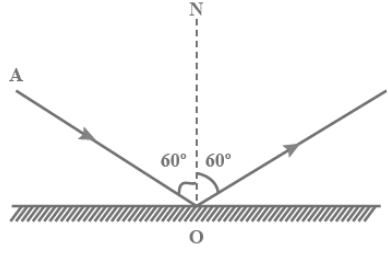
Answer
517.2k+ views
Hint: At an interface between two separate media, reflection is the change in direction of a wavefront such that it returns to the medium from which it came. Light, tone, and water waves are all examples of reflection.
Complete answer:
The angle of the reflected ray is equal to the angle of the incident ray as reflected from a smooth surface with respect to the natural surface, which is a line perpendicular to the surface at the point of contact, according to the law of reflection. At the point of touch of the incident ray, the reflected ray is always in the plane defined by the incident ray and the normal to the surface.
The law of reflection can be used to explain the images created by planes and curved mirrors. The law of reflection states that when light rays strike a smooth surface, the angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence, and that the incident ray, reflected ray, and normal to the surface are all in the same plane. Reflection of light is the process of light rays colliding with a surface and being reflected back.
This form of reflection is generated by plane mirrors with a smooth surface. The picture is transparent and easily recognisable in this situation. Plane mirror images are still simulated, which means they can't be collected on a computer. The law of light reflection is used to determine the path of the reflecting beam. The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection, according to this theorem.
$\angle {\mathbf{i}} = \angle {\mathbf{r}}$
Note: Unlike mirrors, most natural surfaces are rugged on the scale of light wavelengths, and as a result, parallel incident light rays are mirrored irregularly or diffusely in several different directions. As a result, diffuse illumination aids in object recognition and is responsible for the ability to see most illuminated surfaces from any angle.
Complete answer:
The angle of the reflected ray is equal to the angle of the incident ray as reflected from a smooth surface with respect to the natural surface, which is a line perpendicular to the surface at the point of contact, according to the law of reflection. At the point of touch of the incident ray, the reflected ray is always in the plane defined by the incident ray and the normal to the surface.
The law of reflection can be used to explain the images created by planes and curved mirrors. The law of reflection states that when light rays strike a smooth surface, the angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence, and that the incident ray, reflected ray, and normal to the surface are all in the same plane. Reflection of light is the process of light rays colliding with a surface and being reflected back.
This form of reflection is generated by plane mirrors with a smooth surface. The picture is transparent and easily recognisable in this situation. Plane mirror images are still simulated, which means they can't be collected on a computer. The law of light reflection is used to determine the path of the reflecting beam. The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection, according to this theorem.
$\angle {\mathbf{i}} = \angle {\mathbf{r}}$

Note: Unlike mirrors, most natural surfaces are rugged on the scale of light wavelengths, and as a result, parallel incident light rays are mirrored irregularly or diffusely in several different directions. As a result, diffuse illumination aids in object recognition and is responsible for the ability to see most illuminated surfaces from any angle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




