
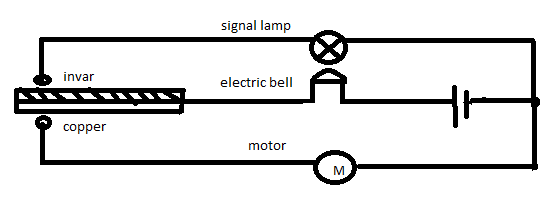
The diagram shows a bimetallic strip used as a thermostat in a circuit. The copper expands more than the invar for the same temperature rise. What will be switched on when the bimetallic strip becomes hot?
A. Bell only
B. Lamp and bell only
C. Motor and bell only
D. Lamp, bell and motor

Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: First here we have to see what bimetallic strips are. A bimetallic strip consists of two distinct materials with different coefficient of expansion which are joined together. The resulting curvature transition or bending is an indispensible characteristic of all thermostatic bimetals in response to temperature transition.
Complete step by step solution:
A bimetal consists of two or more composite materials with various linear thermal expansion coefficients bonded by welding or riveting. The substance with the greater thermal expansion coefficient is classified as the active component and the passive component is that of the lower CTE. Alloys containing iron, manganese, nickel or chromium in different coefficients are typically found in the active portion. Invar an iron-nickel alloy is mostly preferred on the passive side.
Some bimetals have a third layer of copper between the active and passive sides to improve the thermal conductivity and reduce the electrical resistivity of the materials.
Thus as copper stretches rather than invar, the side of copper converges and the side of invar diverges such that bimetallic strips bend upward and upward circuit is short and therefore bell and lamp will turn on.
Hence, option B is correct.
Note: The working of bimetal can be briefly explained as – In a bimetallic strip the multiple expansions compel the flat surface, if warm to bend one way and vice versa. When the strip is warm, the metal with the high thermal expansion coefficient is on the outer side of the curve and on the inner side when cooled. Also owing to the high coefficient of linear expansion of copper, heating copper bends more than invar.
Complete step by step solution:
A bimetal consists of two or more composite materials with various linear thermal expansion coefficients bonded by welding or riveting. The substance with the greater thermal expansion coefficient is classified as the active component and the passive component is that of the lower CTE. Alloys containing iron, manganese, nickel or chromium in different coefficients are typically found in the active portion. Invar an iron-nickel alloy is mostly preferred on the passive side.
Some bimetals have a third layer of copper between the active and passive sides to improve the thermal conductivity and reduce the electrical resistivity of the materials.
Thus as copper stretches rather than invar, the side of copper converges and the side of invar diverges such that bimetallic strips bend upward and upward circuit is short and therefore bell and lamp will turn on.
Hence, option B is correct.
Note: The working of bimetal can be briefly explained as – In a bimetallic strip the multiple expansions compel the flat surface, if warm to bend one way and vice versa. When the strip is warm, the metal with the high thermal expansion coefficient is on the outer side of the curve and on the inner side when cooled. Also owing to the high coefficient of linear expansion of copper, heating copper bends more than invar.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




