
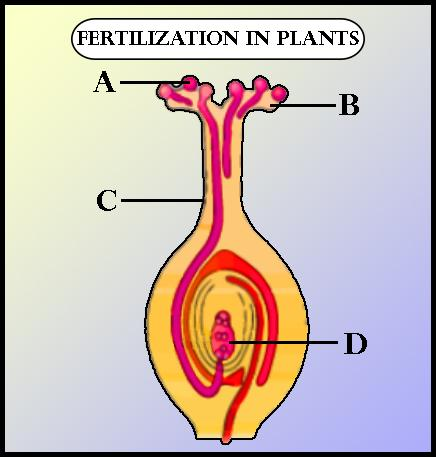
The diagram shows the process of fertilization in flowering plants. Observe it and answer the question. Name the parts of the flower that develops into
(a)Seed and
(b)Fruit after fertilization

Answer
589.2k+ views
Hint: The female basal portion of pistil will mature as fruit enclosing the seed. The fruit is of two types based on the ovary fleshy fruit or dry fruit.
Complete answer:
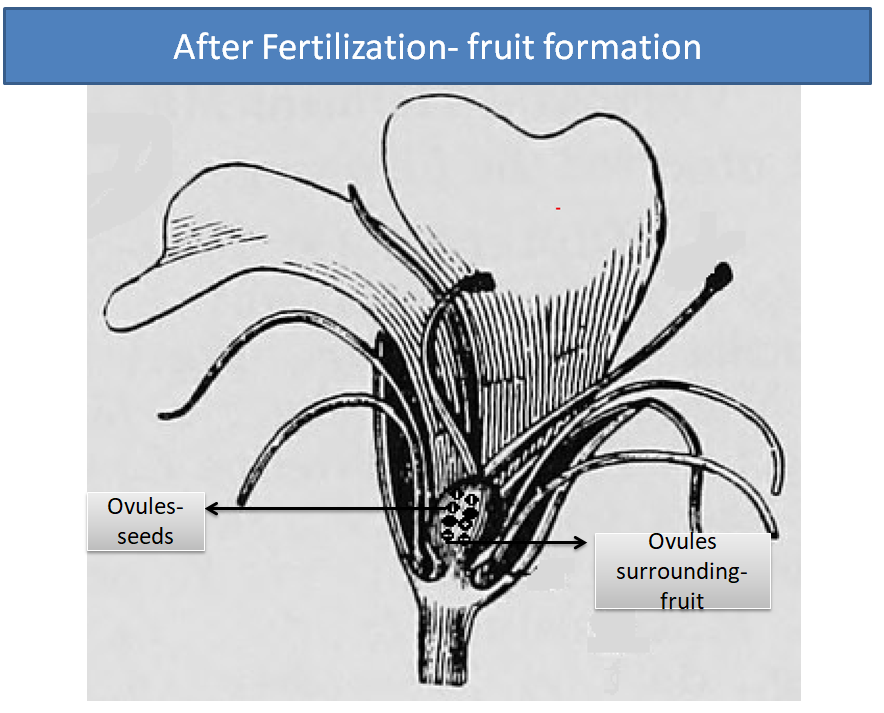
(a) After fertilization, each ovule develops into seeds which means the number of seeds is equal to the number of ovules present in the flower.
(b) After fertilization, the ovary surrounding the ovules develops into the fruit of the plant.
Additional Information
-To understand the process of fertilization in flowers it is important to understand the essential parts of the flower that take part in the reproduction of a flower.
Male reproductive part in plant- Androecium
-Stamen or microsporangia is a male reproductive part that consists of filament- a stalk of a flower, anther- lobed structure, connective- it connects filament and anther.
Female reproductive part in plant – Gynoecium
-Carpel or megasporophyll is a female reproductive part that consists of stigma- the terminal part where pollen grain deposited during pollination, style- long tubular parts, ovary- fertile basal part contain ovule.
- The fertilization in flowers begins with the pollination where the transfer of pollen grain from the anther to the stigma of a flower. The transfer is carried out by either biotic like insects, birds, etc., or by the abiotic factor-like wind and water termed as pollinating agents. The process of pollination occurs in gymnosperms and angiosperms. The pollination is of two types- self-pollination and cross-pollination.
-Fertilization occurs mainly in four stages:
(a)Germination of pollen tune on stigma
Plant male gamete is motile so to reach the ovule pollen tube is germinated by undergoing conformational changes which cause a formation of protruding outwards to form a tube-like structure called pollen tube. Pollen tubes transport the male gamete cells from a pollen grain.
(b)Growth of pollen tube
The male gamete travels through a pollen tube which penetrates the stigma and travels through long tubular style and reaches to the ovary.
(c)Pollen tube entry into the embryo sac
The pollen tube breaks through the ovule from an opening in the ovule termed as micropyle and the pollen burst with the embryo.
(d)Fusion of gametes
After the entry of male gamete into embryo sac the male and female gamete fuses with the egg to form a diploid zygote, this process is termed as syngamy.
Note:
-Synergid – a condition in which one of two small cells living the egg in the mature embryo sec of the flowering plant.
-Parthenocarpy- the process in which the plants that have lost the capacity to produce seeds. Example-oranges.
Complete answer:
(a) After fertilization, each ovule develops into seeds which means the number of seeds is equal to the number of ovules present in the flower.
(b) After fertilization, the ovary surrounding the ovules develops into the fruit of the plant.

Additional Information
-To understand the process of fertilization in flowers it is important to understand the essential parts of the flower that take part in the reproduction of a flower.
Male reproductive part in plant- Androecium
-Stamen or microsporangia is a male reproductive part that consists of filament- a stalk of a flower, anther- lobed structure, connective- it connects filament and anther.
Female reproductive part in plant – Gynoecium
-Carpel or megasporophyll is a female reproductive part that consists of stigma- the terminal part where pollen grain deposited during pollination, style- long tubular parts, ovary- fertile basal part contain ovule.
- The fertilization in flowers begins with the pollination where the transfer of pollen grain from the anther to the stigma of a flower. The transfer is carried out by either biotic like insects, birds, etc., or by the abiotic factor-like wind and water termed as pollinating agents. The process of pollination occurs in gymnosperms and angiosperms. The pollination is of two types- self-pollination and cross-pollination.
-Fertilization occurs mainly in four stages:
(a)Germination of pollen tune on stigma
Plant male gamete is motile so to reach the ovule pollen tube is germinated by undergoing conformational changes which cause a formation of protruding outwards to form a tube-like structure called pollen tube. Pollen tubes transport the male gamete cells from a pollen grain.
(b)Growth of pollen tube
The male gamete travels through a pollen tube which penetrates the stigma and travels through long tubular style and reaches to the ovary.
(c)Pollen tube entry into the embryo sac
The pollen tube breaks through the ovule from an opening in the ovule termed as micropyle and the pollen burst with the embryo.
(d)Fusion of gametes
After the entry of male gamete into embryo sac the male and female gamete fuses with the egg to form a diploid zygote, this process is termed as syngamy.
Note:
-Synergid – a condition in which one of two small cells living the egg in the mature embryo sec of the flowering plant.
-Parthenocarpy- the process in which the plants that have lost the capacity to produce seeds. Example-oranges.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




