
The dorsal root of the spinal cord contains
A. Somatic motor fibers
B. Visceral motor fibers
C. Somatic sensory fibers
D. Visceral sensory fibers
Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint: The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column. It encloses the central canal of the spinal cord, which contains cerebrospinal fluid. The brain and spinal cord together make up the central nervous system (CNS).
Complete answer:
The general somatic afferent fibers arise from neurons in sensory ganglia and are found in all the spinal nerves, except occasionally the first cervical, and conduct impulses of pain, touch, and temperature from the surface of the body through the dorsal roots to the spinal cord and impulses of muscle sense, tendon sense and joint sense from the deeper structures.
-In the dorsal column-medial lemniscus tract, a primary neuron's axon enters the spinal cord and then enters the dorsal column. If the primary axon enters below spinal level T6, the axon travels in the fasciculus gracilis, the medial part of the column. If the axon enters above level T6, then it travels in the fasciculus cuneatus, which is lateral to the fasciculus gracilis.
-The primary axon ascends to the lower medulla, where it leaves its fasciculus and synapses with a secondary neuron in one of the dorsal column nuclei: either the nucleus gracilis or the nucleus cuneatus, depending on the pathway it took. The secondary axon leaves its nucleus and passes anteriorly and medially. The collection of secondary axons that do this are known as internal arcuate fibers.
-The internal arcuate fibers decussate and continue ascending as the contralateral medial lemniscus. Secondary axons from the medial lemniscus finally terminate in the ventral posterolateral nucleus of the thalamus, where they synapse with tertiary neurons. The tertiary neurons ascend via the posterior limb of the internal capsule and end in the primary sensory cortex.
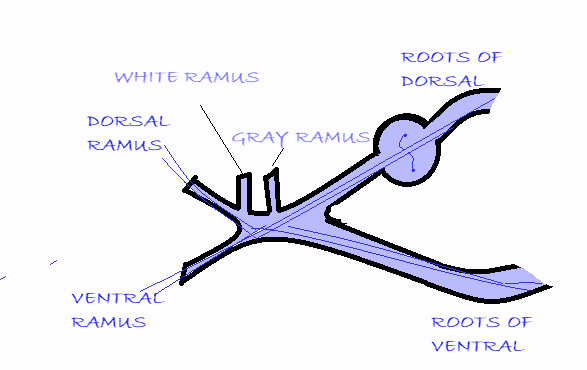
Hence, the correct option is C, i.e., Somatic sensory fibers
Note: A dorsal root ganglion or spinal ganglion is a cluster of neurons in a dorsal root of a spinal nerve. The cell bodies of sensory neurons known as first-order neurons are located in the dorsal root ganglia. The dorsal root ganglia develop in the embryo from neural crest cells, not neural tube. Hence, the spinal ganglia can be regarded as a gray matter of the spinal cord that became translocated to the periphery.
Complete answer:
The general somatic afferent fibers arise from neurons in sensory ganglia and are found in all the spinal nerves, except occasionally the first cervical, and conduct impulses of pain, touch, and temperature from the surface of the body through the dorsal roots to the spinal cord and impulses of muscle sense, tendon sense and joint sense from the deeper structures.
-In the dorsal column-medial lemniscus tract, a primary neuron's axon enters the spinal cord and then enters the dorsal column. If the primary axon enters below spinal level T6, the axon travels in the fasciculus gracilis, the medial part of the column. If the axon enters above level T6, then it travels in the fasciculus cuneatus, which is lateral to the fasciculus gracilis.
-The primary axon ascends to the lower medulla, where it leaves its fasciculus and synapses with a secondary neuron in one of the dorsal column nuclei: either the nucleus gracilis or the nucleus cuneatus, depending on the pathway it took. The secondary axon leaves its nucleus and passes anteriorly and medially. The collection of secondary axons that do this are known as internal arcuate fibers.
-The internal arcuate fibers decussate and continue ascending as the contralateral medial lemniscus. Secondary axons from the medial lemniscus finally terminate in the ventral posterolateral nucleus of the thalamus, where they synapse with tertiary neurons. The tertiary neurons ascend via the posterior limb of the internal capsule and end in the primary sensory cortex.

Hence, the correct option is C, i.e., Somatic sensory fibers
Note: A dorsal root ganglion or spinal ganglion is a cluster of neurons in a dorsal root of a spinal nerve. The cell bodies of sensory neurons known as first-order neurons are located in the dorsal root ganglia. The dorsal root ganglia develop in the embryo from neural crest cells, not neural tube. Hence, the spinal ganglia can be regarded as a gray matter of the spinal cord that became translocated to the periphery.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




