
The end product of the ornithine cycle is
(a) Ammonia
(b) Uric acid
(c) Urea
(d) CO2
Answer
589.2k+ views
Hint: Ornithine cycle takes place in the liver of ureotelic organisms such as amphibians and mammals. It is the most important means of assimilation of ammonia. Citrulline is an important intermediate generated in this cycle.
Complete answer:
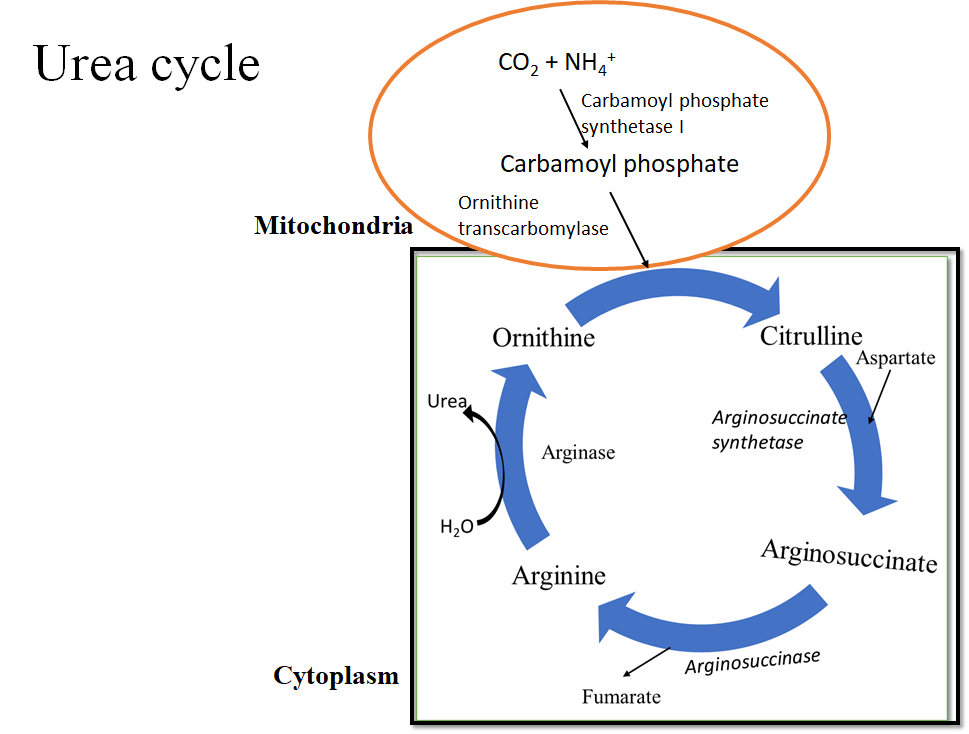
The end product of the ornithine cycle is Urea. The ornithine cycle transforms excess ammonia into urea in the mitochondria of the hepatocytes. The urea cycle is the biochemical pathway that converts nitrogen to urea for excretion from the body.
- Urea as excretory products is eliminated from the body mainly through the urine hence it is seen in ureotelic organisms such as amphibians and mammals.
- Ammonia, that is very harmful to humans, is transformed to urea, which is nontoxic, very soluble, and easily excreted by the kidneys.
- The urea discharged each day by a healthy adult, approximately 30 g, estimates for about 90% of the nitrogenous excretory products.
- Urea is formed in the urea cycle from ammonia and carbon dioxide, and the nitrogen of aspartate.
- The cycle occurs mainly in the mitochondria of the liver cells.
- The urea is produced which then enters the bloodstream and is filtered by the kidneys. It is ultimately excreted in the urine.
- This cycle was the first biochemical cycle to be identified by Hans Krebs and Kurt - Henseleit in 1932, about five years before the revelation of the TCA cycle. This cycle was explained in more detail later on by scientist Ratner and Cohen.
So, the correct answer is “Urea ”.
Note: In rare disease, genetic defects in the enzymes required in the cycle can occur which generally reveal within a few days of birth. The newly born child will generally experience varying periods of emesis and bouts of lethargy. Ultimately the newborn may slip into a coma and evolve into brain damage.
Complete answer:
The end product of the ornithine cycle is Urea. The ornithine cycle transforms excess ammonia into urea in the mitochondria of the hepatocytes. The urea cycle is the biochemical pathway that converts nitrogen to urea for excretion from the body.
- Urea as excretory products is eliminated from the body mainly through the urine hence it is seen in ureotelic organisms such as amphibians and mammals.
- Ammonia, that is very harmful to humans, is transformed to urea, which is nontoxic, very soluble, and easily excreted by the kidneys.
- The urea discharged each day by a healthy adult, approximately 30 g, estimates for about 90% of the nitrogenous excretory products.
- Urea is formed in the urea cycle from ammonia and carbon dioxide, and the nitrogen of aspartate.
- The cycle occurs mainly in the mitochondria of the liver cells.
- The urea is produced which then enters the bloodstream and is filtered by the kidneys. It is ultimately excreted in the urine.
- This cycle was the first biochemical cycle to be identified by Hans Krebs and Kurt - Henseleit in 1932, about five years before the revelation of the TCA cycle. This cycle was explained in more detail later on by scientist Ratner and Cohen.

So, the correct answer is “Urea ”.
Note: In rare disease, genetic defects in the enzymes required in the cycle can occur which generally reveal within a few days of birth. The newly born child will generally experience varying periods of emesis and bouts of lethargy. Ultimately the newborn may slip into a coma and evolve into brain damage.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




