
The enolic form of acetone contains: -
(a)- \[10\sigma -bonds\text{ }2\pi -bonds\text{ }and\text{ }1\text{ }lonepair\]
(b)- \[9\sigma -bonds\text{ }2\pi -bonds\text{ }and\text{ 2 }lonepairs\]
(c)- \[8\sigma -bonds\text{ }2\pi -bonds\text{ }and\text{ 2 }lonepairs\]
(d)- \[9\sigma -bonds\text{ 1}\pi -bond\text{ }and\text{ 2 }lonepairs\]
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: For the enolic form, the oxy group changes to the hydroxyl group. The double bond shifts from carbon-carbon to carbon-oxygen. Enolic form occurs because of a special type of bonding.
Complete step by step answer:
In simple aldehydes and ketones like acetaldehyde, acetone, etc., the amount of enolic form is negligibly small. However, if the enolic form is stabilized by intramolecular hydrogen bonding or resonance, the amount of enolic form is much greater than the keto form.
In acetone, the enolic form is stabilized by intramolecular hydrogen-bonding.
The formula of acetone is \[C{{H}_{3}}-CO-C{{H}_{3}}\]
It is the ketonic form.
The formula of the enolic form of acetone is \[C{{H}_{2}}=C(OH)-C{{H}_{3}}\].
The occurrence of keto-enol form is because of tautomerism. It is a special kind of functional isomerism in which the isomers exist in dynamic equilibrium with each other. It arises due to the migration of a hydrogen atom from one polyvalent atom to the other within the same molecule with the necessary rearrangement of linkages. The isomers obtained are called tautomers.
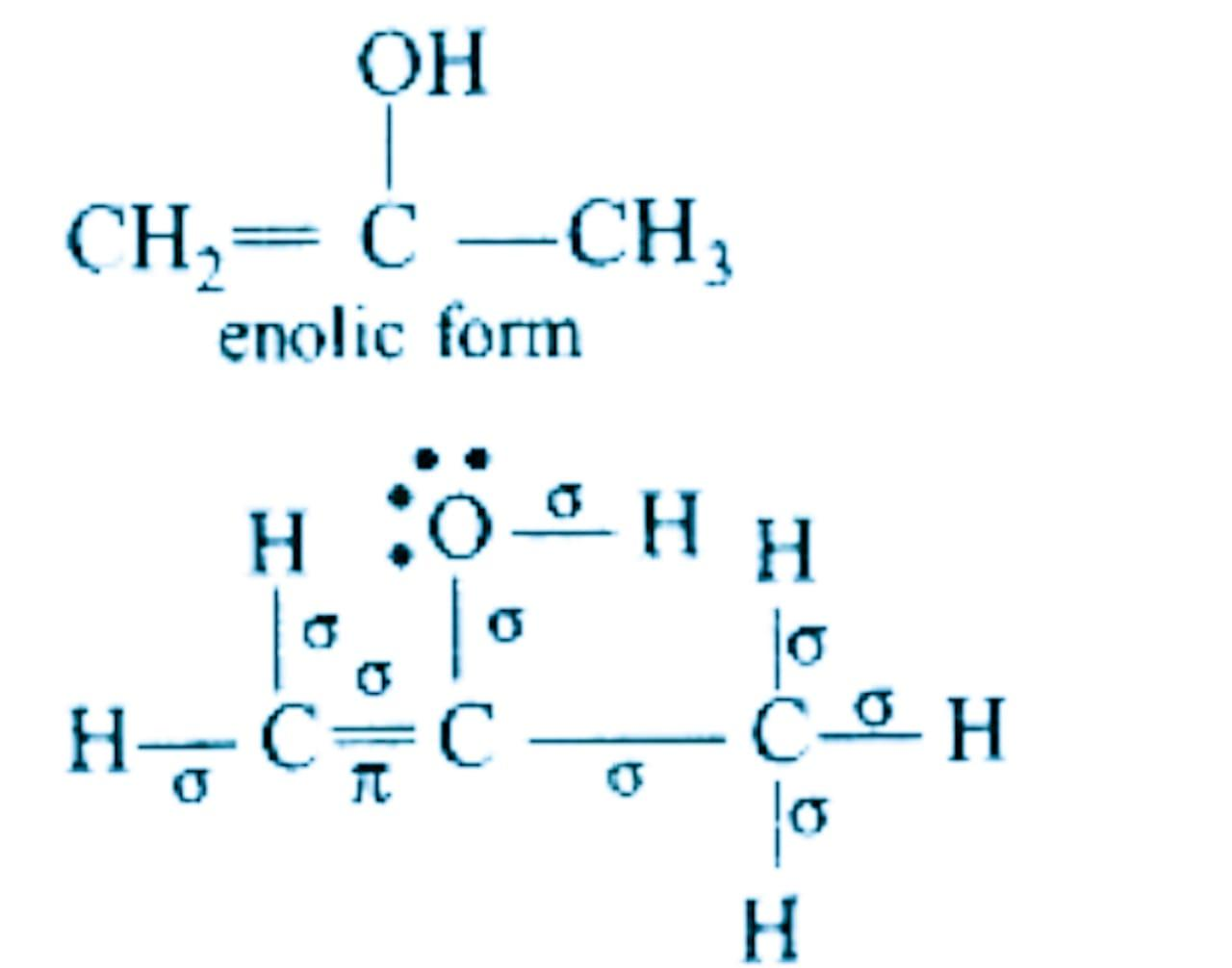
In the compound above there are \[9\sigma -bonds\].
There is \[\text{1}\pi -bond\], which has shifted from carbon-oxygen double bond in keto form to carbon-carbon double in enol form.
There are 2 lone pairs on the oxygen atom.
Hence, the correct option is (d)- \[9\sigma -bonds\text{ 1}\pi -bond\text{ }and\text{ 2 }lonepairs\].
Note: You may get confused between ketonic and enolic form. While converting ketonic to enolic form or vice-versa the valency of each atom should be checked and completed, to avoid the mistake.
Complete step by step answer:
In simple aldehydes and ketones like acetaldehyde, acetone, etc., the amount of enolic form is negligibly small. However, if the enolic form is stabilized by intramolecular hydrogen bonding or resonance, the amount of enolic form is much greater than the keto form.
In acetone, the enolic form is stabilized by intramolecular hydrogen-bonding.
The formula of acetone is \[C{{H}_{3}}-CO-C{{H}_{3}}\]
It is the ketonic form.
The formula of the enolic form of acetone is \[C{{H}_{2}}=C(OH)-C{{H}_{3}}\].
The occurrence of keto-enol form is because of tautomerism. It is a special kind of functional isomerism in which the isomers exist in dynamic equilibrium with each other. It arises due to the migration of a hydrogen atom from one polyvalent atom to the other within the same molecule with the necessary rearrangement of linkages. The isomers obtained are called tautomers.

In the compound above there are \[9\sigma -bonds\].
There is \[\text{1}\pi -bond\], which has shifted from carbon-oxygen double bond in keto form to carbon-carbon double in enol form.
There are 2 lone pairs on the oxygen atom.
Hence, the correct option is (d)- \[9\sigma -bonds\text{ 1}\pi -bond\text{ }and\text{ 2 }lonepairs\].
Note: You may get confused between ketonic and enolic form. While converting ketonic to enolic form or vice-versa the valency of each atom should be checked and completed, to avoid the mistake.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




