
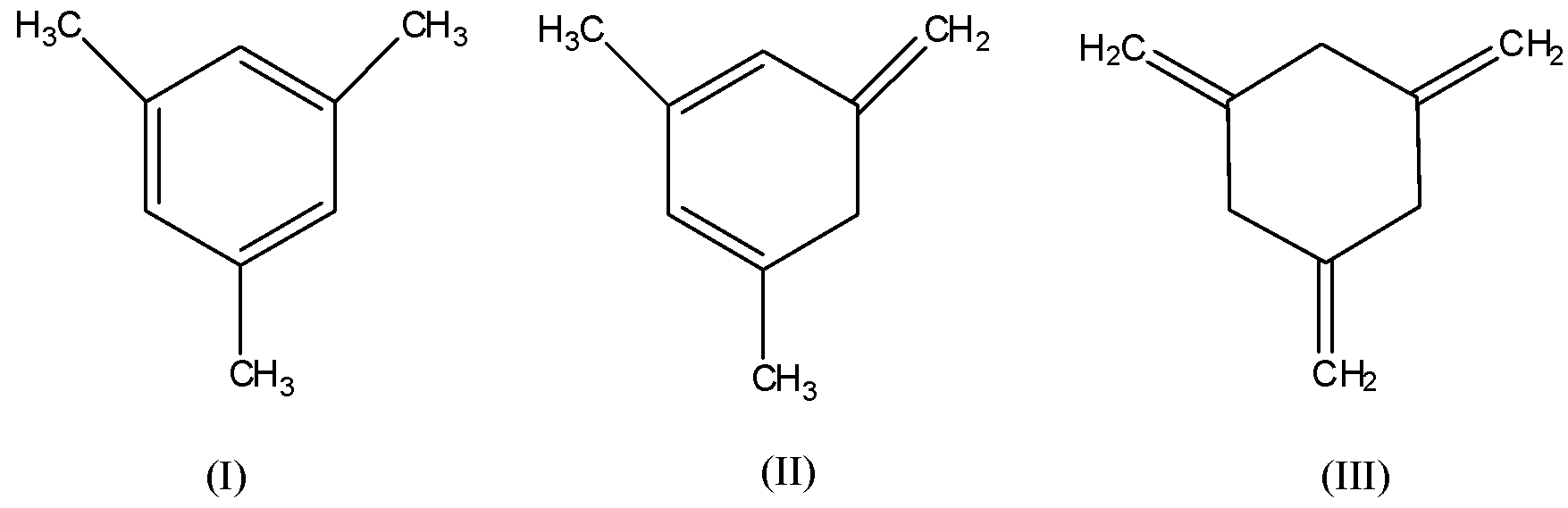
The enthalpy of hydrogenation of those compounds will be in the order as:
A) II > III > I
B) II > I > III
C) I > II > III
D) III > II > I

Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: Enthalpy of hydrogenation is a measure of the stability of carbon-carbon double bonds. It is defined as the enthalpy change when one mole of an unsaturated compound reacts with an excess of hydrogen to become a fully saturated compound. Order of enthalpy of hydrogenation is reverse to the order of stability of alkenes.
Complete answer:
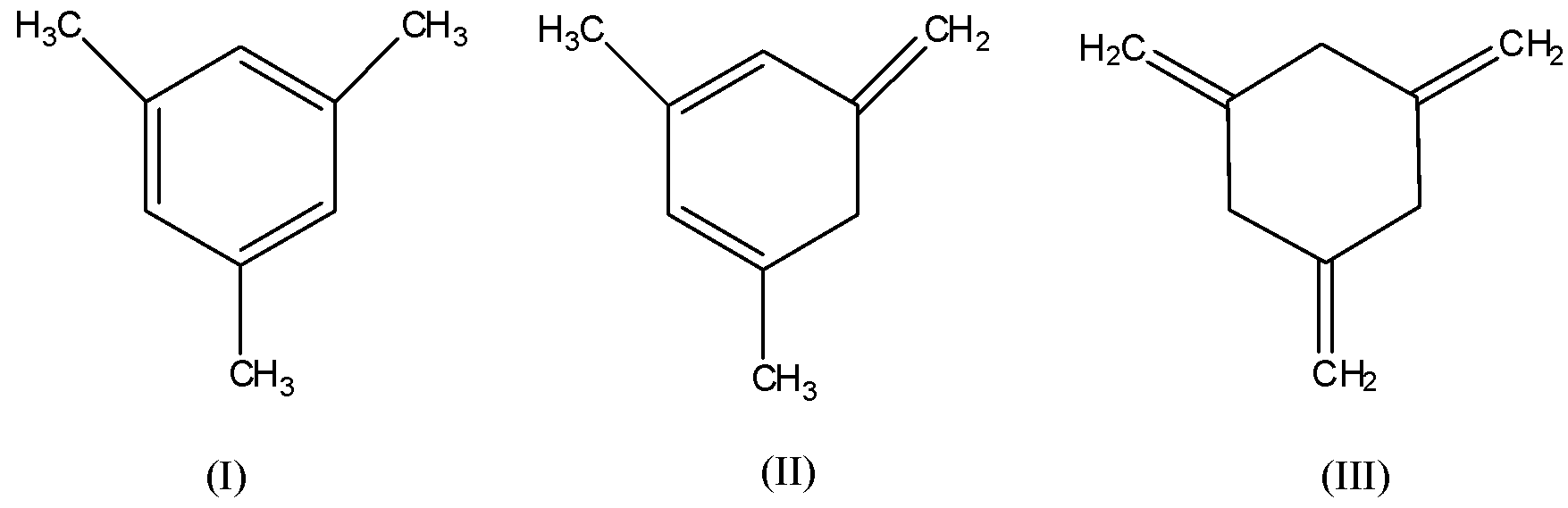
The phenomenon of addition of hydrogen to the double bonds that is, in unsaturated compounds to convert them into saturated compounds is known as hydrogenation. Enthalpy of hydrogenation is the enthalpy change when one mole of an unsaturated compound reacts with an excess of hydrogen to become a fully saturated compound at atmospheric pressure and room temperature. It is used to compare the stability of pi-bonded molecules. Given all the three structures are pi-bonded molecules and they are as follows:
Mathematically, heat of hydrogenation is inversely proportional to the stability of unsaturated compounds as:
${\text{Heat of hydrogenation }} \propto \dfrac{1}{{{\text{Stability of unsaturated compound}}}}$
It means if the compound which is most stable has the lowest heat of hydrogenation and the compound which is least stable has the highest heat of hydrogenation.
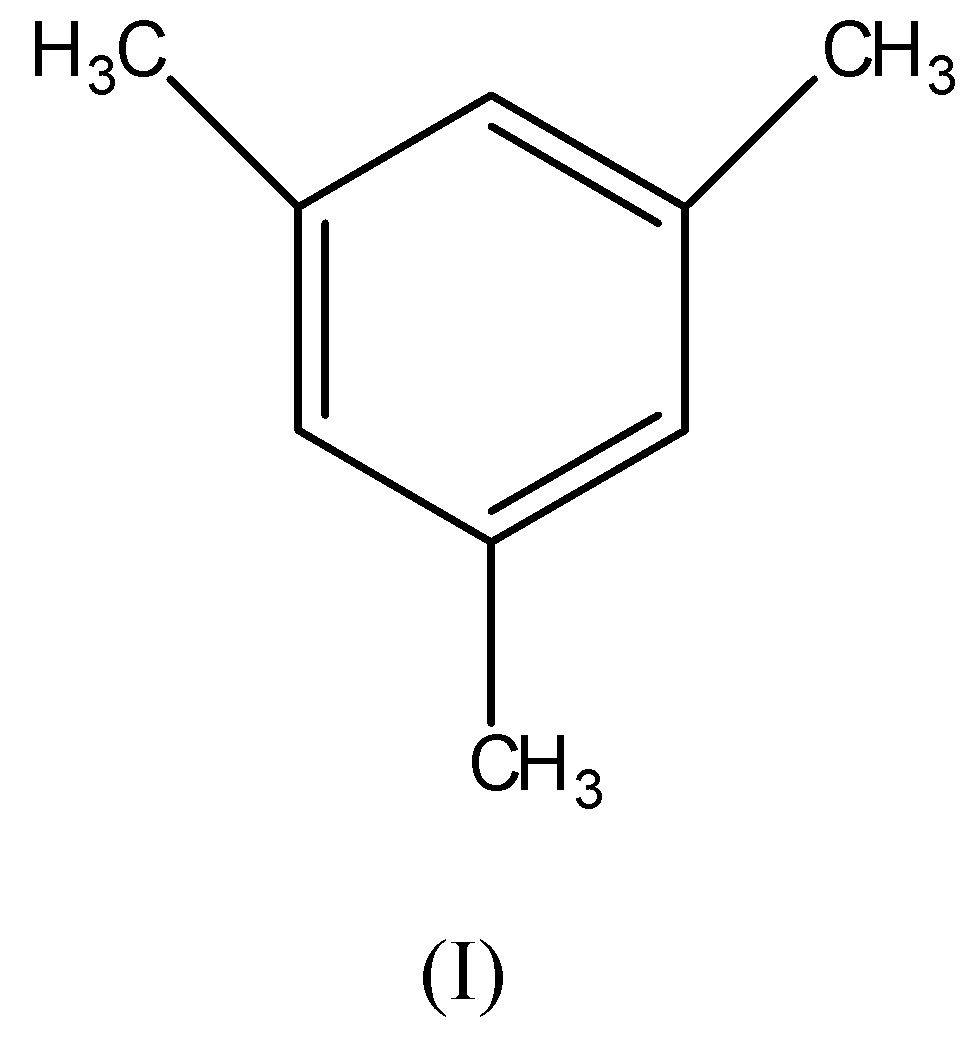
From the given compounds, compound (I) is most stable due to aromatic character. Its pi-bonds are in conjugation with each other in the ring and hence, the conjugation makes the compound stable.
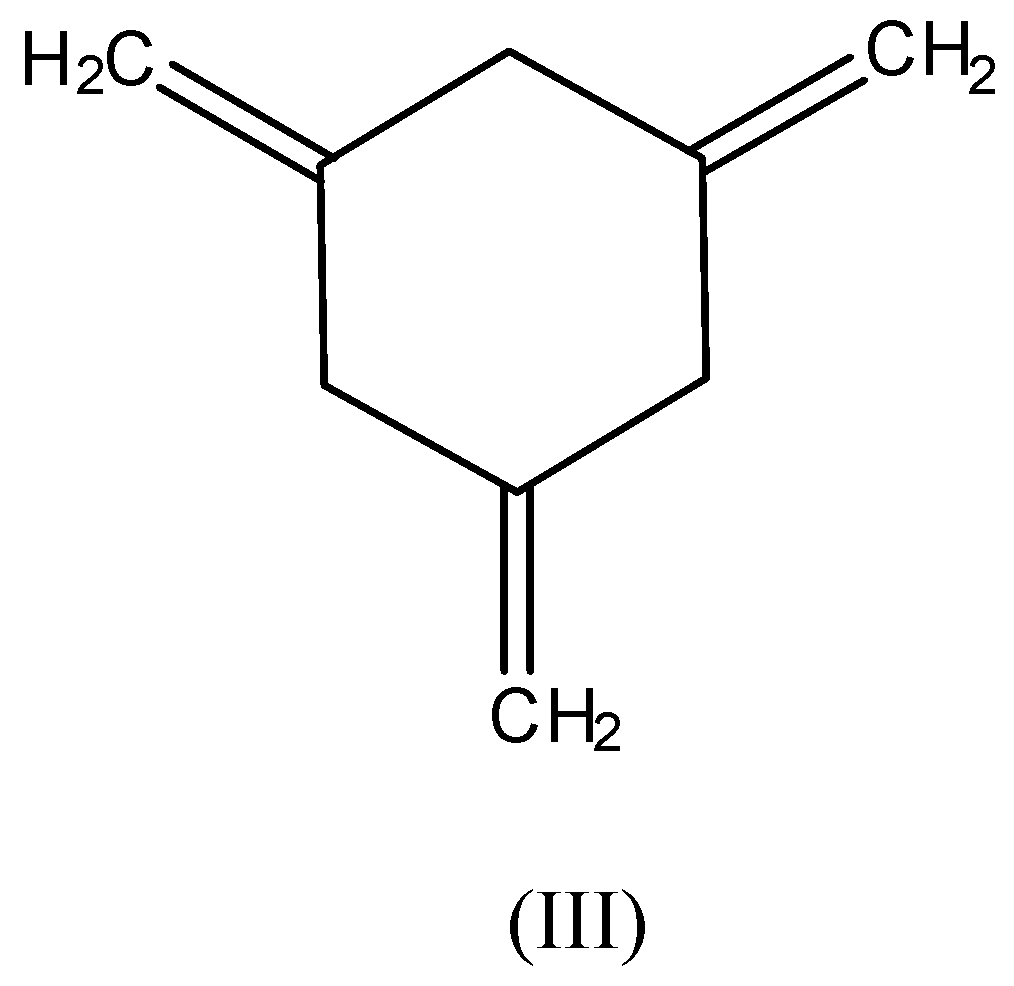
The compound (III) is least stable as no resonance is present there. All the pi-bonds are outside the ring hence, no conjugation of pi-bonds.
Hence, stability of compound (II) will be in between that of compound (I) and (III).
Therefore, order of stability of compounds: I > II > III
Hence, order of enthalpy of hydrogenation: III > II > I
Thus, option D is correct.
Note:
During the hydrogenation process, strong $\sigma $-bonds formed at the cost of breaking weak $\pi $-bonds. Thus, energy is released to the surroundings during the process. Hence, the hydrogenation process is exothermic in nature and enthalpy of hydrogenation has a negative value.
Complete answer:
The phenomenon of addition of hydrogen to the double bonds that is, in unsaturated compounds to convert them into saturated compounds is known as hydrogenation. Enthalpy of hydrogenation is the enthalpy change when one mole of an unsaturated compound reacts with an excess of hydrogen to become a fully saturated compound at atmospheric pressure and room temperature. It is used to compare the stability of pi-bonded molecules. Given all the three structures are pi-bonded molecules and they are as follows:

Mathematically, heat of hydrogenation is inversely proportional to the stability of unsaturated compounds as:
${\text{Heat of hydrogenation }} \propto \dfrac{1}{{{\text{Stability of unsaturated compound}}}}$
It means if the compound which is most stable has the lowest heat of hydrogenation and the compound which is least stable has the highest heat of hydrogenation.

From the given compounds, compound (I) is most stable due to aromatic character. Its pi-bonds are in conjugation with each other in the ring and hence, the conjugation makes the compound stable.

The compound (III) is least stable as no resonance is present there. All the pi-bonds are outside the ring hence, no conjugation of pi-bonds.
Hence, stability of compound (II) will be in between that of compound (I) and (III).
Therefore, order of stability of compounds: I > II > III
Hence, order of enthalpy of hydrogenation: III > II > I
Thus, option D is correct.
Note:
During the hydrogenation process, strong $\sigma $-bonds formed at the cost of breaking weak $\pi $-bonds. Thus, energy is released to the surroundings during the process. Hence, the hydrogenation process is exothermic in nature and enthalpy of hydrogenation has a negative value.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




