
The enzyme nitrogenase is a
(a) Cu-Fe protein
(b) Ni-Fe protein
(c) Mo-Fe protein
(d) Ni-Cu protein
Answer
582k+ views
Hint: The enzyme nitrogenase is present in prokaryotes that can fix nitrogen in higher plants. It consists of a cofactor with two elements which makes up the site of nitrogen fixation. One of the elements is also a component of chlorophyll.
Complete answer:
Nitrogen-fixing bacteria convert atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia using the enzyme nitrogenase complex, which is the primary enzyme encoded by the nif genes
The nitrogenase enzyme is a Mo-Fe protein and catalyzes the conversion of atmospheric nitrogen to ammonia which is the first stable product of nitrogen fixation. As the enzyme nitrogenase is extremely sensitive to molecular oxygen, therefore, the root nodules of bacteria have adaptations that ensure that the enzyme is protected from oxygen. To protect these enzymes, the nodules contain an oxygen scavenger called leghaemoglobin.
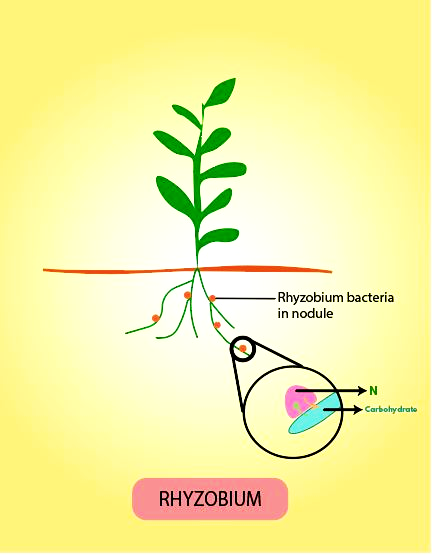
Additional Information: Species of rod-shaped bacteria Rhizobium form an endosymbiotic nitrogen-fixing association with roots of the leguminous plants such as sweet pea, and lentils. The process of symbiotic nitrogen fixation proceed this way:
-Rhizobia multiply and colonize the root hair cells of legumes. The bacteria invade the root hair and enter the cortex via an infection thread.
-In the cortex region of the plant, nodule formation begins. The nodule, thus formed, establishes a direct vascular connection with the host for the exchange of nutrients.
-The enzyme nitrogenase complex performs the important task of catalyzing the conversion of atmospheric nitrogen to ammonia.
-The ammonia is protonated to form ammonium ion, which is used by the plants to synthesize amino acids.
So, the correct answer is ‘Mo-Fe protein.’
Note: -Some prokaryotes fix nitrogen without forming any symbiotic association. They live freely in the soil and include both aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. E.g. Azotobacter (aerobic), Rhodospirillum(Anaerobic).
-The microbe Frankia also produces such nitrogen-fixing nodules on the roots of non-leguminous plants like Alnus.
Complete answer:
Nitrogen-fixing bacteria convert atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia using the enzyme nitrogenase complex, which is the primary enzyme encoded by the nif genes
The nitrogenase enzyme is a Mo-Fe protein and catalyzes the conversion of atmospheric nitrogen to ammonia which is the first stable product of nitrogen fixation. As the enzyme nitrogenase is extremely sensitive to molecular oxygen, therefore, the root nodules of bacteria have adaptations that ensure that the enzyme is protected from oxygen. To protect these enzymes, the nodules contain an oxygen scavenger called leghaemoglobin.
Additional Information: Species of rod-shaped bacteria Rhizobium form an endosymbiotic nitrogen-fixing association with roots of the leguminous plants such as sweet pea, and lentils. The process of symbiotic nitrogen fixation proceed this way:
-Rhizobia multiply and colonize the root hair cells of legumes. The bacteria invade the root hair and enter the cortex via an infection thread.
-In the cortex region of the plant, nodule formation begins. The nodule, thus formed, establishes a direct vascular connection with the host for the exchange of nutrients.
-The enzyme nitrogenase complex performs the important task of catalyzing the conversion of atmospheric nitrogen to ammonia.
-The ammonia is protonated to form ammonium ion, which is used by the plants to synthesize amino acids.
So, the correct answer is ‘Mo-Fe protein.’
Note: -Some prokaryotes fix nitrogen without forming any symbiotic association. They live freely in the soil and include both aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. E.g. Azotobacter (aerobic), Rhodospirillum(Anaerobic).
-The microbe Frankia also produces such nitrogen-fixing nodules on the roots of non-leguminous plants like Alnus.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




