
The equation of motion of a compound pendulum is
A. $\dfrac{{{d^2}x}}{{d{t^2}}} + {\omega ^2}x = 0$
B. $\dfrac{{{d^2}\theta }}{{d{t^2}}} + {\omega ^2}\theta = 0$
C. $F = - kx$
D. $\dfrac{{d\theta }}{{d{t^2}}} + {\omega ^2}\theta = 0$
Answer
595.5k+ views
Hint: A compound pendulum is basically a rigid body allowed to oscillate about a horizontal axis passing through it. So the compound pendulum is almost a simple pendulum but has an angular displacement associated with it. Derive the equation of compound pendulum using necessary conditions for SHM and compare with the options for the right answer.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The conditions of an ideal pendulum cannot be realized in actual practice. So a compound pendulum is used to get rid of most defects caused by the simple pendulum. A compound pendulum consists of a rigid body that can oscillate freely about a horizontal axis passing through it.
Consider a rigid body of any shape and mass m capable of oscillating freely about a horizontal axis passing through it perpendicular to the plane.
Let O be the center of suspension of the body and G its center of gravity vertically below O at a distance l in the position of rest. When the body is displaced through a small angle $\theta $ to the dotted position, the center of gravity is shifted to position G’ and its weight mg acts vertically downwards at G’.
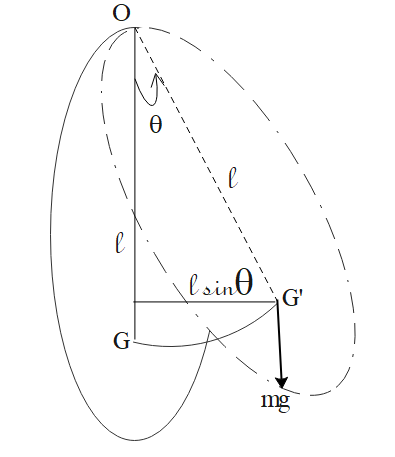
If the pendulum is now released a restoring couple acts on it and brings it back to its initial position. But due to inertia, it overshoots the mark and hence starts oscillating about the mean position.
The moment of the restoring couple or Torque,
$\tau = - mg \times G'A = - mgl\sin \theta \approx - mgl\theta \cdots \cdots \cdots \left( 1 \right)$
Since the angle $\theta $ through which the pendulum is displaced is small so that$\sin \theta \approx \theta $.
This restoring couple gives rise to an angular acceleration$\alpha $ in the pendulum. If $I$is the moment of inertia of the rigid body about aan axis passing through its center of suspension, then restoring couple is given by:
$\tau = I\alpha = I\dfrac{{{d^2}\theta }}{{d{t^2}}} \cdots \cdots \cdots \cdots \left( 2 \right)$
Comparing equation (1) and (2), we get:
$\eqalign{
& I\dfrac{{{d^2}\theta }}{{d{t^2}}} = - mgl\theta \cr
& {\text{or }}\dfrac{{{d^2}\theta }}{{d{t^2}}} = - \dfrac{{mgl}}{I}\theta \cr
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d^2}\theta }}{{d{t^2}}} \propto \theta \cr} $
Clearly, the equation of a compound pendulum is a second order derivative of angular displacement$\theta $.
Therefore, the correct option is B i.e., $\dfrac{{{d^2}\theta }}{{d{t^2}}} + {\omega ^2}\theta = 0$
Note: The center of suspension and center of oscillation of a compound pendulum is interchangeable in nature for a compound pendulum. This can be practically proved using a Kater’s pendulum, which is also known as a reversible pendulum.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The conditions of an ideal pendulum cannot be realized in actual practice. So a compound pendulum is used to get rid of most defects caused by the simple pendulum. A compound pendulum consists of a rigid body that can oscillate freely about a horizontal axis passing through it.
Consider a rigid body of any shape and mass m capable of oscillating freely about a horizontal axis passing through it perpendicular to the plane.
Let O be the center of suspension of the body and G its center of gravity vertically below O at a distance l in the position of rest. When the body is displaced through a small angle $\theta $ to the dotted position, the center of gravity is shifted to position G’ and its weight mg acts vertically downwards at G’.

If the pendulum is now released a restoring couple acts on it and brings it back to its initial position. But due to inertia, it overshoots the mark and hence starts oscillating about the mean position.
The moment of the restoring couple or Torque,
$\tau = - mg \times G'A = - mgl\sin \theta \approx - mgl\theta \cdots \cdots \cdots \left( 1 \right)$
Since the angle $\theta $ through which the pendulum is displaced is small so that$\sin \theta \approx \theta $.
This restoring couple gives rise to an angular acceleration$\alpha $ in the pendulum. If $I$is the moment of inertia of the rigid body about aan axis passing through its center of suspension, then restoring couple is given by:
$\tau = I\alpha = I\dfrac{{{d^2}\theta }}{{d{t^2}}} \cdots \cdots \cdots \cdots \left( 2 \right)$
Comparing equation (1) and (2), we get:
$\eqalign{
& I\dfrac{{{d^2}\theta }}{{d{t^2}}} = - mgl\theta \cr
& {\text{or }}\dfrac{{{d^2}\theta }}{{d{t^2}}} = - \dfrac{{mgl}}{I}\theta \cr
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d^2}\theta }}{{d{t^2}}} \propto \theta \cr} $
Clearly, the equation of a compound pendulum is a second order derivative of angular displacement$\theta $.
Therefore, the correct option is B i.e., $\dfrac{{{d^2}\theta }}{{d{t^2}}} + {\omega ^2}\theta = 0$
Note: The center of suspension and center of oscillation of a compound pendulum is interchangeable in nature for a compound pendulum. This can be practically proved using a Kater’s pendulum, which is also known as a reversible pendulum.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




