
The equation of two sides of a square whose area is 25 square units are $3x - 4y = 0$ and $4x + 3y = 0$ . The equations of the other two sides of the square are
a.$3x - 4y \pm 25 = 0,4x + 3y \pm 25 = 0$
b.$3x - 4y \pm 5 = 0,4x + 3y \pm 5 = 0$
c.$3x - 4y \pm 5 = 0,4x + 3y \pm 25 = 0$
d.None of these
Answer
561.9k+ views
Hint: With the given area we can find the length of the side of the square using $area = {a^2}squints$ and since it’s a square opposite sides are parallel and we know that the equation of parallel lines differ only by a constant .Hence the equation of the lines parallel to the given lines are $3x - 4y + m = 0$ and $4x + 3y + n = 0$ and we can find the distance between parallel lines using formula $d = \dfrac{{c - e}}{{\sqrt {{a^2} + {b^2}} }}$ and equating to 5 we get the value of m and n
Complete step-by-step answer:
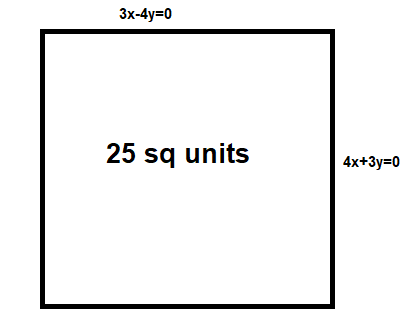
We are given the equations of two sides of the square
They are $3x - 4y = 0$ and $4x + 3y = 0$
We are given the area of the square to be 25 square units
We know the area of a square is given by the formula
$ \Rightarrow area = {a^2}squints$
Where a is the side of the square
Therefore
$
\Rightarrow {a^2} = 25 \\
\Rightarrow a = \pm 5 \\
$
Therefore the side of the square is 5 units
Since it is a square we know that the opposite sides are parallel
We know that the equation of parallel lines differ only by a constant
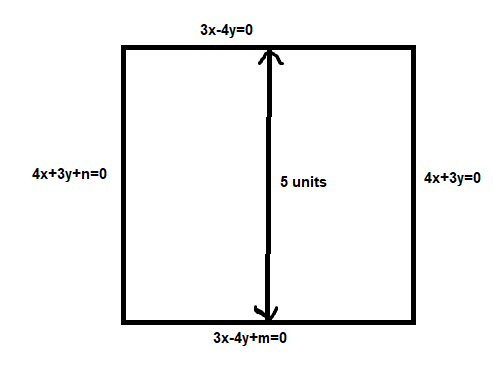
Hence the equation of the lines parallel to the given lines are
$ \Rightarrow 3x - 4y + m = 0$
$ \Rightarrow 4x + 3y + n = 0$
We can find the distance between two parallel lines $ax + by + c = 0$ and $ax + by + e = 0$ using the formula
$ \Rightarrow d = \dfrac{{c - e}}{{\sqrt {{a^2} + {b^2}} }}$
From the square diagram we get that the lines $3x - 4y + m = 0$ and $3x - 4y = 0$
And since the side of the square is 5 units , the distance between these lines is also 5 units
$
\Rightarrow 5 = \dfrac{{m - 0}}{{\sqrt {{3^2} + {4^2}} }} \\
\Rightarrow 5 = \dfrac{m}{{\sqrt {9 + 16} }} = \dfrac{m}{{\sqrt {25} }} \\
\Rightarrow 5 = \dfrac{m}{{ \pm 5}} \\
\Rightarrow m = \pm 25 \\
$
From the square diagram we get that the lines $4x + 3y + n = 0$ and $4x + 3y = 0$
And since the side of the square is 5 units , the distance between these lines is also 5 units
$
\Rightarrow 5 = \dfrac{{n - 0}}{{\sqrt {{4^2} + {3^2}} }} \\
\Rightarrow 5 = \dfrac{n}{{\sqrt {16 + 9} }} = \dfrac{n}{{\sqrt {25} }} \\
\Rightarrow 5 = \dfrac{n}{{ \pm 5}} \\
\Rightarrow n = \pm 25 \\
$
Hence the equation of the other two sides are
$ \Rightarrow 3x - 4y \pm 25 = 0$
$ \Rightarrow 4x + 3y \pm 25 = 0$
Therefore the correct option is a
Note: Lines in a plane that never meet, even if we extend them, are called parallel lines. As they never meet, the distance between the parallel lines remains constant
The slopes of parallel lines are always equal.
Even if these two line segments were extended to infinity, there would never be a point of intersection between the two of them
Complete step-by-step answer:
We are given the equations of two sides of the square
They are $3x - 4y = 0$ and $4x + 3y = 0$
We are given the area of the square to be 25 square units

We know the area of a square is given by the formula
$ \Rightarrow area = {a^2}squints$
Where a is the side of the square
Therefore
$
\Rightarrow {a^2} = 25 \\
\Rightarrow a = \pm 5 \\
$
Therefore the side of the square is 5 units
Since it is a square we know that the opposite sides are parallel
We know that the equation of parallel lines differ only by a constant
Hence the equation of the lines parallel to the given lines are
$ \Rightarrow 3x - 4y + m = 0$
$ \Rightarrow 4x + 3y + n = 0$

We can find the distance between two parallel lines $ax + by + c = 0$ and $ax + by + e = 0$ using the formula
$ \Rightarrow d = \dfrac{{c - e}}{{\sqrt {{a^2} + {b^2}} }}$
From the square diagram we get that the lines $3x - 4y + m = 0$ and $3x - 4y = 0$
And since the side of the square is 5 units , the distance between these lines is also 5 units
$
\Rightarrow 5 = \dfrac{{m - 0}}{{\sqrt {{3^2} + {4^2}} }} \\
\Rightarrow 5 = \dfrac{m}{{\sqrt {9 + 16} }} = \dfrac{m}{{\sqrt {25} }} \\
\Rightarrow 5 = \dfrac{m}{{ \pm 5}} \\
\Rightarrow m = \pm 25 \\
$
From the square diagram we get that the lines $4x + 3y + n = 0$ and $4x + 3y = 0$
And since the side of the square is 5 units , the distance between these lines is also 5 units
$
\Rightarrow 5 = \dfrac{{n - 0}}{{\sqrt {{4^2} + {3^2}} }} \\
\Rightarrow 5 = \dfrac{n}{{\sqrt {16 + 9} }} = \dfrac{n}{{\sqrt {25} }} \\
\Rightarrow 5 = \dfrac{n}{{ \pm 5}} \\
\Rightarrow n = \pm 25 \\
$
Hence the equation of the other two sides are
$ \Rightarrow 3x - 4y \pm 25 = 0$
$ \Rightarrow 4x + 3y \pm 25 = 0$
Therefore the correct option is a
Note: Lines in a plane that never meet, even if we extend them, are called parallel lines. As they never meet, the distance between the parallel lines remains constant
The slopes of parallel lines are always equal.
Even if these two line segments were extended to infinity, there would never be a point of intersection between the two of them
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




