
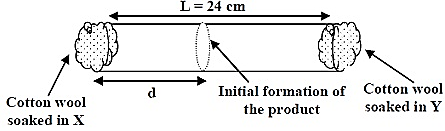
The experimental value of d is found to be smaller than the estimate obtained using Graham's law. This is due to the:
A. Larger mean free path for X as compared to that of Y
B. Larger mean free path for Y as compared to that of X
C. increased collision frequency of Y with the inert gas as compared to that X with the inert gas.
D. increased collision frequency of X with the inert gas as compared to that of Y with inert.

Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: For this problem, we have to study Graham's law of diffusion and the relation between the mean free path and collision frequency. After which we can determine the reason behind the small value of d.
Complete step by step answer:
- In the given question, we have to explain the reason behind the smaller value of d by using Graham's law of diffusion.
- Now, we know that according to Graham's law of diffusion, the rate of effusion of the gases of the two gases has the inverse effect on the square root of the molecular mass of the gas.
- Also, we know that collision frequency is defined as the average rate of the collision of between two reactant molecules per unit time in a given volume of the container.
- So, when the molecules are present close to each other, the rate of the collision frequency increases.
- The increase in the collision frequency of the X molecules occurs with the inert gas molecules due to which the mean free path decreases.
- Now, due to the decreases in the mean free path of the molecules, the molecular speed of the gaseous molecules also decreases.
- The molecular decreases because the distance required for the collision also decreases.
- Thus, the value of d is smaller as compared to that of the Y.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: In the problem, the mean free path of the gas particles is defined as the average distance travelled that can be travelled by the colliding particles. The temperature affects the mean free path because when the temperature increases the kinetic energy of the molecules also increases due to which the collision frequency will also increase.
Complete step by step answer:
- In the given question, we have to explain the reason behind the smaller value of d by using Graham's law of diffusion.
- Now, we know that according to Graham's law of diffusion, the rate of effusion of the gases of the two gases has the inverse effect on the square root of the molecular mass of the gas.
- Also, we know that collision frequency is defined as the average rate of the collision of between two reactant molecules per unit time in a given volume of the container.
- So, when the molecules are present close to each other, the rate of the collision frequency increases.
- The increase in the collision frequency of the X molecules occurs with the inert gas molecules due to which the mean free path decreases.
- Now, due to the decreases in the mean free path of the molecules, the molecular speed of the gaseous molecules also decreases.
- The molecular decreases because the distance required for the collision also decreases.
- Thus, the value of d is smaller as compared to that of the Y.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: In the problem, the mean free path of the gas particles is defined as the average distance travelled that can be travelled by the colliding particles. The temperature affects the mean free path because when the temperature increases the kinetic energy of the molecules also increases due to which the collision frequency will also increase.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




