
The eye rotates in the orbit by -
(a)6 muscles
(b)3 muscles
(c)4 muscles
(d)5 muscles
Answer
579.9k+ views
Hint: The eyes are the visual organs of the body. We use them to see objects around us. The eyes move in various directions in order to focus on an object or a scene perfectly. Their voluntary and involuntary movement occurs due to muscles. These muscles help the eye to move in various directions.
Complete answer:
There are six muscles that are present in the eye orbit, also known as the socket or cavity, that are responsible for the rotation of the eye. They are known as extraocular muscles.
- The muscles are lateral, medial, inferior, and superior rectus muscles that move the eye outwards, inwards, downwards, and upwards, and the inferior and superior oblique muscles that help in adjusting the movements.
Additional Information: - These muscles form the extraocular anatomy of the eye. The anatomy consists of the extraocular muscles, conjunctiva, lacrimal gland, Tenon’s capsule, sclera, and cornea.
- The nerves that are involved in the movement of the muscles are trochlear, oculomotor, and abducens. The nuclei of these nerves are present on the brain stem.
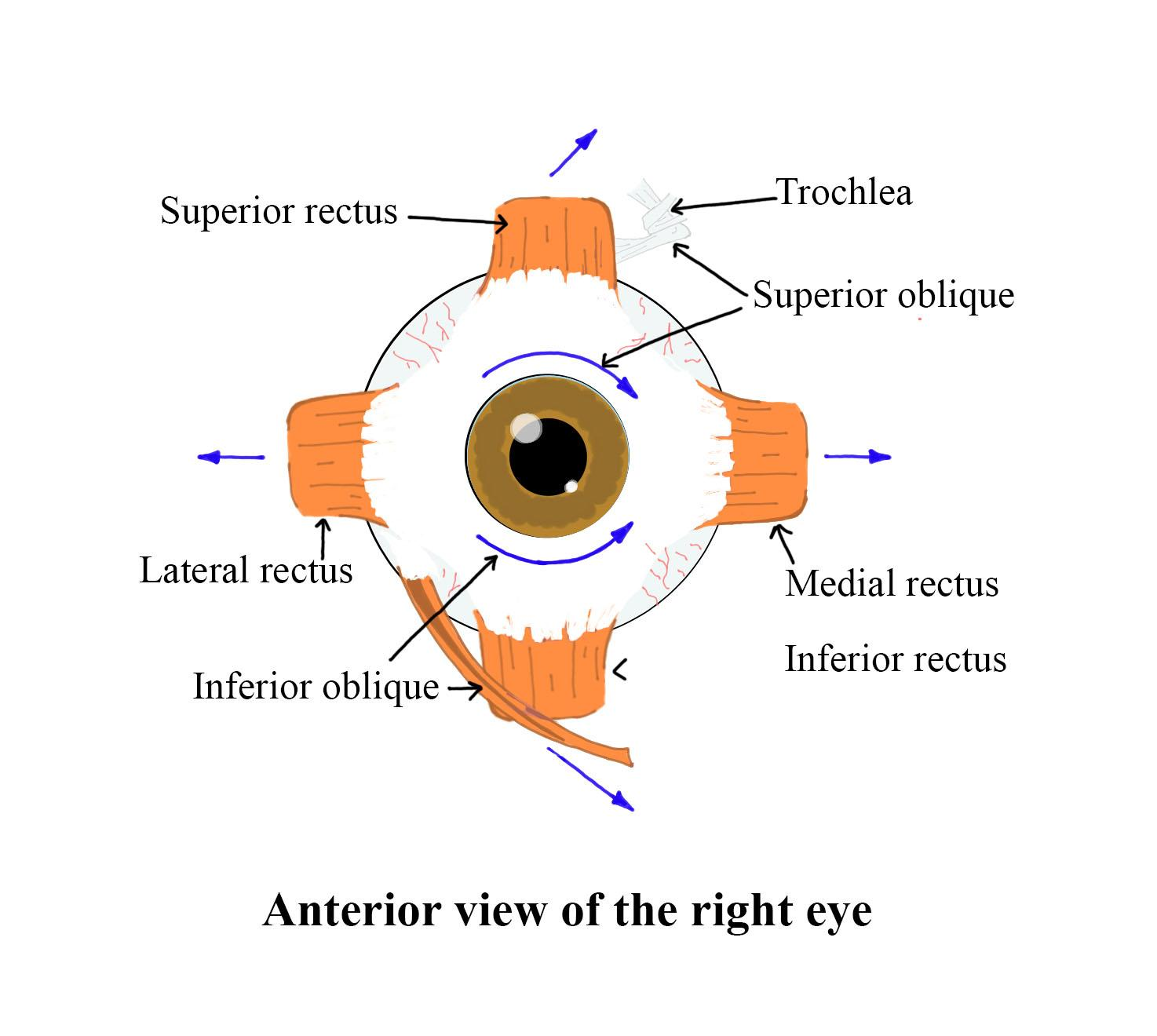
So, the correct answer is ‘6 muscles’.
Note: The intraocular anatomy of the eye consists of the anterior chamber, iris, pupil, lens, ciliary body, vitreous, retina, photoreceptors, macula, retinal pigment epithelium, choroid, uveal tract, optic nerve, optic chiasm, and visual cortex.
- The involuntary movement of the eye is controlled by the vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR). It is a reflex that stabilizes the gaze during head movement with eye movement as the vestibular system is activated.
- The weakness of eye muscles is known as ophthalmoplegia.
Complete answer:
There are six muscles that are present in the eye orbit, also known as the socket or cavity, that are responsible for the rotation of the eye. They are known as extraocular muscles.
- The muscles are lateral, medial, inferior, and superior rectus muscles that move the eye outwards, inwards, downwards, and upwards, and the inferior and superior oblique muscles that help in adjusting the movements.
Additional Information: - These muscles form the extraocular anatomy of the eye. The anatomy consists of the extraocular muscles, conjunctiva, lacrimal gland, Tenon’s capsule, sclera, and cornea.
- The nerves that are involved in the movement of the muscles are trochlear, oculomotor, and abducens. The nuclei of these nerves are present on the brain stem.

So, the correct answer is ‘6 muscles’.
Note: The intraocular anatomy of the eye consists of the anterior chamber, iris, pupil, lens, ciliary body, vitreous, retina, photoreceptors, macula, retinal pigment epithelium, choroid, uveal tract, optic nerve, optic chiasm, and visual cortex.
- The involuntary movement of the eye is controlled by the vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR). It is a reflex that stabilizes the gaze during head movement with eye movement as the vestibular system is activated.
- The weakness of eye muscles is known as ophthalmoplegia.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




