
The figure given below represents an experiment to demonstrate a particular aspect of photosynthesis. The alphabet ‘A’ represents a certain condition inside the flask.
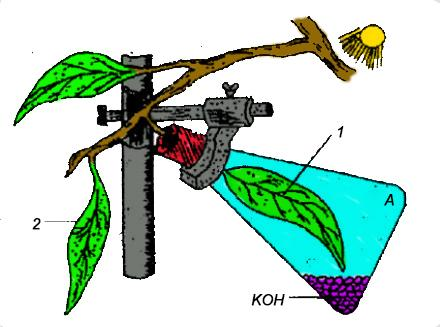
(i) What is the aim of the experiment?
(ii) Identify the special condition inside the flask.
(iii) Name an alternative chemical that can be used instead of KOH.
(iv) In what manner do leaves 1 and 2 differ at the end of the starch test?

Answer
572.7k+ views
Hint: The purpose of the experiment is to define the need for a greenhouse gas for the photosynthesis process. Inside the flask, the unique state is the lack of a compound whose solid shape is called dry ice. As an alternate chemical for KOH, carbonate products, caustic soda, etc. may be used.
Complete answer:
(i) The purpose of the experiment is to demonstrate the requirement of $C{ O }_{ 2 }$ for the photosynthesis process.
(ii) In the flask, the unique condition is that there is no $C{ O }_{ 2 }$ in the air within the flask as all carbon dioxide is removed by the KOH. Thus, the leaf does not receive ambient $C{ O }_{ 2 }$ within the flask.
(iii) The alternative chemicals that can be used instead of KOH are soda lime (NaOH & $Ca\left( { OH }_{ 2 } \right) $) , CaO (limestone) , and potassium pyrogallate.
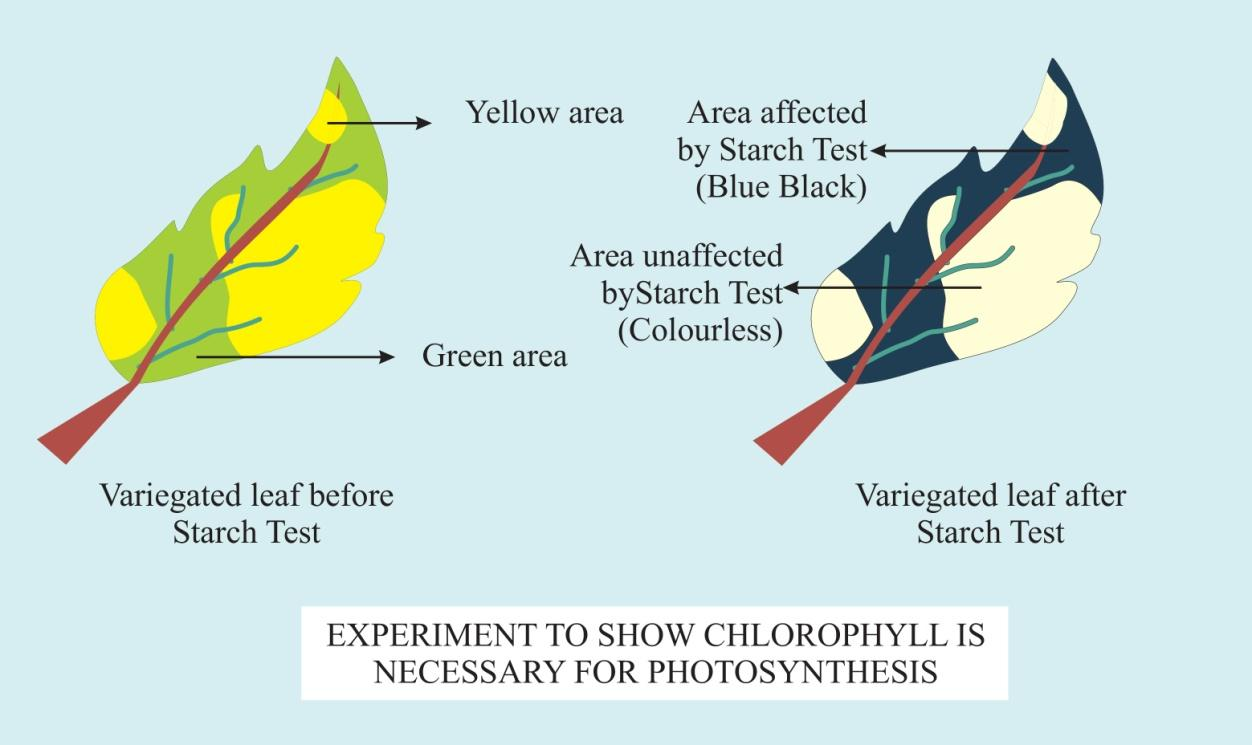
(iv) The absence of $C{ O }_{ 2 }$ inside the flask does not allow the starch to be produced by leaf 1, and at the end of the starch test, the leaf does not turn black while leaf 2 turns black.
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound that consists of one carbon and two atoms of oxygen. At a low concentration, it is found in the Earth's atmosphere and functions as a greenhouse gas, and its solid-state is called dry ice.
Limestone is a carbonate sedimentary rock consisting primarily of skeletal fragments of certain marine organisms. Example: Corals. The minerals calcite and aragonite, which are various crystal types of calcium carbonate $\left( CaC{ O }_{ 3 } \right) $, are its main materials.
Sodium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula NaOH, also known as lye and caustic soda.
The iodine-starch test is a chemical reaction used to test for iodine or for the presence of starch.
Note: Photosynthesis is the process used by plants, algae, and some bacteria to harness energy from sunlight and turn it into chemical energy. The mechanism by which green plants and many other species turn light energy into chemical energy is photosynthesis. Light energy is consumed and used during photosynthesis in green plants to turn water, carbon dioxide, and minerals into oxygen and energy-rich organic compounds.
Complete answer:
(i) The purpose of the experiment is to demonstrate the requirement of $C{ O }_{ 2 }$ for the photosynthesis process.
(ii) In the flask, the unique condition is that there is no $C{ O }_{ 2 }$ in the air within the flask as all carbon dioxide is removed by the KOH. Thus, the leaf does not receive ambient $C{ O }_{ 2 }$ within the flask.
(iii) The alternative chemicals that can be used instead of KOH are soda lime (NaOH & $Ca\left( { OH }_{ 2 } \right) $) , CaO (limestone) , and potassium pyrogallate.
(iv) The absence of $C{ O }_{ 2 }$ inside the flask does not allow the starch to be produced by leaf 1, and at the end of the starch test, the leaf does not turn black while leaf 2 turns black.


Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound that consists of one carbon and two atoms of oxygen. At a low concentration, it is found in the Earth's atmosphere and functions as a greenhouse gas, and its solid-state is called dry ice.
Limestone is a carbonate sedimentary rock consisting primarily of skeletal fragments of certain marine organisms. Example: Corals. The minerals calcite and aragonite, which are various crystal types of calcium carbonate $\left( CaC{ O }_{ 3 } \right) $, are its main materials.
Sodium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula NaOH, also known as lye and caustic soda.
The iodine-starch test is a chemical reaction used to test for iodine or for the presence of starch.
Note: Photosynthesis is the process used by plants, algae, and some bacteria to harness energy from sunlight and turn it into chemical energy. The mechanism by which green plants and many other species turn light energy into chemical energy is photosynthesis. Light energy is consumed and used during photosynthesis in green plants to turn water, carbon dioxide, and minerals into oxygen and energy-rich organic compounds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




