
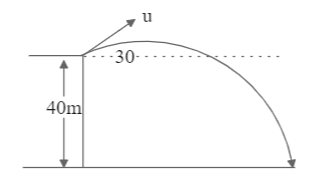
The figure shows a projectile thrown with speed $u = 20m/s$ at an angle of 30 degrees with horizontal from the top of a building 40 m high. Then, calculate the horizontal range of the projectile.
(A) $20\sqrt 3 $ m
(B) $40\sqrt 3 $ m
(C) 40 m
(D) 20 m

Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint:
Projectile motion occurs when an object is thrown with some velocity into the air. For this kind of motion, the components of the velocity with which the object is thrown determine the distance travelled in the horizontal and vertical direction, alike.
Formula used: $R = u\cos \theta t$, where R is the horizontal range covered by the object thrown with velocity u and angle $\theta $, in time t.
Complete step by step answer:
We have an object that is thrown from some height, making an angle with the horizontal. This object will eventually come down due to the influence of the gravitational acceleration, and we are required to find this distance.
The data that is provided to us includes:
Speed $u = 20m/s$
Height in vertical direction $s = - 40m$ [As distances measured downwards have a negative sign]
Angle made with the horizontal $\theta = 30^\circ $
We know that distance in vertical direction for projectile motion is given as:
$\Rightarrow s = {u_v}t - \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}$ [Eq. 1]
The vertical component of the speed will be given by:
$\Rightarrow {u_v} = u\sin \theta = 20\sin 30 = 10$m/s
Substituting this in Eq. 1:
$\Rightarrow - 40 = 10t - \dfrac{1}{2}10{t^2} = 10t - 5{t^2}$
$\Rightarrow {t^2} - 2t - 8 = 0$
We take out commons to solve this quadratic equation as:
$\Rightarrow {t^2} - 4t + 2t + 8 = 0$
$\Rightarrow t(t - 4) + 2(t - 4) = 0$
Solving for time t, we get:
$\Rightarrow (t + 2)(t - 4) = 0$
Hence, $t = 4$ as time cannot be negative.
Now, we know that the horizontal range is given as:
$\Rightarrow R = u\cos \theta t$
So, inputting the values:
$\Rightarrow R = 20\cos 30 \times 4 = 80 \times \dfrac{{\sqrt3 }}{2} = 40\sqrt 3 m$
Hence, the correct answer is option (B).
Note:
The objects that experience projectile motion have a constant velocity in the horizontal direction, but a constantly changing velocity in the vertical direction. This combination results in the trajectory similar to that of a parabola. Projectile motion is mostly in sports like golf, baseball, cricket as the ball is hit into the air.
Projectile motion occurs when an object is thrown with some velocity into the air. For this kind of motion, the components of the velocity with which the object is thrown determine the distance travelled in the horizontal and vertical direction, alike.
Formula used: $R = u\cos \theta t$, where R is the horizontal range covered by the object thrown with velocity u and angle $\theta $, in time t.
Complete step by step answer:
We have an object that is thrown from some height, making an angle with the horizontal. This object will eventually come down due to the influence of the gravitational acceleration, and we are required to find this distance.
The data that is provided to us includes:
Speed $u = 20m/s$
Height in vertical direction $s = - 40m$ [As distances measured downwards have a negative sign]
Angle made with the horizontal $\theta = 30^\circ $
We know that distance in vertical direction for projectile motion is given as:
$\Rightarrow s = {u_v}t - \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}$ [Eq. 1]
The vertical component of the speed will be given by:
$\Rightarrow {u_v} = u\sin \theta = 20\sin 30 = 10$m/s
Substituting this in Eq. 1:
$\Rightarrow - 40 = 10t - \dfrac{1}{2}10{t^2} = 10t - 5{t^2}$
$\Rightarrow {t^2} - 2t - 8 = 0$
We take out commons to solve this quadratic equation as:
$\Rightarrow {t^2} - 4t + 2t + 8 = 0$
$\Rightarrow t(t - 4) + 2(t - 4) = 0$
Solving for time t, we get:
$\Rightarrow (t + 2)(t - 4) = 0$
Hence, $t = 4$ as time cannot be negative.
Now, we know that the horizontal range is given as:
$\Rightarrow R = u\cos \theta t$
So, inputting the values:
$\Rightarrow R = 20\cos 30 \times 4 = 80 \times \dfrac{{\sqrt3 }}{2} = 40\sqrt 3 m$
Hence, the correct answer is option (B).
Note:
The objects that experience projectile motion have a constant velocity in the horizontal direction, but a constantly changing velocity in the vertical direction. This combination results in the trajectory similar to that of a parabola. Projectile motion is mostly in sports like golf, baseball, cricket as the ball is hit into the air.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




