
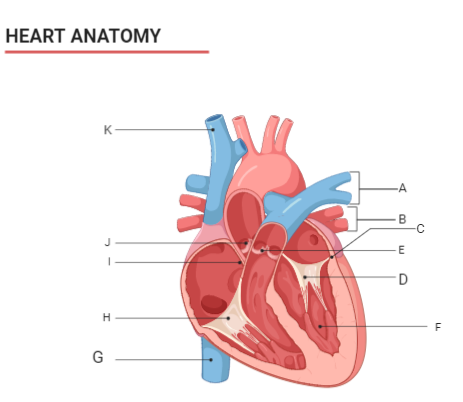
The figure shows the vertical section of the human heart identifying the parts A to K.

Answer
555k+ views
Hint: The heart is particularly critical in the human body. It's the same
The pulmonary system's chief organ. A very complex muscle bag divided into a structurally complex human heart is a septum. It is found in the center of our chest between the lungs in the thoracic upper chest. The human heart is an organ that pumps blood through the body, transfers oxygen and nutrients across the body, eliminates carbon dioxide and other waste.
Complete step by step answer:
A-To oxygenate and expel excess carbon dioxide, the pulmonary artery brings oxygen-depleted blood to the lungs (see pulmonary circulation).
B-The veins that transfer oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart are the pulmonary veins. The four major pulmonary veins, two from each lung that flow into the left atrium of the heart, are the largest pulmonary veins.
C-One of the four chambers of the heart, positioned on the left posterior side, is the left atrium. Its main functions are to serve as a holding chamber for the return of blood from the lungs and to act as a pump to bring blood to other areas of the heart.
D-The pulmonary valve (sometimes referred to as the pulmonary valve) is the heart's semi-lunar valve between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery and has three cusps.
E-The bicuspid valve is also known as the mitral valve. This is one of four valves of the heart that help avoid the backward flow of blood as it passes through the heart.
F-The stout wall separating the ventricles, the lower chambers of the heart, from one another is the interventricular septum (IVS, or ventricular septum, or septum inferius during development).
G-A broad vein that transports the deoxygenated blood from the lower and middle body to the right atrium of the heart is the inferior vena cava (or IVC).
H-One of the two major valves on the right side of the heart is the tricuspid valve. Normally, there are three flaps (leaflets) in the tricuspid valve that open and close, allowing blood to flow through the heart from the right atrium to the right ventricle, and stopping blood from flowing backward.
I-The atrial septum between the two upper chambers of the heart (atria). The septum is a wall that separates the left and right sides of the heart.
J-The aortic valve is a valve between the left ventricle and the aorta in the human heart. It is one of the heart's two semilunar valves, with the pulmonary valve being the other. There are 4 valves in the heart; the mitral and the tricuspid valves are the other two.
K-The superior vena cava (SVC) is the superior of the two venae cavae, the great venous trunks that carry deoxygenated blood back to the right atrium of the heart from systemic circulation. It is a short-length vein with a wide diameter (24 mm) which receives a venous return from the upper half of the body, above the diaphragm.
Note: A healthy heart is vital for an individual and well-being. It may cause a disorder called the cholesterol plaque of the coronary artery disease that can limit blood supplies to the heart over the years. The diminished arteries face a greater risk of complete blockage from a sudden blood clot (called a heart attack).
The pulmonary system's chief organ. A very complex muscle bag divided into a structurally complex human heart is a septum. It is found in the center of our chest between the lungs in the thoracic upper chest. The human heart is an organ that pumps blood through the body, transfers oxygen and nutrients across the body, eliminates carbon dioxide and other waste.
Complete step by step answer:

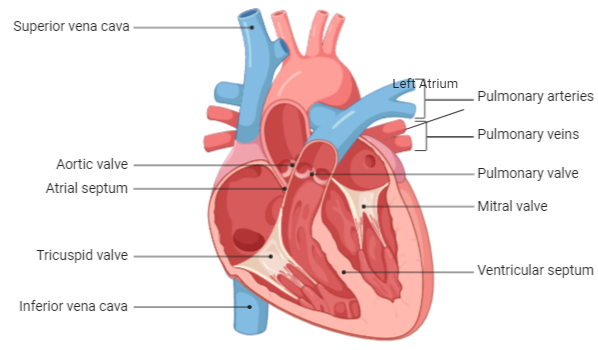
A-To oxygenate and expel excess carbon dioxide, the pulmonary artery brings oxygen-depleted blood to the lungs (see pulmonary circulation).
B-The veins that transfer oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart are the pulmonary veins. The four major pulmonary veins, two from each lung that flow into the left atrium of the heart, are the largest pulmonary veins.
C-One of the four chambers of the heart, positioned on the left posterior side, is the left atrium. Its main functions are to serve as a holding chamber for the return of blood from the lungs and to act as a pump to bring blood to other areas of the heart.
D-The pulmonary valve (sometimes referred to as the pulmonary valve) is the heart's semi-lunar valve between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery and has three cusps.
E-The bicuspid valve is also known as the mitral valve. This is one of four valves of the heart that help avoid the backward flow of blood as it passes through the heart.
F-The stout wall separating the ventricles, the lower chambers of the heart, from one another is the interventricular septum (IVS, or ventricular septum, or septum inferius during development).
G-A broad vein that transports the deoxygenated blood from the lower and middle body to the right atrium of the heart is the inferior vena cava (or IVC).
H-One of the two major valves on the right side of the heart is the tricuspid valve. Normally, there are three flaps (leaflets) in the tricuspid valve that open and close, allowing blood to flow through the heart from the right atrium to the right ventricle, and stopping blood from flowing backward.
I-The atrial septum between the two upper chambers of the heart (atria). The septum is a wall that separates the left and right sides of the heart.
J-The aortic valve is a valve between the left ventricle and the aorta in the human heart. It is one of the heart's two semilunar valves, with the pulmonary valve being the other. There are 4 valves in the heart; the mitral and the tricuspid valves are the other two.
K-The superior vena cava (SVC) is the superior of the two venae cavae, the great venous trunks that carry deoxygenated blood back to the right atrium of the heart from systemic circulation. It is a short-length vein with a wide diameter (24 mm) which receives a venous return from the upper half of the body, above the diaphragm.
Note: A healthy heart is vital for an individual and well-being. It may cause a disorder called the cholesterol plaque of the coronary artery disease that can limit blood supplies to the heart over the years. The diminished arteries face a greater risk of complete blockage from a sudden blood clot (called a heart attack).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




